J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Aug;21(4):608-613. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.4.608.
Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Pediatric Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia and Pleural Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jyssim@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2157809
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.4.608
Abstract
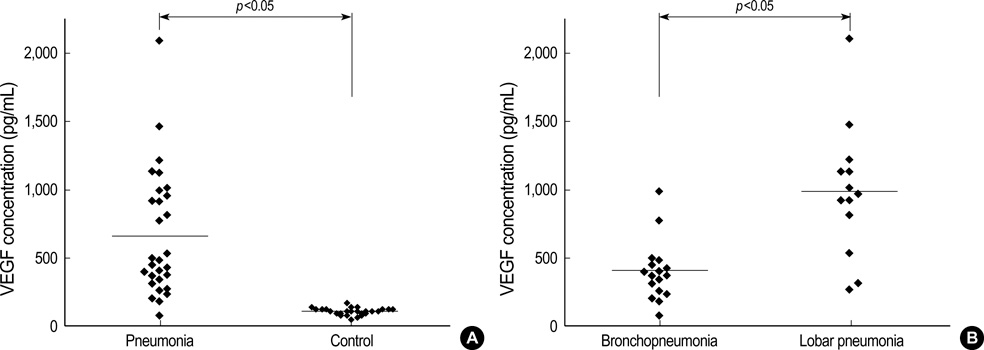
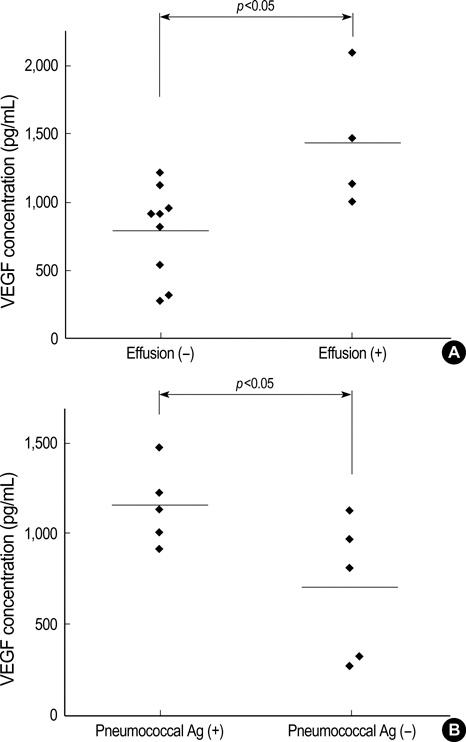
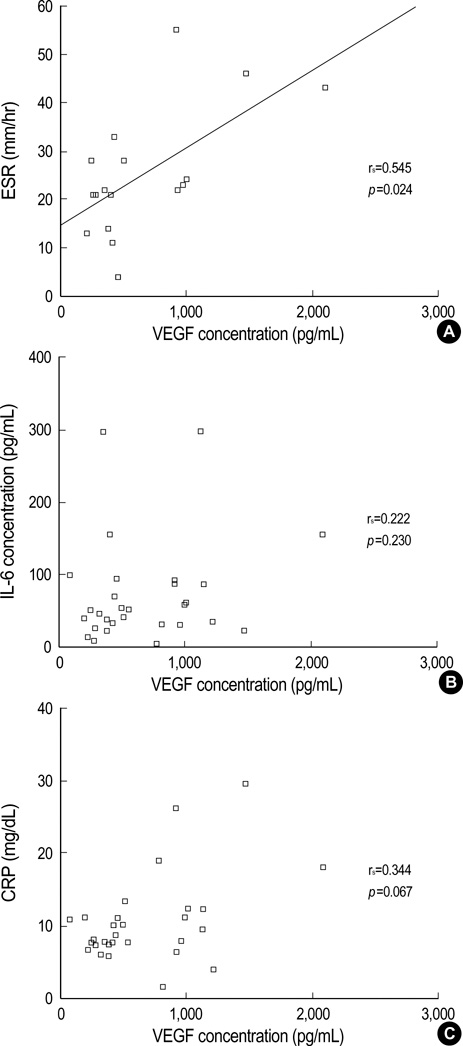
- This study investigated the serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in children with community-acquired pneumonia. Serum VEGF levels were measured in patients with pneumonia (n=29) and in control subjects (n=27) by a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The pneumonia group was classified into bronchopneumonia with pleural effusion (n=1), bronchopneumonia without pleural effusion (n=15), lobar pneumonia with pleural effusion (n=4), and lobar pneumonia without pleural effusion (n=9) groups based on the findings of chest radiographs. We also measured serum IL-6 levels and the other acute inflammatory parameters. Serum levels of VEGF in children with pneumonia were significantly higher than those in control subjects (p<0.01). Children with lobar pneumonia with or without effusion showed significantly higher levels of serum VEGF than children with bronchopneumonia. For lobar pneumonia, children with pleural effusion showed higher levels of VEGF than those without pleural effusion. Children with a positive urinary S. pneumonia antigen test also showed higher levels of VEGF than those with a negative result. Serum IL-6 levels did not show significant differences between children with pneumonia and control subjects. Serum levels of VEGF showed a positive correlation with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the children with pneumonia. In conclusion, VEGF may be one of the key mediators that lead to lobar pneumonia and parapneumonic effusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A/*blood
Streptococcus pneumoniae/growth & development/immunology
Pneumonia, Bacterial/*blood/complications/microbiology
Pleural Effusion/*blood/complications/microbiology
Mycoplasma pneumoniae/growth & development/immunology
Male
Interleukin-6/blood
Infant
Humans
Female
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Community-Acquired Infections/blood/microbiology
Child, Preschool
Child
Antigens, Bacterial/immunology
Antibodies, Bacterial/immunology
Adolescent
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children during the recent 3 epidemics
Hwa Hyun Wy, Dong Hoon Min, Deok Soo Kim, Moon Soo Park, Jae Won Shim, Hye Lim Jung, Jung Yeon Shim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(1):8-14. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.1.8.
Reference
-
1. Fang GD, Fine M, Orloff J, Arisumi D, Yu VL, Kapoor W, Grayston JT, Wang SP, Kohler R, Muder RR, Yee YC, Ribs JD, Vickers RM. New and emerging etiologies for community-acquired pneumonia with implications for therapy. A prospective multicenter study of 359 cases. Medicine. 1990. 69:307–316.2. Kolditz M, Halank M, Hoffken G. Parapneumonic effusion and pleural empyema; topical aspects of classification, diagnosis and treatment. Pneumologie. 2004. 58:83–91.3. Dvorak HF, Detmar M, Claffey KP, Nagy JA, Van De Water L, Senger DR. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor - an important mediator of angiogenesis in malignancy and inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995. 107:233–235.4. Ferrara N. Molecular and biological properties of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Mol Med. 1999. 77:527–543.
Article5. Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the regulation of angiogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. 55:15–36.6. Kraft A, Weindel K, Ochs A, Marth C, Zmija J, Schumacher P, Unger C, Marmé D, Gastl G. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the sera and effusions of patients with malignant and nonmalignant disease. Cancer. 1999. 85:178–187.
Article7. Hoshino M, Takahashi M, Aoike N. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and angiogenin immunoreactivity in asthmatic airways and its relationship to angiogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 107:295–301.
Article8. Hoshino M, Nakamura Y, Hamid QA. Gene expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors and angiogenesis in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 107:1034–1038.
Article9. Choi JH, Suh YJ, Lee SK, Suh CH, Nahm DH, Park HS. Acute and chronic changes of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in induced sputum of toluene diisocyanate (TDI)-induced asthma patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2004. 19:359–363.10. Alatas F, Alatas O, Metintas M, Ozarslan A, Erginel S, Yildirim H. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest. 2004. 125:2156–2159.
Article11. Nishigaki Y, Fujiuchi S, Yamazaki Y, Matsumoto H, Takeda A, Fujita Y, Okamoto K, Fujikane T, Shimizu T, Kikuchi K. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor in acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:774–778.
Article12. Simler NR, Brenchley PE, Horrocks AW, Greaves SM, Hasleton PS, Egan JJ. Angiogenic cytokines in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Thorax. 2004. 59:581–585.
Article13. Shim JY, Jung HL, Park MS, Keum DH. Vascular endothelial growth factor in children with lower respiratory tract disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:S137.
Article14. McColley SA, Stellmach V, Boas SR, Jain M, Crawford SE. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor is elevated in cystic fibrosis and decreases with treatment of acute pulmonary exacerbation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1877–1880.
Article15. McDonald DM. Angiogenesis and remodeling of airway vasculature in chronic inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 164:39–45.
Article16. Tsokos M, Pufe T, Paulsen F, Anders S, Mentlein R. Pulmonary expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in sepsis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003. 127:331–335.
Article17. Mohammed KA, Nasreen N, Hardwick J, Logie CS, Patterson CE, Antony VB. Bacterial induction of pleural mesothelial monolayer barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. 281:119–125.
Article18. van Der Flier M, Coenjaerts F, Kimpen JL, Hoepelman AM, Geelen SP. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor by human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 2000. 68:4792–4794.
Article19. Hong JY, Lee HJ, Piedra PA, Choi EH, Park KH, Koh YY, Kim WS. Lower respiratory tract infections due to adenovirus in hospitalized Korean children: epidemiology, clinical features, and prognosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:1423–1429.
Article20. Marcos MA, Jimenez de Anta MT, de la Bellacasa JP, Gonzalez J, Martinez E, Garcia E, Mensa J, de Roux A, Torres A. Rapid urinary antigen test for diagnosis of pneumococcal community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:209–214.
Article21. Van der Eerden MM, Vlaspolder F, de Graaff CS, Groot T, Jansen HM, Boersma WG. Value of intensive diagnostic microbiological investigation in low- and high-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005. 24:241–249.
Article22. Smith MD, Derrington P, Evans R, Creek M, Morris R, Dance DA, Cartwright K. Rapid diagnosis of bacteremic pneumococcal infections in adults by using the Binax NOW Streptococcus pneumoniae urinary antigen test: a prospective, controlled clinical evaluation. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:2810–2813.
Article23. Neuman MI, Harper MB. Evaluation of a rapid urine antigen assay for the detection of invasive pneumococcal disease in children. Pediatrics. 2003. 112:1279–1282.
Article24. Cheng D, Rodriguez RM, Perkett EA, Rogers J, Bienvenu G, Lappalainen U, Light RW. Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural fluid. Chest. 1999. 116:760–765.
Article25. Cheng D, Lee YC, Rogers JT, Perkett EA, Moyers JP, Rodrigues RM, Light RW. Vascular endothelial growth factor level correlates with transforming growth factor beta isoform levels in pleural effusions. Chest. 2000. 118:1747–1753.26. Yanagawa H, Takeuchi E, Suzuki Y, Ohmoto Y, Bando H, Sone S. Vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant pleural effusion associated with lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1999. 48:396–400.
Article27. Thickett DR, Armstrong L, Millar AB. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions. Thorax. 1999. 54:707–710.
Article28. Grove CS, Lee YC. Vascular endothelial growth factor: the key mediator in pleural effusion formation. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2002. 8:294–301.
Article29. Yeo KT, Wang HH, Nagy JA, Sioussat TM, Ledbetter SR, Hoogewerf AJ, Zhou Y, Masse EM, Senger DR, Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions. Cancer Res. 1993. 53:2912–2918.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions
- Significance of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Pleural Effusion
- Diagnostic Value of C-Veactive Protein and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Differentiation of Pleural Effusions
- Clinical Significance of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Patients with Lung Cancer and Tuberculous Pleurisy
- Serum vascular endothelial growth factor as a marker of asthma exacerbation