Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 Jan;6(1):89-94. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.1.89.
Autologous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Patients With Severe Recalcitrant Atopic Dermatitis: A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. dhnahm@gmail.com
- 2Yonsei-Ajou Pediatric Clinic, Gwang-Ju, Korea.
- KMID: 2166949
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.1.89
Abstract
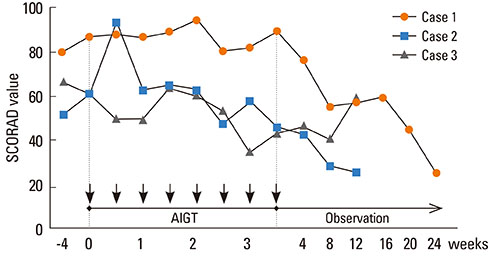
- The management of severe recalcitrant atopic dermatitis (AD) is a challenging issue for clinicians and patients. We hypothesized that repeated intramuscular injections of autologous immunoglobulin (autologous immunoglobulin therapy: AIGT) might induce clinical improvements in patients with AD by stimulation of the active immune response to antigen-binding-site of pathogenic antibodies. We tried AIGT in 3 adult patients with severe recalcitrant AD whose clinical conditions could not be effectively controlled by medical treatments (including oral cyclosporine) for more than 2 years. Autologous immunoglobulin was purified from the autologous plasma by affinity chromatography using Protein A. The patients were treated by an intramuscular injection of 50 mg of autologous immunoglobulin twice a week for 4 weeks. A clinical severity score of AD (SCORAD value) showed a decrease greater than 30% at 8 weeks after the initiation of AIGT compared with the baseline before the initiation of AIGT in all 3 patients with severe recalcitrant AD. No significant side effects from treatment were observed. Further studies with larger numbers of patients are required to evaluate the clinical usefulness of AIGT for AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Clinical Efficacy of Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapy in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
Dong-Ho Nahm, Myoung-Eun Kim, Byul Kwon, Su-Mi Cho, Areum Ahn
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(6):1420-1426. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1420.Retrospective Analysis on the Effects of House Dust Mite Specific Immunotherapy for More Than 3 Years in Atopic Dermatitis
Jungsoo Lee, Hemin Lee, Seongmin Noh, Byung Gi Bae, Jung U Shin, Chang Ook Park, Kwang Hoon Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(2):393-398. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.393.Personalized Immunomodulatory Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis: An Allergist's View
Dong-Ho Nahm
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(4):355-363. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.355.
Reference
-
1. Akdis CA, Akdis M, Bieber T, Bindslev-Jensen C, Boguniewicz M, Eigenmann P, Hamid Q, Kapp A, Leung DY, Lipozencic J, Luger TA, Muraro A, Novak N, Platts-Mills TA, Rosenwasser L, Scheynius A, Simons FE, Spergel J, Turjanmaa K, Wahn U, Weidinger S, Werfel T, Zuberbier T. European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/PRACTALL Consensus Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:152–169.2. Novak N, Bieber T, Leung DY. Immune mechanisms leading to atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:6 Suppl. S128–S139.3. Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:1483–1494.4. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic eczema. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980; 92:Suppl. S44–S47.5. Buchacher A, Iberer G. Purification of intravenous immunoglobulin G from human plasma--aspects of yield and virus safety. Biotechnol J. 2006; 1:148–163.6. Machiels JJ, Somville MA, Lebrun PM, Lebecque SJ, Jacquemin MG, Saint-Remy JM. Allergic bronchial asthma due to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus hypersensitivity can be efficiently treated by inoculation of allergen-antibody complexes. J Clin Invest. 1990; 85:1024–1035.7. European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology. 1993; 186:23–31.8. Kim ME, Kim JE, Sung JM, Lee JW, Choi GS, Nahm DH. Safety of accelerated schedules of subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy with house dust mite extract in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1159–1164.9. Steffen C. Why a historical approach has clinical benefits: Staphylococcus toxoid and autohemotherapy. Skinmed. 2005; 4:316–319.10. Schäfer T. Epidemiology of complementary alternative medicine for asthma and allergy in Europe and Germany. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004; 93:2 Suppl 1. S5–S10.11. Asefi M, Augustin M. Regulative therapy: treatment with nonspecific stimulants in dermatology in traditional and modern perspectives. Forsch Komplementarmed. 1999; 6:Suppl 2. 9–13.12. Pittler MH, Armstrong NC, Cox A, Collier PM, Hart A, Ernst E. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of autologous blood therapy for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2003; 148:307–313.13. Staubach P, Onnen K, Vonend A, Metz M, Siebenhaar F, Tschentscher I, Opper B, Magerl M, Lüdtke R, Kromminga A, Maurer M. Autologous whole blood injections to patients with chronic urticaria and a positive autologous serum skin test: a placebo-controlled trial. Dermatology. 2006; 212:150–159.14. Bajaj AK, Saraswat A, Upadhyay A, Damisetty R, Dhar S. Autologous serum therapy in chronic urticaria: old wine in a new bottle. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008; 74:109–113.15. Wallmann J, Pali-Schöll I, Jensen-Jarolim E. Anti-Ids in allergy: timeliness of a classic concept. World Allergy Organ J. 2010; 3:195–201.16. Shoenfeld Y. The idiotypic network in autoimmunity: antibodies that bind antibodies that bind antibodies. Nat Med. 2004; 10:17–18.17. Lamb SR, Rademaker M. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2001; 2:67–74.18. Schuster SJ, Neelapu SS, Gause BL, Janik JE, Muggia FM, Gockerman JP, Winter JN, Flowers CR, Nikcevich DA, Sotomayor EM, McGaughey DS, Jaffe ES, Chong EA, Reynolds CW, Berry DA, Santos CF, Popa MA, McCord AM, Kwak LW. Vaccination with patient-specific tumor-derived antigen in first remission improves disease-free survival in follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2787–2794.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Autologous Immunoglobulin Therapy in Patients With Severe Recalcitrant Atopic Dermatitis: Long-Term Changes of Clinical Severity and Laboratory Parameters
- Serum IgE Level in Patients of Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic Dermatitis with Molluscum Contagiosum
- A Study on the Cell - Mediated Immunity of Patients with Apopic Dermatitis
- Age-related Changes in the Frequency of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-center Retrospective Study
- A Study on the Relationship of the Severity of Atopic Dermatitis, Serum IgE and IFN-gamma