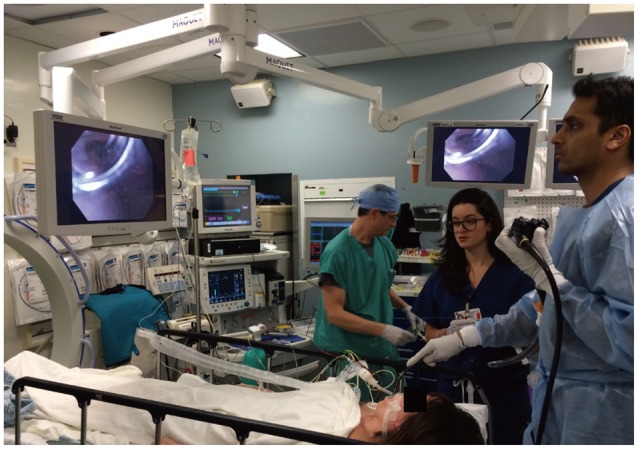
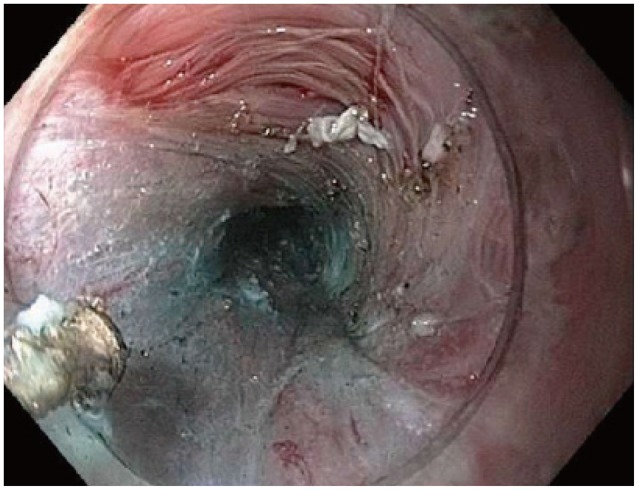
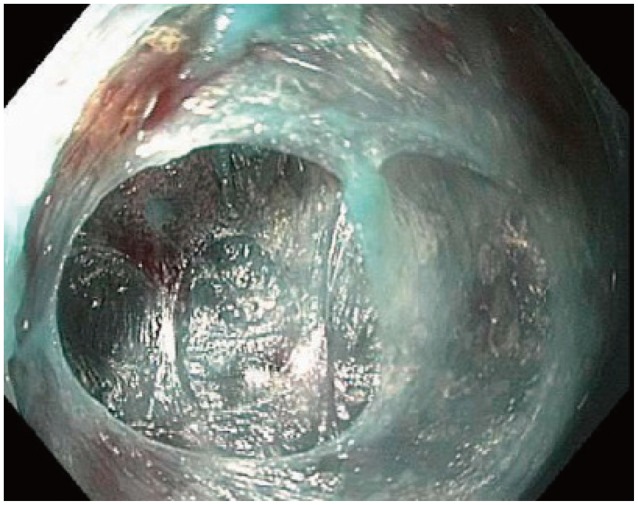
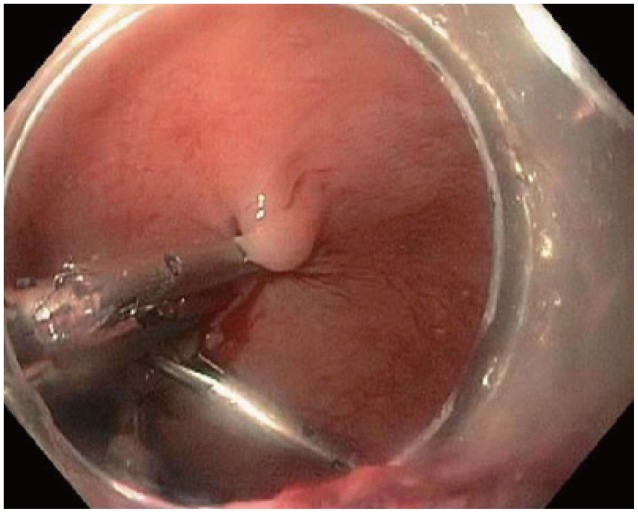
Clin Endosc.
2014 Sep;47(5):389-397. 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.389.
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy: Establishing a New Program
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA. mkahaleh@gmail.com
- 2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO, USA.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Nagasaki University Hospital, Nagasaki, Japan.
- 4Gastroenterologia y Endoscopia Digestiva, Hospital Central de la Policia Nacional, Bogota, Colombia.
- KMID: 2165368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.389
Abstract
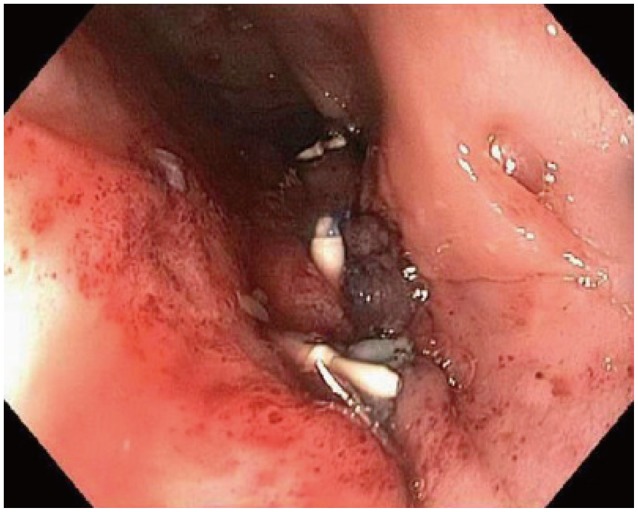
- Achalasia is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by incomplete relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and aperistalsis of the esophageal body. Treatment of achalasia is aimed at decreasing the resting pressure in the LES. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), derived from natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) and advances in endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), presents a novel, minimally invasive, and curative endoscopic treatment for achalasia. POEM involves an esophageal mucosal incision followed by creation of a submucosal tunnel crossing the esophagogastric junction and myotomy before closure of the mucosal incision. Although the procedure is technically demanding and requires a certain degree of skill and competency, treatment success is high (90%) with low complication rates. Since the first described POEM in humans in 2010, it has been used increasingly at centers worldwide. This article reviews available published clinical studies demonstrating POEM efficacy and safety in order to present a proposal on how to establish a dedicated POEM program and reach base proficiency for the procedure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Experience with Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia and Spastic Esophageal Motility Disorders at a Tertiary U.S. Center
Maen Masadeh, Peter Nau, Subhash Chandra, Jagpal Klair, John Keech, Kalpaj Parekh, Rami El Abiad, Henning Gerke
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(3):321-327. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.110.
Reference
-
1. Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Presentation, diagnosis, and management of achalasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:887–897. PMID: 23395699.
Article2. Vaezi MF, Pandolfino JE, Vela MF. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of achalasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:1238–1249. PMID: 23877351.
Article3. Stavropoulos SN, Modayil R, Friedel D. Achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2013; 23:53–75. PMID: 23168119.
Article4. Richter JE. The diagnosis and misdiagnosis of achalasia: it does not have to be so difficult. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:1010–1011. PMID: 21699819.
Article5. Kessing BF, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. Erroneous diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease in achalasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:1020–1024. PMID: 21683804.
Article6. Verlaan T, Rohof WO, Bredenoord AJ, Eberl S, Rösch T, Fockens P. Effect of peroral endoscopic myotomy on esophagogastric junction physiology in patients with achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:39–44. PMID: 23453184.
Article7. Campos GM, Vittinghoff E, Rabl C, et al. Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:45–57. PMID: 19106675.8. Lake JM, Wong RK. Review article: the management of achalasia: a comparison of different treatment modalities. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 24:909–918. PMID: 16948803.9. Vela MF, Richter JE, Khandwala F, et al. The long-term efficacy of pneumatic dilatation and Heller myotomy for the treatment of achalasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:580–587. PMID: 16630776.
Article10. Vaezi MF, Richter JE. Diagnosis and management of achalasia. American College of Gastroenterology Practice Parameter Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:3406–3412. PMID: 10606295.11. Zerbib F, Thétiot V, Richy F, Benajah DA, Message L, Lamouliatte H. Repeated pneumatic dilations as long-term maintenance therapy for esophageal achalasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:692–697. PMID: 16635216.
Article12. Katzka DA, Castell DO. Review article: an analysis of the efficacy, perforation rates and methods used in pneumatic dilation for achalasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:832–839. PMID: 21848630.
Article13. Boeckxstaens GE, Annese V, des Varannes SB, et al. Pneumatic dilation versus laparoscopic Heller's myotomy for idiopathic achalasia. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1807–1816. PMID: 21561346.
Article14. Khashab MA, Kalloo AN. NOTES: current status and new horizons. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:704–710. PMID: 22349111.
Article15. Pasricha PJ, Hawari R, Ahmed I, et al. Submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy: a novel experimental approach for the treatment of achalasia. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:761–764. PMID: 17703382.
Article16. Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:265–271. PMID: 20354937.
Article17. Teitelbaum EN, Hungness ES. Peroral endoscopic myotomy periprocedural evaluation: predicting and measuring outcomes. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15:135–139.
Article18. Eckardt VF. Clinical presentations and complications of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2001; 11:281–292. PMID: 11319062.19. von Renteln D, Inoue H, Minami H, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:411–417. PMID: 22068665.
Article20. Sharata A, Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanström LL. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is safe and effective in the setting of prior endoscopic intervention. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013; 17:1188–1192. PMID: 23609138.
Article21. Stavropoulos SN, Modayil R, Friedel D. Extended indications and contraindications for peroral endoscopic myotomy. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15:149–152.
Article22. Stavropoulos SN, Modayil RJ, Friedel D, Savides T. The International Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy Survey (IPOEMS): a snapshot of the global POEM experience. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:3322–3338. PMID: 23549760.
Article23. Stavropoulos SN, Iqbal S, Modayil R, Dejesus D. Per oral endoscopic myotomy, equipment and technique: a step-by-step explanation. Video J Encycl GI Endosc. 2013; 1:96–100.
Article24. Inoue H, Tianle KM, Ikeda H, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia: technique, indication, and outcomes. Thorac Surg Clin. 2011; 21:519–525. PMID: 22040634.
Article25. Hungness ES, Teitelbaum EN, Santos BF, et al. Comparison of perioperative outcomes between peroral esophageal myotomy (POEM) and laparoscopic Heller myotomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013; 17:228–235. PMID: 23054897.
Article26. Leeuwenburgh I, Scholten P, Alderliesten J, et al. Long-term esophageal cancer risk in patients with primary achalasia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:2144–2149. PMID: 20588263.
Article27. Swanström LL, Rieder E, Dunst CM. A stepwise approach and early clinical experience in peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia and esophageal motility disorders. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 213:751–756. PMID: 21996484.
Article28. Swanstrom LL, Kurian A, Dunst CM, Sharata A, Bhayani N, Rieder E. Long-term outcomes of an endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: the POEM procedure. Ann Surg. 2012; 256:659–667. PMID: 22982946.29. Zhou PH, Li QL, Yao LQ, et al. Peroral endoscopic remyotomy for failed Heller myotomy: a prospective single-center study. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:161–166. PMID: 23389963.
Article30. Li QL, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, et al. Early diagnosis and management of delayed bleeding in the submucosal tunnel after peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:370–374. PMID: 23680177.31. Li H, Linghu E, Wang X. Fibrin sealant for closure of mucosal penetration at the cardia during peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). Endoscopy. 2012; 44(Suppl 2 UCTN):E215–E216. PMID: 22622752.
Article32. Saxena P, Chavez YH, Kord Valeshabad A, Kalloo AN, Khashab MA. An alternative method for mucosal flap closure during peroral endoscopic myotomy using an over-the-scope clipping device. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:579–581. PMID: 23592391.
Article33. Ling T, Pei Q, Pan J, et al. Successful use of a covered, retrievable stent to seal a ruptured mucosal flap safety valve during peroral endoscopic myotomy in a child with achalasia. Endoscopy. 2013; 45(Suppl 2 UCTN):E63–E64. PMID: 23526520.
Article34. Kurian AA, Bhayani NH, Reavis K, Dunst C, Swanström L. Endoscopic suture repair of full-thickness esophagotomy during per-oral esophageal myotomy for achalasia. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:3910. PMID: 23708719.
Article35. Familiari P, Marchese M, Boskoski I, Costamagna G. Peroral endoscopic myotomy safety data. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15:144–148.
Article36. Chiu PW, Wu JC, Teoh AY, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of achalasia: from bench to bedside (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:29–38. PMID: 23043852.
Article37. Ren Z, Zhong Y, Zhou P, et al. Perioperative management and treatment for complications during and after peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia (EA) (data from 119 cases). Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:3267–3272. PMID: 22609984.
Article38. Baldaque-Silva F, Marques M, Ramalho R, Vilas-Boas F, Afonso M, Macedo G. Case description of cap retention in the submucosal tunnel during peroral endoscopic myotomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1586. PMID: 23034613.
Article39. Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Sharata A, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanström LL. Peroral endoscopic esophageal myotomy: defining the learning curve. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:719–725. PMID: 23394838.
Article40. Shiwaku H, Inoue H, Beppu R, et al. Successful treatment of diffuse esophageal spasm by peroral endoscopic myotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:149–150. PMID: 22482919.
Article41. Yoshida A, Inoue H, Ikeda H, et al. Clinical results of POEM (per-oral endoscopic myotomy) for esophageal achalasia in 161 consecutive cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75(4 Suppl):AB212.42. Zhou PH, Yao L, Zhang YQ, et al. Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia: 205 cases report. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75(4 Suppl):AB132–AB133.43. Maselli R, Inoue H, Misawa M, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in a 3-year-old girl with severe growth retardation, achalasia, and Down syndrome. Endoscopy. 2012; 44(Suppl 2 UCTN):E285–E287. PMID: 22933258.
Article44. Onimaru M, Inoue H, Ikeda H, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy is a viable option for failed surgical esophagocardiomyotomy instead of redo surgical Heller myotomy: a single center prospective study. J Am Coll Surg. 2013; 217:598–605. PMID: 23891071.
Article45. Khashab MA, Sharaiha RZ, Saxena P, et al. Novel technique of auto-tunneling during peroral endoscopic myotomy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:119–122. PMID: 23261101.
Article46. Eleftheriadis N, Inoue H, Ikeda H, et al. Training in peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2012; 8:329–342. PMID: 22888256.
Article47. Desilets DJ, Romanelli JR, Earle DB. Starting a peroral endoscopic myotomy program at your institution. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15:157–159.
Article48. Khashab MA. Thoughts on starting a peroral endoscopic myotomy program. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:109–110. PMID: 23261100.
Article49. von Renteln D, Vassiliou MC, Rösch T. Training for peroral endoscopic myotomy. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15:153–156.50. Rohof WO, Hirsch DP, Kessing BF, Boeckxstaens GE. Efficacy of treatment for patients with achalasia depends on the distensibility of the esophagogastric junction. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:328–335. PMID: 22562023.
Article51. Costamagna G, Marchese M, Familiari P, Tringali A, Inoue H, Perri V. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for oesophageal achalasia: preliminary results in humans. Dig Liver Dis. 2012; 44:827–832. PMID: 22609465.
Article52. Von Renteln D, Fuchs KH, Fockens P, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: an international prospective multicenter study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:309–311. PMID: 23665071.
Article53. Stavropoulos SN, Modayil RJ, Brathwaite CE, et al. POEM (per oral endoscopic myotomy): 3 year experience by a gastroenterologist at a US center. Still safe and effective even in patients with advanced age, severe achalasia and severe comorbidities. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77(5 Suppl):AB459.54. Lee BH, Shim KY, Hong SJ, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of achalasia: initial results of a Korean study. Clin Endosc. 2013; 46:161–167. PMID: 23614126.
Article55. Minami H, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia: clinical impact of 28 cases. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26:43–51. PMID: 23581563.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
- Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience
- Double-Scope Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) for Esophageal Achalasia: The First Trial of a New Double-Scope POEM
- Two-Stage Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Sigmoid-Type Achalasia
- Efficacy and Safety of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy With Short Myotomy for Type I and II Achalasia