Restor Dent Endod.
2016 May;41(2):148-153. 10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.148.
Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of fused teeth with transposition: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, Health Sciences Institute of Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Viseu, Portugal. miguelbcardoso@gmail.com
- KMID: 2163298
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.148
Abstract
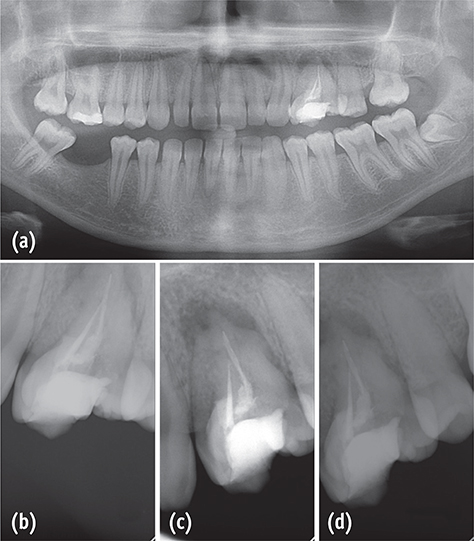
- Tooth transposition is a disorder in which a permanent tooth develops and erupts in the normal position of another permanent tooth. Fusion and gemination are developmental disturbances presenting as the union of teeth. This article reports the nonsurgical retreatment of a very rare case of fused teeth with transposition. A patient was referred for endodontic treatment of her maxillary left first molar in the position of the first premolar, which was adjacent to it on the distobuccal side. Orthopantomography and periapical radiography showed two crowns sharing the same root, with a root canal treatment and an associated periapical lesion. Tooth fusion with transposition of a maxillary molar and a premolar was diagnosed. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed. At four yr follow-up, the tooth was asymptomatic and the radiolucency around the apical region had decreased, showing the success of our intervention. The diagnosis and treatment of fused teeth require special attention. The canal system should be carefully explored to obtain a full understanding of the anatomy, allowing it to be fully cleaned and obturated. Thermoplastic techniques were useful in obtaining hermetic obturation. A correct anatomical evaluation improves the set of treatment options under consideration, leading to a higher likelihood of esthetically and functionally successful treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Knezević A, Travan S, Tarle Z, Sutalo J, Janković B, Ciglar I. Double tooth. Coll Antropol. 2002; 26:667–672.2. Kavadia-Tsatala S, Sidiropoulou S, Kaklamanos EG, Chatziyanni A. Tooth transpositions associated with dental anomalies and treatment management in a sample of orthodontic patients. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2003; 28:19–25.
Article3. Tannenbaum KA, Alling EE. Anomalous tooth development. Case reports of gemination and twinning. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963; 16:883–887.4. Cho KM, Jang JH, Park SH. Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: a case report. Restor Dent Endod. 2014; 39:319–323.
Article5. Gadimli C, Sari Z. Interdisciplinary treatment of a fused lower premolar with supernumerary tooth. Eur J Dent. 2011; 5:349–353.
Article6. G S, Jena A. Prevalence and incidence of gemination and fusion in maxillary lateral incisors in odisha population and related case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:2326–2329.7. Gallottini L, Barbato Bellatini RC, Migliau G. Endodontic treatment of a fused tooth. Report of a case. Minerva Stomatol. 2007; 56:633–638.8. Aryanpour S, Bercy P, Van Nieuwenhuysen JP. Endodontic and periodontal treatments of a geminated mandibular first premolar. Int Endod J. 2002; 35:209–214.
Article9. Liang RZ, Wu JT, Wu YN, Smales RJ, Hu M, Yu JH, Zhang GD. Bilateral maxillary fused second and third molars: a rare occurrence. Int J Oral Sci. 2012; 4:231–234.
Article10. Salem Milani A. Endodontic management of a fused mandibular second molar and paramolar: a case report. Iran Endod J. 2010; 5:131–134.11. Song CK, Chang HS, Min KS. Endodontic management of supernumerary tooth fused with maxillary first molar by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010; 36:1901–1904.
Article12. Weinstein T, Rosano G, Del Fabbro M, Taschieri S. Endodontic treatment of a geminated maxillary second molar using an endoscope as magnification device. Int Endod J. 2010; 43:443–450.
Article13. Asgary S. Endodontic treatment of a maxillary second molar with developmental anomaly: a case report. Iran Endod J. 2007; 2:73–76.14. Mader CL. Fusion of teeth. J Am Dent Assoc. 1979; 98:62–64.
Article15. Rotstein I, Moshonov J, Cohenca N. Endodontic therapy for a fused mandibular molar. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1997; 13:149–151.16. Milazzo A, Alexander SA. Fusion, gemination, oligodontia, and taurodontism. J Pedod. 1982; 6:194–199.17. Yücel AC, Güler E. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment of geminated teeth: a case report. J Endod. 2006; 32:1214–1216.
Article18. Camm JH, Wood AJ. Gemination, fusion and supernumerary tooth in the primary dentition: report of case. ASDC J Dent Child. 2015; 56:60–61.19. Brook AH, Winter GB. Double teeth. A retrospective study of 'geminate' and 'fuse' teeth in children. Br Dent J. 1970; 129:123–130.
Article20. Tsesis I, Steinbock N, Rosenberg E, Kaufman AY. Endodontic treatment of developmental anomalies in posterior teeth: treatment of geminated/fused teethreport of two cases. Int Endod J. 2003; 36:372–379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic factors influencing clinical outcome of nonsurgical endodontic treatment
- A new post removal technique using ATD tugging device
- Multidisciplinary management of a fused maxillary central incisor moved through the midpalatal suture: A case report
- Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: a conservative approach
- Prevalence of referral reasons and clinical symptoms for endodontic referrals