Ann Dermatol.
2011 Oct;23(Suppl 2):S141-S143. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S2.S141.
Linear Focal Elastosis Following Striae Distensae: Further Evidence of Keloidal Repair Process in the Pathogenesis of Linear Focal Elastosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. tyyoon@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2156774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S2.S141
Abstract
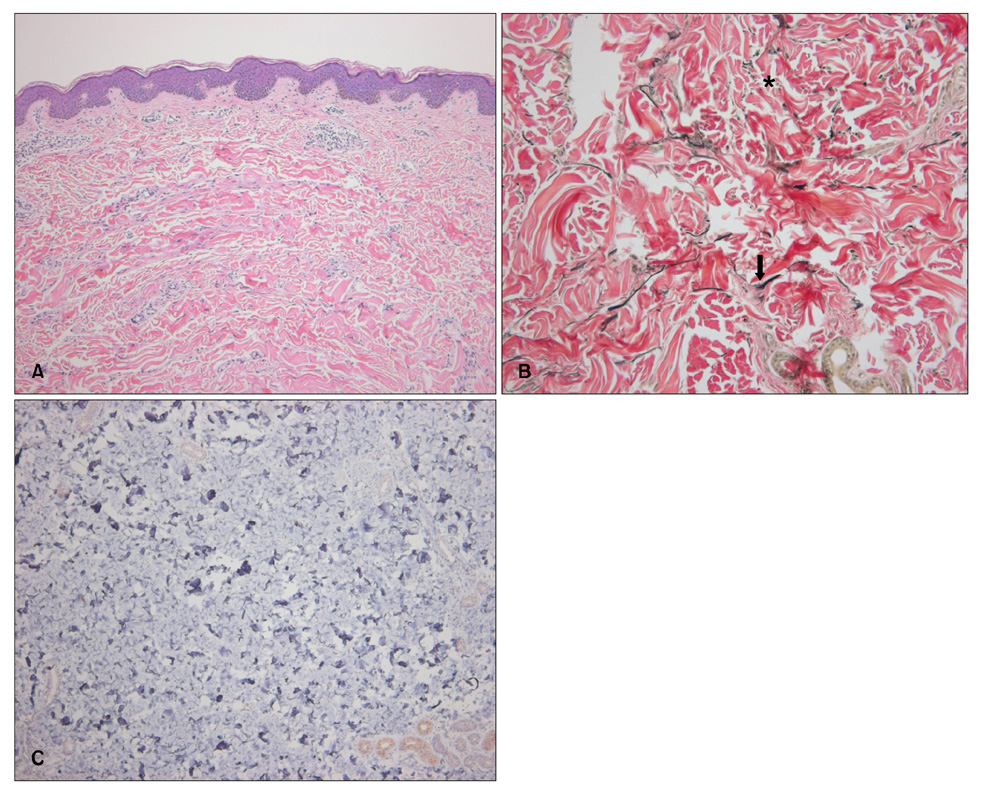
- Linear focal elastosis (LFE) is a rare dermal elastosis characterized by hypertrophic yellowish linear plaques and increased abnormal elastic tissues in the lumbosacral area. Although the pathogenesis of this disorder remains unknown, it may be associated with keloidal repair process (KRP) of elastic tissues in striae distensae (SD), because there have been some reported cases of LFE accompanied by SD. We herein report a 14-year-old boy with LFE following SD in the lumbar region. Our case supports the hypothesis of KRP in the pathogenesis of LFE. Immunohistochemical study for transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) was negative. Therefore, we assume that the pathogenesis of KRP in LFE is different from that of keloid development, which is the TGF-beta signaling pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burket JM, Zelickson AS, Padilla RS. Linear focal elastosis (elastotic striae). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 20:633–636.
Article2. Lewis KG, Bercovitch L, Dill SW, Robinson-Bostom L. Acquired disorders of elastic tissue: part I. Increased elastic tissue and solar elastotic syndromes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004. 51:1–21.
Article3. Hagari Y, Norimoto M, Mihara M. Linear focal elastosis associated with striae distensae in an elderly woman. Cutis. 1997. 60:246–248.4. Chang SE, Park IJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. Two cases of linear focal elastosis (elastotic striae). J Dermatol. 1998. 25:395–399.5. Hashimoto K. Linear focal elastosis: keloidal repair of striae distensae. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998. 39:309–313.
Article6. Ahn GB, Chang SH, Yoon TY. Two cases of linear focal elastosis. Ann Dermatol. 1999. 11:117–120.
Article7. Chang SE, Lee JY, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. Linear focal elastosis associated with striae distensae. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:127–129.8. Lim SH, Ha JH, Kang HA, Park HJ, Baek SC, Kim JW, et al. Linear focal elastosis associated with striae distensae in an atopic patient. Korean J Dermatol. 2001. 39:504–506.9. Ramlogan D, Tan BB, Garrido M. Linear focal elastosis. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 145:188–190.
Article10. Inaloz HS, Kirtak N, Karakok M, Ozgoztasi O. Facial linear focal elastosis: a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2003. 42:558–560.
Article11. Hagari Y, Mihara M, Morimura T, Shimao S. Linear focal elastosis. An ultrastructural study. Arch Dermatol. 1991. 127:1365–1368.
Article12. Zheng P, Lavker RM, Kligman AM. Anatomy of striae. Br J Dermatol. 1985. 112:185–193.
Article13. Beer TW, Lam MH, Heenan PJ. Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Johnson BL, Murphy GF, Xu G, editors. Tumors of fibrous tissue involving the skin. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 2008. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin;981–988.14. Sato M. Upregulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway induced by transforming growth factor-beta in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006. 86:300–307.
Article