Healthc Inform Res.
2016 Apr;22(2):81-88. 10.4258/hir.2016.22.2.81.
GEE: An Informatics Tool for Gene Expression Data Explore
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul National University Biomedical Informatics (SNUBI), Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. juhan@snu.ac.kr
- 2Systems Biomedical Informatics–National Core Research Center (SBI-NCRC), Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2166935
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2016.22.2.81
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Major public high-throughput functional genomic data repositories, including the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and ArrayExpress have rapidly expanded. As a result, a large number of diverse high-throughput functional genomic data retrieval systems have been developed. However, high-throughput functional genomic data retrieval remains challenging.
METHODS
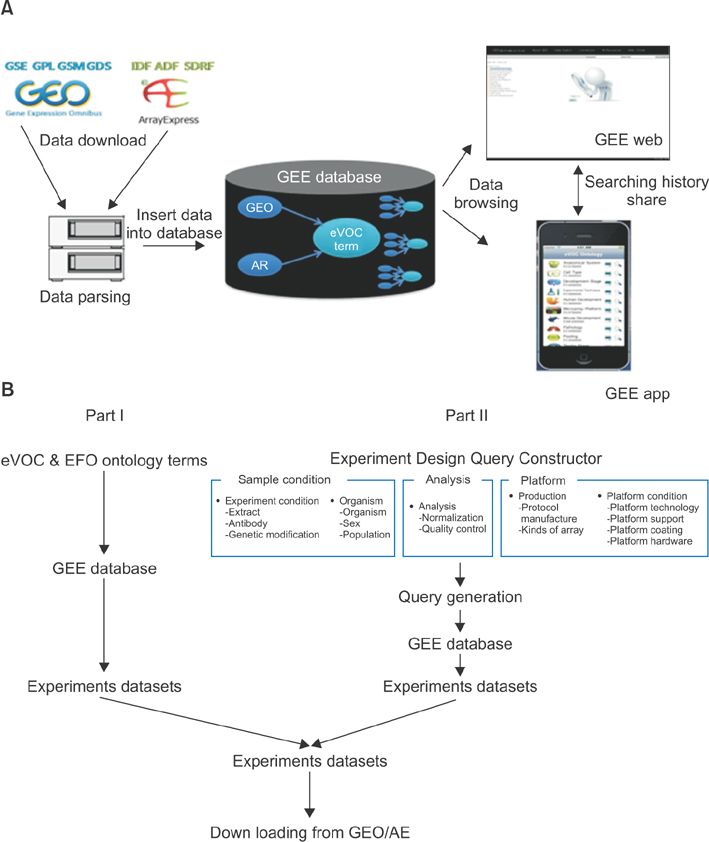
We developed Gene Expression data Explore (GEE), the first powerful, flexible web and mobile search application for searching whole-genome epigenetic data and microarray data in public databases, such as GEO and ArrayExpress.
RESULTS
GEE provides an elaborate, convenient interface of query generation competences not available via various high-throughput functional genomic data retrieval systems, including GEO, ArrayExpress, and Atlas. In particular, GEE provides a suitable query generator using eVOC, the Experimental Factor Ontology (EFO), which is well represented with a variety of high-throughput functional genomic data experimental conditions. In addition, GEE provides an experimental design query constructor (EDQC), which provides elaborate retrieval filter conditions when the user designs real experiments.
CONCLUSIONS
The web version of GEE is available at http://www.snubi.org/software/gee, and its app version is available from the Apple App Store.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Evangelista C, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for high-throughput functional genomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37(Database issue):D885–D890.
Article2. Parkinson H, Sarkans U, Kolesnikov N, Abeygunawardena N, Burdett T, Dylag M, et al. ArrayExpress update: an archive of microarray and high-throughput sequencing-based functional genomics experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011; 39(Database issue):D1002–D1004.3. Cheng WC, Tsai ML, Chang CW, Huang CL, Chen CR, Shu WY, et al. Microarray meta-analysis database (M(2) DB): a uniformly pre-processed, quality controlled, and manually curated human clinical microarray database. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010; 11:421.4. Kapushesky M, Adamusiak T, Burdett T, Culhane A, Farne A, Filippov A, et al. Gene Expression Atlas update: a value-added database of microarray and sequencing-based functional genomics experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012; 40(Database issue):D1077–D1081.5. Coletti MH, Bleich HL. Medical subject headings used to search the biomedical literature. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2001; 8(4):317–323.
Article6. Malone J, Holloway E, Adamusiak T, Kapushesky M, Zheng J, Kolesnikov N, et al. Modeling sample variables with an Experimental Factor Ontology. Bioinformatics. 2010; 26(8):1112–1118.
Article7. Kelso J, Visagie J, Theiler G, Christoffels A, Bardien S, Smedley D, et al. eVOC: a controlled vocabulary for unifying gene expression data. Genome Res. 2003; 13(6A):1222–1230.
Article8. Noy NF, Shah NH, Whetzel PL, Dai B, Dorf M, Griffith N, et al. BioPortal: ontologies and integrated data resources at the click of a mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37(Web Server issue):W170–W173.
Article9. Rayner TF, Rocca-Serra P, Spellman PT, Causton HC, Farne A, Holloway E, et al. A simple spreadsheet-based, MIAME-supportive format for microarray data: MAGE-TAB. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006; 7:489.
Article10. Lu Z, Wilbur WJ, McEntyre JR, Iskhakov A, Szilagyi L. Finding query suggestions for PubMed. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2009; 2009:396–400.11. Ivliev AE, 't Hoen PA, Villerius MP, den Dunnen JT, Brandt BW. Microarray retriever: a web-based tool for searching and large scale retrieval of public microarray data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36(Web Server issue):W327–W331.
Article12. Zhu Y, Davis S, Stephens R, Meltzer PS, Chen Y. GEOmetadb: powerful alternative search engine for the Gene Expression Omnibus. Bioinformatics. 2008; 24(23):2798–2800.
Article13. Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia. 2007; 9(2):166–180.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- TRAPR: R Package for Statistical Analysis and Visualization of RNA-Seq Data
- Development of Microarray Gene Expression Database for MicroArray Gene Expression Markup Language
- Gene Expression Pattern Analysis via Latent Variable Models Coupled with Topographic Clustering
- Genomic Medicine and Bio-Medical Informatics
- HisCoM-PAGE: software for hierarchical structural component models for pathway analysis of gene expression data