Clin Endosc.
2016 Mar;49(2):147-156. 10.5946/ce.2015.044.
Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Where Do We Stand?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
- 2Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA. sdsinghal@gmail.com
- KMID: 2165038
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.044
Abstract
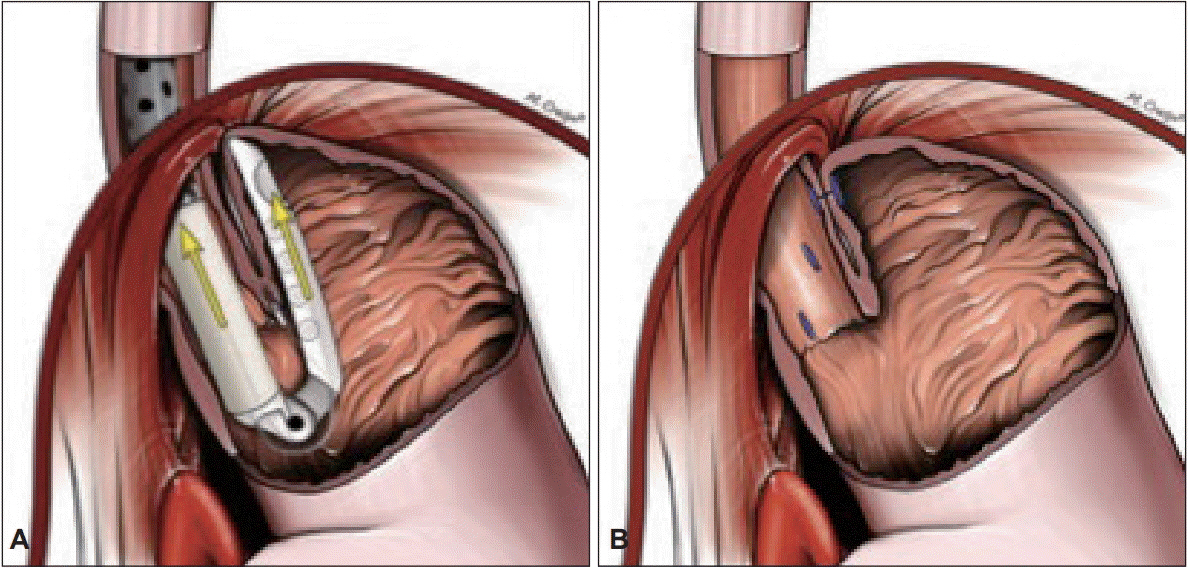
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic, progressive, and costly medical condition affecting a substantial proportion of the world population, predominantly the Western population. The available treatment options for patients with refractory GERD symptoms are limited to either laparoscopic surgery with significant sequelae or potentially lifelong, high-dose proton pump inhibitor therapy. The restoration of the antireflux competence of the gastroesophageal junction at the anatomic and physiologic levels is critical for the effective long-term treatment of GERD. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) surgery is a safe, well-tolerated, and effective treatment that has yielded significant symptomatic improvement in patients with medically refractory GERD symptoms. In this review article, we have summarized case series and reports describing the role of TIF for patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms. The reported indications, techniques, complications, and success rates are also discussed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Endoscopic Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Revisited
Zaheer Nabi, D. Nageshwar Reddy
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(5):408-416. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.133.
Reference
-
1. Dent J. Landmarks in the understanding and treatment of reflux disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24 Suppl 3:S5–S14.
Article2. Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S. Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2005; 54:710–717.
Article3. Heidelbaugh JJ, Gill AS, Van Harrison R, Nostrant TT. Atypical presentations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am Fam Physician. 2008; 78:483–488.4. Fass R. Effect of gastroesophageal reflux disease on sleep. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25 Suppl 1:S41–S44.
Article5. Friedenberg FK, Hanlon A, Vanar V, et al. Trends in gastroesophageal reflux disease as measured by the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:1911–1917.
Article6. Toghanian S, Wahlqvist P, Johnson DA, Bolge SC, Liljas B. The burden of disrupting gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a database study in US and European cohorts. Clin Drug Investig. 2010; 30:167–178.7. Reavis KM, Perry KA. Transoral incisionless fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014; 11:341–350.
Article8. Trad KS, Simoni G, Barnes WE, et al. Efficacy of transoral fundoplication for treatment of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease incompletely controlled with high-dose proton-pump inhibitors therapy: a randomized, multicenter, open label, crossover study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:174.
Article9. Toomey P, Teta A, Patel K, Ross S, Sukharamwala P, Rosemurgy AS. Transoral incisionless fundoplication: is it as safe and efficacious as a Nissen or Toupet fundoplication? Am Surg. 2014; 80:860–867.
Article10. Wilson EB, Barnes WE, Mavrelis PG, et al. The effects of transoral incisionless fundoplication on chronic GERD patients: 12-month prospective multicenter experience. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2014; 24:36–46.11. Cadière GB, Buset M, Muls V, et al. Antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX: 12-month results of a prospective multicenter study. World J Surg. 2008; 32:1676–1688.
Article12. Rinsma NF, Farré R, Bouvy ND, Masclee AA, Conchillo JM. The effect of endoscopic fundoplication and proton pump inhibitors on baseline impedance and heartburn severity in GERD patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015; 27:220–228.
Article13. Rinsma NF, Smeets FG, Bruls DW, et al. Effect of transoral incisionless fundoplication on reflux mechanisms. Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:941–949.
Article14. Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, Vailati C, Passaretti S. Long-term efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx (Tif 2.0) and factors affecting outcomes in GERD patients followed for up to 6 years: a prospective single-center study. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:2770–2780.15. Trad KS, Turgeon DG, Deljkich E. Long-term outcomes after transoral incisionless fundoplication in patients with GERD and LPR symptoms. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:650–660.
Article16. Kumta NA, Kedia P, Sethi A, Kahaleh M. Transoral incisionless fundoplication for treatment of refractory GERD after peroral endoscopic myotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:224–225.
Article17. Hunter JG, Kahrilas PJ, Bell RC, et al. Efficacy of transoral fundoplication vs omeprazole for treatment of regurgitation in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015; 148:324–333. e5.
Article18. Cadière GB, Rajan A, Germay O, Himpens J. Endoluminal fundoplication by a transoral device for the treatment of GERD: a feasibility study. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:333–342.
Article19. Bell RC, Cadière GB. Transoral rotational esophagogastric fundoplication: technical, anatomical, and safety considerations. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2387–2399.
Article20. Velanovich V. The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus. 2007; 20:130–134.
Article21. Allen CJ, Parameswaran K, Belda J, Anvari M. Reproducibility, validity, and responsiveness of a disease-specific symptom questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus. 2000; 13:265–270.
Article22. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J Voice. 2002; 16:274–277.
Article23. Shaw M, Dent J, Beebe T, et al. The Reflux Disease Questionnaire: a measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2008; 6:31.
Article24. Chan Y, Ching JY, Cheung CM, et al. Development and validation of a disease-specific quality of life questionnaire for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: the GERD-QOL questionnaire. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 31:452–460.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Treatment of Refractory Gastroesohageal Reflux Disease
- Esophgeal Perforation and Bilateral Empyema Following Endoscopic EsophyX Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication
- Safe implementation of transoral incisionless fundoplication as a new technique in a tertiary care center
- A Case of Postfundoplication Dysphagia without Symptomatic Improvement after Endoscopic Dilatation
- Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer and Reflux Disease