Korean J Radiol.
2015 Jun;16(3):586-592. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.586.
Percutaneous Unilateral Biliary Metallic Stent Placement in Patients with Malignant Obstruction of the Biliary Hila and Contralateral Portal Vein Steno-Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. radgwon@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2155528
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.586
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the outcomes of percutaneous unilateral metallic stent placement in patients with a malignant obstruction of the biliary hila and a contralateral portal vein steno-occlusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty patients with a malignant hilar obstruction and unilobar portal vein steno-occlusion caused by tumor invasion or preoperative portal vein embolization were enrolled in this retrospective study from October 2010 to October 2013. All patients were treated with percutaneous placement of a biliary metallic stent, including expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE)-covered stents in 27 patients and uncovered stents in 33 patients.
RESULTS
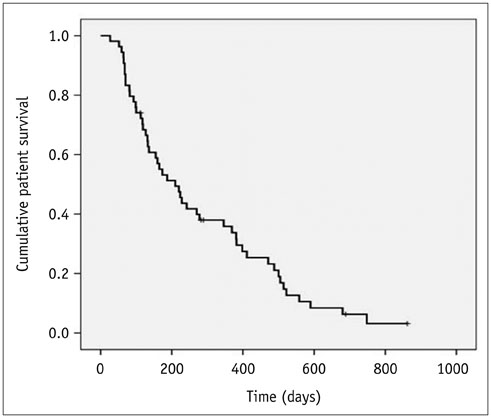
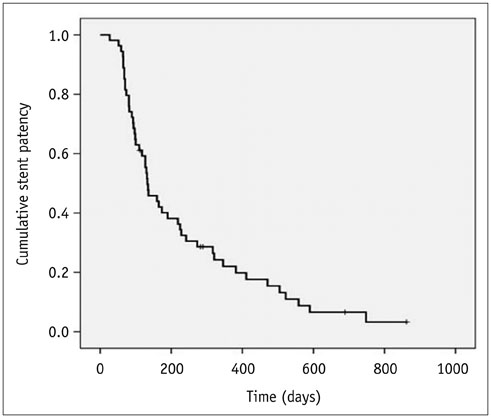
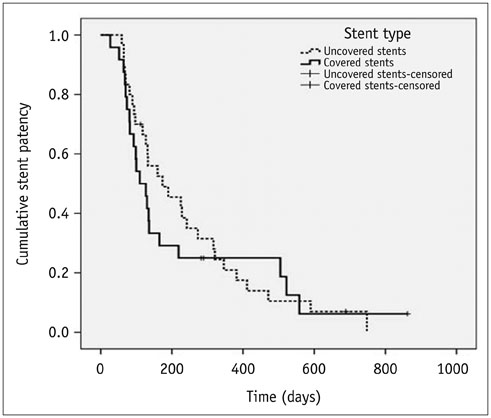
A total of 70 stents were successfully placed in 60 patients. Procedural-related minor complications, including self-limiting hemobilia (n = 2) and cholangitis (n = 4) occurred in six (10%) patients. Acute cholecystitis occurred in two patients. Successful internal drainage was achieved in 54 (90%) of the 60 patients. According to a Kaplan-Meier analysis, median survival time was 210 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 135-284 days), and median stent patency time was 133 days (95% CI, 94-171 days). No significant difference in stent patency was observed between covered and uncovered stents (p = 0.646). Stent dysfunction occurred in 16 (29.6%) of 54 patients after a mean of 159 days (range, 65-321 days).
CONCLUSION
Unilateral placement of ePTFE-covered and uncovered stents in the hepatic lobe with a patent portal vein is a safe and effective method for palliative treatment of patients with a contralateral portal vein steno-occlusion caused by an advanced hilar malignancy or portal vein embolization. No significant difference in stent patency was detected between covered and uncovered metallic stents.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Biliary Tract Neoplasms/surgery
Cholangitis/etiology
Cholestasis/*surgery
Female
Hemobilia/etiology
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Liver/blood supply/pathology/surgery
Liver Neoplasms/surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Palliative Care/methods
Polytetrafluoroethylene
Portal Vein/pathology/*surgery
Retinal Vein Occlusion/*surgery
Retrospective Studies
Stents/*adverse effects
Treatment Outcome
Polytetrafluoroethylene
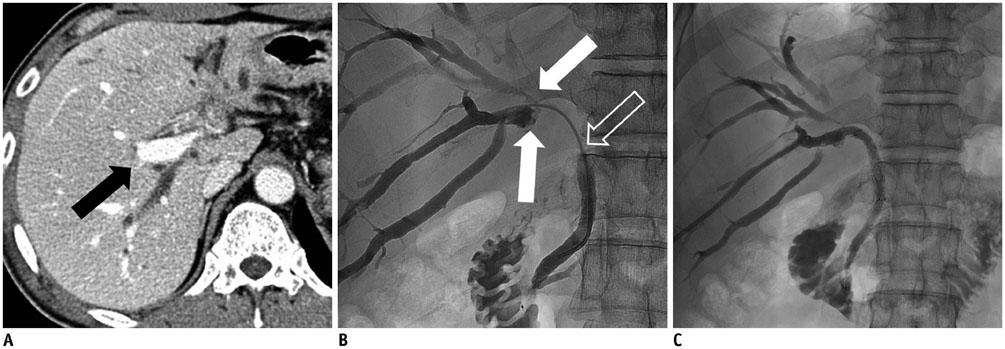
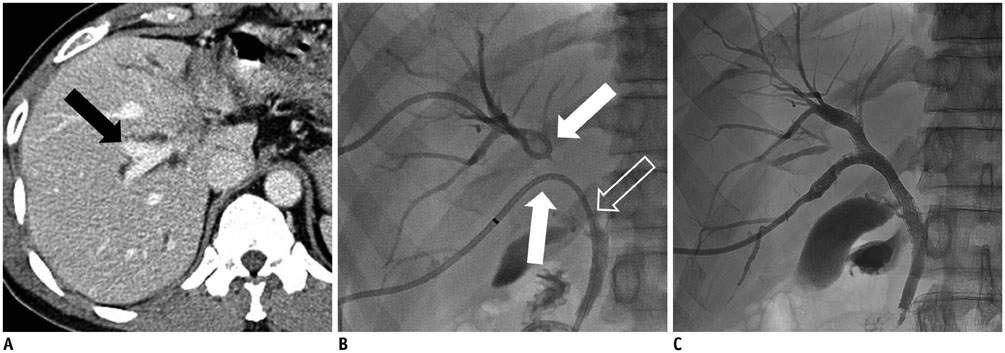
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Percutaneous Metallic Stent Placement for Palliative Management of Malignant Biliary Hilar Obstruction
Dong Jae Shim, Dong Il Gwon, Kichang Han, Yook Kim, Gi-Young Ko, Ji Hoon Shin, Heung Kyu Ko, Jin Hyoung Kim, Jong Woo Kim, Hyun-Ki Yoon, Kyu-Bo Sung
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):597-605. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.597.
Reference
-
1. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Sung KB, Yoon HK, Shin JH, Kim JH, et al. Percutaneous biliary metallic stent placement in patients with unilobar portal vein occlusion caused by advanced hilar malignancy: outcome of unilateral versus bilateral stenting. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:795–801.2. Bae JI, Park AW, Choi SJ, Kim HP, Lee SJ, Park YM, et al. Crisscross-configured dual stent placement for trisectoral drainage in patients with advanced biliary hilar malignancies. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:1614–1619.3. De Palma GD, Pezzullo A, Rega M, Persico M, Patrone F, Mastantuono L, et al. Unilateral placement of metallic stents for malignant hilar obstruction: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:50–53.4. Inal M, Akgül E, Aksungur E, Seydaoğlu G. Percutaneous placement of biliary metallic stents in patients with malignant hilar obstruction: unilobar versus bilobar drainage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1409–1416.5. Kawamoto H, Tsutsumi K, Harada R, Fujii M, Kato H, Hirao K, et al. Endoscopic deployment of multiple JOSTENT SelfX is effective and safe in treatment of malignant hilar biliary strictures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 6:401–408.6. Kim CW, Park AW, Won JW, Kim S, Lee JW, Lee SH. T-configured dual stent placement in malignant biliary hilar duct obstructions with a newly designed stent. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004; 15:713–717.7. Kim JY, Kang DH, Kim HW, Choi CW, Kim ID, Hwang JH, et al. Usefulness of slimmer and open-cell-design stents for endoscopic bilateral stenting and endoscopic revision in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:1109–1115.8. Naitoh I, Ohara H, Nakazawa T, Ando T, Hayashi K, Okumura F, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:552–557.9. Adam A. Metallic biliary endoprostheses. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1994; 17:127–132.10. Chang WH, Kortan P, Haber GB. Outcome in patients with bifurcation tumors who undergo unilateral versus bilateral hepatic duct drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 47:354–362.11. Cowling MG, Adam AN. Internal stenting in malignant biliary obstruction. World J Surg. 2001; 25:355–359. discussion 359-361.12. De Palma GD, Galloro G, Siciliano S, Iovino P, Catanzano C. Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic hepatic duct drainage in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction: results of a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:547–553.13. Polydorou AA, Cairns SR, Dowsett JF, Hatfield AR, Salmon PR, Cotton PB, et al. Palliation of proximal malignant biliary obstruction by endoscopic endoprosthesis insertion. Gut. 1991; 32:685–689.14. Yi R, Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK, Kim JH, Shin JH, et al. Percutaneous unilateral placement of biliary covered metallic stent in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction and contralateral portal vein occlusion. Acta Radiol. 2012; 53:742–749.15. Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA. Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14(9 Pt 2):S199–S202.16. Ichikawa H, Yamanaka K, Tobe T, Mizumoto R. Bile secretion in regenerating liver--a comparison of hepatic resection and ligation of the portal vein branch in dogs. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1984; 19:320–327.17. Sadakari Y, Miyoshi A, Ohtsuka T, Kohya N, Takahashi T, Matsumoto K, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic portal embolization for persistent bile leakage after hepatic resection: report of a case. Surg Today. 2008; 38:668–671.18. Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Iwata M, Kondo A, Isaji S, Uemoto S, et al. Refractory biliary leak from intrahepatic biliary-enteric anastomosis treated by selective portal vein embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:1279–1281.19. Hadjis NS, Adam A, Gibson R, Blenkharn JI, Benjamin IS, Blumgart LH. Nonoperative approach to hilar cancer determined by the atrophy-hypertrophy complex. Am J Surg. 1989; 157:395–399.20. Hann LE, Getrajdman GI, Brown KT, Bach AM, Teitcher JB, Fong Y, et al. Hepatic lobar atrophy: association with ipsilateral portal vein obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 167:1017–1021.21. Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, Shima Y, Moriyama N, Yamada T, Makuuchi M. Hepatic lobar atrophy following obstruction of the ipsilateral portal vein from hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Radiology. 1986; 160:389–393.22. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK, Kim JH, Lee JM, Ohm JY, et al. Prospective evaluation of a newly designed T-configured stent graft system for palliative treatment of advanced hilar malignant biliary obstructions. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21:1410–1418.23. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK, Kim YJ, Kim TH, Lee WH, et al. Safety and efficacy of percutaneous Y-configured covered stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a prospective, pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23:528–534.24. Hong HP, Seo TS, Cha IH, Yu JR, Mok YJ, Oh JH, et al. Percutaneous placement of self-expandable metallic stents in patients with obstructive jaundice secondary to metastatic gastric cancer after gastrectomy. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:789–796.25. Kang BC, Lee SW, Chung HH. A newly designed Y-shaped covered stent in the palliative treatment of hepatic hilar malignant obstruction: case report. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:97–101.26. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Kim JH, Yoon HK, Lee IS, Kim KA, et al. A comparative analysis of PTFE-covered and uncovered stents for palliative treatment of malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:W463–W469.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interventional radiologic approach to hilar malignant biliary obstruction
- Portal Vein Occlusion after Biliary Metal Stent Placement in Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
- Endoscopic Stent Placement in the Palliation of Malignant Biliary Obstruction
- Delayed Hemobilia Caused by Penetration of Biliary Plastic Stent into Portal Vein
- Combined Treatment with Metallic Stent Placement and Radiotherapy in Malignant Biliary Obstruction