Hip Pelvis.
2015 Mar;27(1):1-8. 10.5371/hp.2015.27.1.1.
Hip Arthroscopy: Where We Are, and Where We Are Going
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. mspark@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Veteran's Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Carollo Hospital, Suncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2156013
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.1.1
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 417:112–120.2. Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1012–1018.3. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Prospective analysis of hip arthroscopy with 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16:578–587.
Article4. Bellaïche L, Lequesne M, Gedouin JE, Laude F, Boyer T. French Arthroscopy Society. Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010; 96:8 Suppl. S44–S52.
Article5. Lequesne M, Bellaïche L. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: an update. Joint Bone Spine. 2012; 79:249–255.
Article6. Tannast M, Siebenrock KA. Conventional radiographs to assess femoroacetabular impingement. Instr Course Lect. 2009; 58:203–212.7. Lequesne MG, Laredo JD. The faux profil (oblique view) of the hip in the standing position. Contribution to the evaluation of osteoarthritis of the adult hip. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998; 57:676–681.
Article8. Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:556–560.9. Vaughn ZD, Safran MR. Arthroscopic femoral osteoplasty/for cam-type femoroacetabular impingement in the athlete. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2010; 18:90–99.
Article10. Rakhra KS. Magnetic resonance imaging of acetabular labral tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:Suppl 2. 28–34.
Article11. Botser IB, Smith TW Jr, Nasser R, Domb BG. Open surgical dislocation versus arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: a comparison of clinical outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:270–278.
Article12. Matsuda DK, Carlisle JC, Arthurs SC, Wierks CH, Philippon MJ. Comparative systematic review of the open dislocation, mini-open, and arthroscopic surgeries for femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:252–269.
Article13. Harris JD, McCormick FM, Abrams GD, et al. Complications and reoperations during and after hip arthroscopy: a systematic review of 92 studies and more than 6,000 patients. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:589–595.
Article14. Larson CM, Giveans MR, Stone RM. Arthroscopic debridement versus refixation of the acetabular labrum associated with femoroacetabular impingement: mean 3.5-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:1015–1021.
Article15. Audenaert EA, Peeters I, Vigneron L, Baelde N, Pattyn C. Hip morphological characteristics and range of internal rotation in femoroacetabular impingement. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:1329–1336.
Article16. Kubiak-Langer M, Tannast M, Murphy SB, Siebenrock KA, Langlotz F. Range of motion in anterior femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 458:117–124.
Article17. Kelly BT, Bedi A, Robertson CM, Dela Torre K, Giveans MR, Larson CM. Alterations in internal rotation and alpha angles are associated with arthroscopic cam decompression in the hip. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:1107–1112.
Article18. Ilizaliturri VM Jr. Complications of arthroscopic femoroacetabular impingement treatment: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:760–768.
Article19. Domb BG, Stake CE, Finley ZJ, Chen T, Giordano BD. Influence of capsular repair versus unrepaired capsulotomy on 2-year clinical outcomes after arthroscopic hip preservation surgery. Arthroscopy. Published online December 16, 2014. DOI: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.10.014.
Article20. Philippon MJ, Schenker ML. Athletic hip injuries and capsular laxity. Oper Tech Orthop. 2005; 15:261–266.
Article21. Philippon MJ, Schenker ML, Briggs KK, Maxwell RB. Can microfracture produce repair tissue in acetabular chondral defects? Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:46–50.
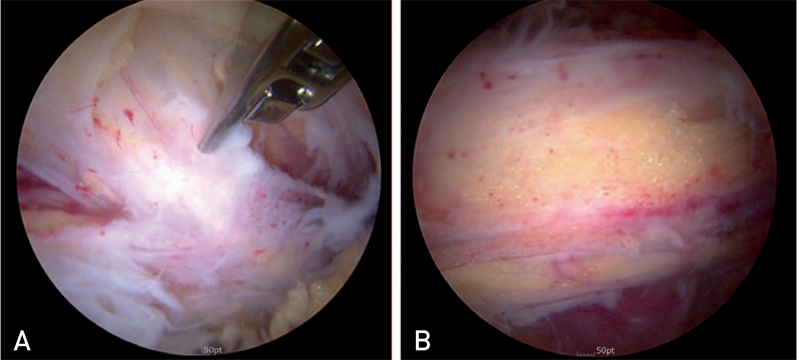
Article22. Karthikeyan S, Roberts S, Griffin D. Microfracture for acetabular chondral defects in patients with femoroacetabular impingement: results at second-look arthroscopic surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:2725–2730.
Article23. Domb BG, Redmond JM, Dunne KF, Stake CE, Gupta A. A matched-pair controlled study of microfracture of the hip with average 2-year follow-up: Do full-thickness chondral defects portend an inferior prognosis in hip arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. Published online December 10, 2014. DOI: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.10.011.
Article24. Geyer MR, Philippon MJ, Fagrelius TS, Briggs KK. Acetabular labral reconstruction with an iliotibial band autograft: outcome and survivorship analysis at minimum 3-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:1750–1756.
Article25. Matsuda DK, Burchette RJ. Arthroscopic hip labral reconstruction with a gracilis autograft versus labral refixation: 2-year minimum outcomes. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:980–987.
Article26. Ross JR, Larson CM, Adeoyo O, Kelly BT, Bedi A. Residual deformity is the most common reason for revision hip arthroscopy: a three-dimensional CT study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. Published online December 5, 2014. DOI: 10.1007/s11999-014-4069-9.
Article27. Philippon MJ, Stubbs AJ, Schenker ML, Maxwell RB, Ganz R, Leunig M. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: osteoplasty technique and literature review. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:1571–1580.
Article28. Philippon MJ, Ejnisman L, Ellis HB, Briggs KK. Outcomes 2 to 5 years following hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement in the patient aged 11 to 16 years. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:1255–1261.
Article29. Park MS, Yoon SJ, Kim YJ, Chung WC. Hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: the changing nature and severity of associated complications over time. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:957–963.
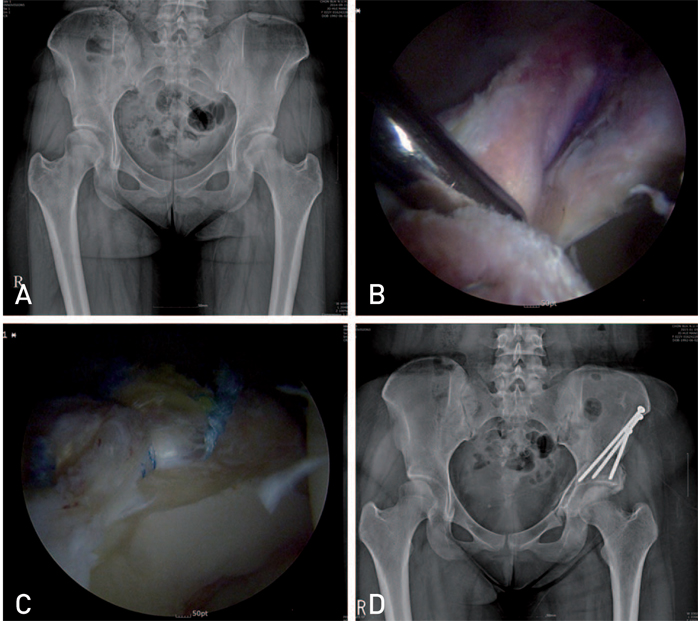
Article30. Park MS, Yoon SJ, Choi SM. Arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of femoral head fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28:e164–e168.
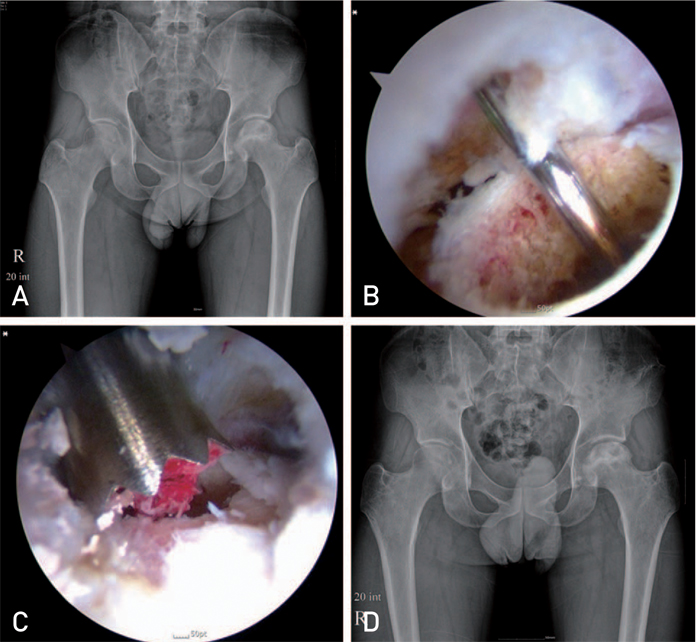
Article31. Pierannunzii L. Endoscopic and arthroscopic assistance in femoral head core decompression. Arthrosc Tech. 2012; 1:e225–e230.
Article32. Ellenrieder M, Tischer T, Kreuz PC, Fröhlich S, Fritsche A, Mittelmeier W. Arthroscopically assisted therapy of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013; 25:85–94.33. Martin HD, Shears SA, Johnson JC, Smathers AM, Palmer IJ. The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:172–181.
Article