Clin Endosc.
2014 Jan;47(1):104-107.
A Case of Postfundoplication Dysphagia without Symptomatic Improvement after Endoscopic Dilatation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. HJPARK21@yuhs.ac
Abstract
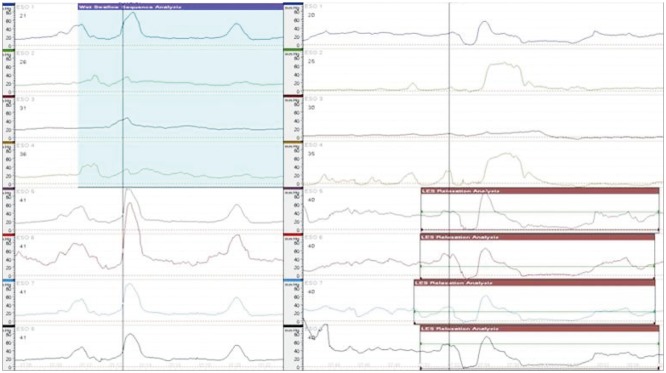
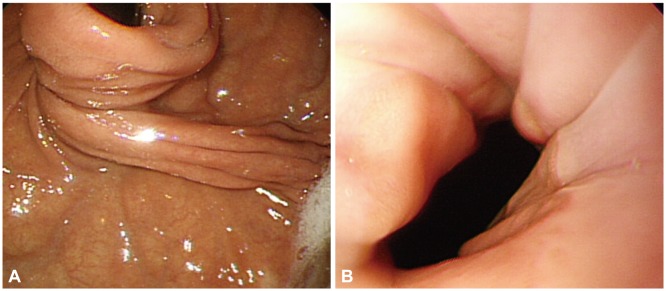
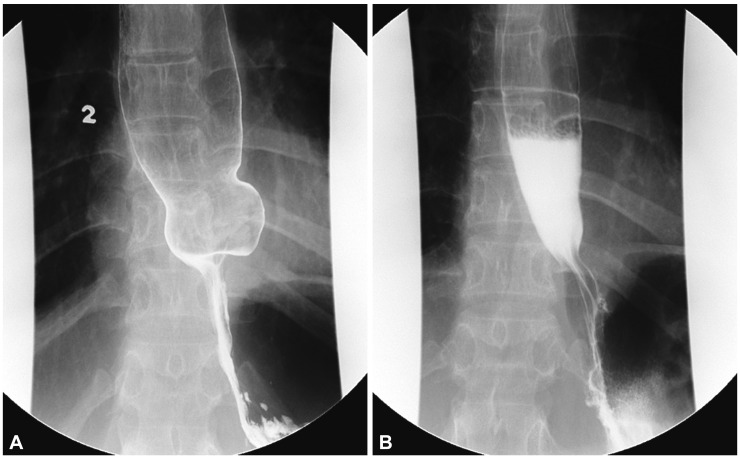
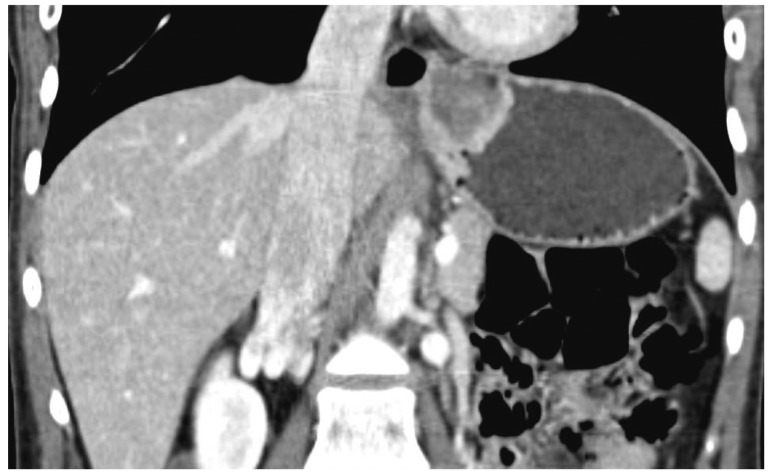
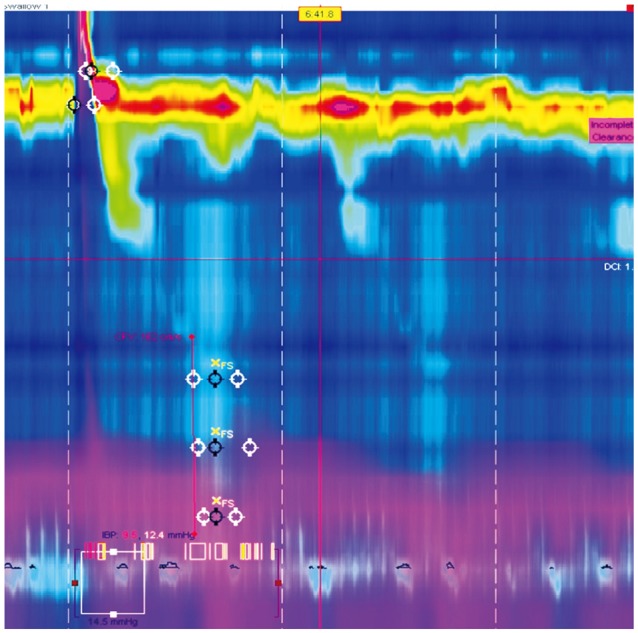
- Laparoscopic fundoplication is a treatment option for gastroesophageal reflux disease refractory to medical treatment. When deciding whether or not to undergo surgery, patients with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease and esophageal motility disorder need to fully understand the operative procedure, postoperative complications, and residual symptoms such as dysphagia, globus sensation, and recurrence of reflux. Herein, we report a case of a patient diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease and aperistalsis who underwent Nissen (total, 360degrees) fundoplication after lack of response to medical treatment and subsequently underwent pneumatic dilatation due to unrelieved postoperative dysphagia and globus sensation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tsereteli Z, Sporn E, Astudillo JA, Miedema B, Eubanks WS, Thaler K. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is a good option in patients with abnormal esophageal motility. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:2292–2295. PMID: 19172353.
Article2. Novitsky YW, Wong J, Kercher KW, Litwin DE, Swanstrom LL, Heniford BT. Severely disordered esophageal peristalsis is not a contraindication to laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:950–954. PMID: 17177077.
Article3. Chan WW, Haroian LR, Gyawali CP. Value of preoperative esophageal function studies before laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:2943–2949. PMID: 21424193.
Article4. Malhi-Chowla N, Gorecki P, Bammer T, Achem SR, Hinder RA, Devault KR. Dilation after fundoplication: timing, frequency, indications, and outcome. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:219–223. PMID: 11818926.
Article5. Mattox HE 3rd, Albertson DA, Castell DO, Richter JE. Dysphagia following fundoplication: "slipped" fundoplication versus achalasia complicated by fundoplication. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990; 85:1468–1472. PMID: 2239875.6. Herron DM, Swanström LL, Ramzi N, Hansen PD. Factors predictive of dysphagia after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc. 1999; 13:1180–1183. PMID: 10594261.
Article7. Wo JM, Trus TL, Richardson WS, et al. Evaluation and management of postfundoplication dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:2318–2322. PMID: 8931410.8. Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Granderath UM, Pointner R. Gas-related symptoms after laparoscopic 360 degrees Nissen or 270 degrees Toupet fundoplication in gastrooesophageal reflux disease patients with aerophagia as comorbidity. Dig Liver Dis. 2007; 39:312–318. PMID: 17306636.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting the Response to Endoscopic Dilatation Therapy for Benign Esophageal Stricture
- A Case of Successful Management of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis with Endoscopic Balloon Dilatation
- A Case of Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
- A Case of Dysphagia Lusoria
- A Case of Plummer - Vinson Syndrome Treated with Endoscopic Balloon Dilatation