J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Jun;25(6):888-894. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.888.
Clinical Presentations and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Perinatal Stroke in Preterm and Term Neonates: A Case Series
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. choicw@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2150868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.888
Abstract
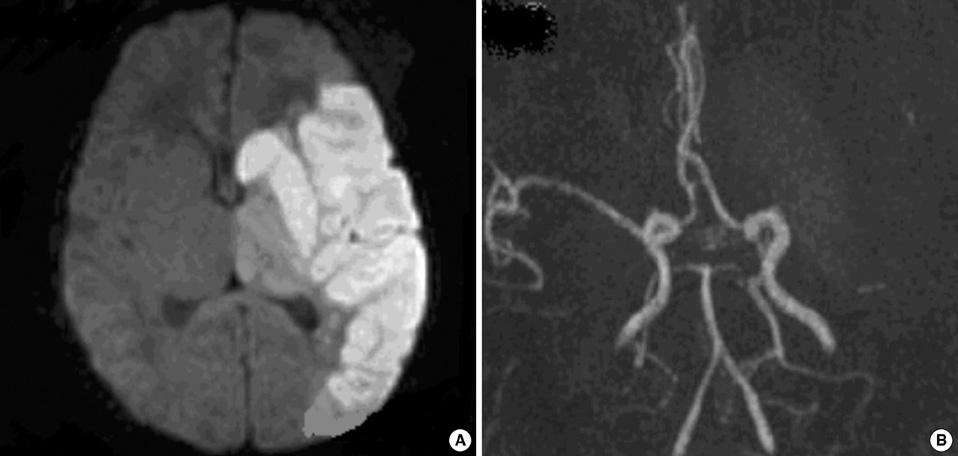
- Perinatal stroke in neonates can lead to disability in later life. However, its etiology and prognosis are poorly understood. The aim of this study was to describe clinical presentations and neurodevelopmental outcomes of our case series of perinatal stroke in Korea. Thirteen term and preterm neonates who were diagnosed with perinatal stroke in two university hospitals from March 2003 to March 2007 were enrolled. Seven term and 6 preterm neonates were diagnosed with perinatal stroke, based on the brain MRI findings. Perinatal stroke presented with seizure (4/13), perinatal distress (3/13) in term neonates, whereas stroke in preterm neonates did not present with noticeable clinical symptoms. Only one neonate had positive thrombophilic test (homozygous C677T polymorphism for MTHFR). Ten neonates had infarctions in the territory of the middle cerebral artery (MCA), and 3 neonates had borderzone infarctions between the anterior cerebral artery and MCA. Neurodevelopmental outcome was abnormal in 4 neonates. Infarction in MCA main branch or posterior limb of internal capsule showed an abnormal neurodevelopmental outcome. Our study is the first systematic study of perinatal stroke in Korea, and shows its clinical presentations and neurodevelopmental outcomes. The population-based study on incidence and prognosis of perinatal stroke in Korea is required in the future.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Neonatal Cerebral Infarction associated with Mutation in homozygous
MTHFR C677T Gene
Ji Ye Ahn, Min Seon Choi, Jae Hee Lee, Sang Kee Park
Korean J Perinatol. 2015;26(4):348-351. doi: 10.14734/kjp.2015.26.4.348.
Reference
-
1. Lee J, Croen LA, Backstrand KH, Yoshida CK, Henning LH, Lindan C, Ferriero DM, Fullerton HJ, Barkovich AJ, Wu YW. Maternal and infant characteristics associated with perinatal arterial stroke in the infant. JAMA. 2005. 293:723–729.
Article2. Boardman JP, Ganesan V, Rutherford MA, Saunders DE, Mercuri E, Cowan F. Magnetic resonance image correlates of hemiparesis after neonatal and childhood middle cerebral artery stroke. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:321–326.
Article3. Sreenan C, Bhargava R, Robertson CM. Cerebral infarction in the term newborn: clinical presentation and long-term outcome. J Pediatr. 2000. 137:351–355.
Article4. Wu YW, March WM, Croen LA, Grether JK, Escobar GJ, Newman TB. Perinatal stroke in children with motor impairment: a population-based study. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:612–619.
Article5. Ricci D, Mercuri E, Barnett A, Rathbone R, Cota F, Haataja L, Rutherford M, Dubowitz L, Cowan F. Cognitive outcome at early school age in term-born children with perinatally acquired middle cerebral artery territory infarction. Stroke. 2008. 39:403–410.
Article6. McLinden A, Baird AD, Westmacott R, Anderson PE, deVeber G. Early cognitive outcome after neonatal stroke. J Child Neurol. 2007. 22:1111–1116.
Article7. Lee J, Croen LA, Lindan C, Nash KB, Yoshida CK, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ, Wu YW. Predictors of outcome in perinatal arterial stroke: a population-based study. Ann Neurol. 2005. 58:303–308.
Article8. De Vries LS, Groenendaal F, Eken P, van Haastert IC, Rademaker KJ, Meiners LC. Infarcts in the vascular distribution of the middle cerebral artery in preterm and fullterm infants. Neuropediatrics. 1997. 28:88–96.
Article9. Sran SK, Baumann RJ. Outcome of neonatal strokes. Am J Dis Child. 1988. 142:1086–1088.
Article10. Estan J, Hope P. Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997. 76:F88–F93.
Article11. Benders MJ, Groenendaal F, Uiterwaal CS, Nikkels PG, Bruinse HW, Nievelstein RA. Maternal and infant characteristics associated with perinatal arterial stroke in the preterm infant. Stroke. 2007. 38:1759–1765.
Article12. De Vries LS, Van der Grond J, Van Haastert IC, Groenendaal F. Prediction of outcome in new-born infants with arterial ischaemic stroke using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropediatrics. 2005. 36:12–20.
Article13. Cowan F, Pennock J, Hanrahan J, Manji KP, Edwards AD. Early detection of cerebral infarction and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in neonates using diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropediatrics. 1994. 25:172–175.14. Huppi PS, Inder TE. Magnetic resonance techniques in the evaluation of the perinatal brain: recent advances and future directions. Semin Neonatol. 2001. 6:195–210.
Article15. Gillard JH, Papadakis NG, Martin K, Price CJ, Warburton EA, Antoun NM, Huang CL, Carpenter TA, Pickard JD. MR diffusion tensor imaging of white matter tract disruption in stroke at 3 T. Br J Radiol. 2001. 74:642–647.16. Kirton A, Shroff M, Visvanathan T, deVeber G. Quantified corticospinal tract diffusion restriction predicts neonatal stroke outcome. Stroke. 2007. 38:974–980.
Article17. Mercuri E, Rutherford M, Cowan F, Pennock J, Counsell S, Papadimitriou M, Azzopardi D, Bydder G, Dubowitz L. Early prognostic indicators of outcome in infants with neonatal cerebral infarction: a clinical, electroencephalogram, and magnetic resonance imaging study. Pediatrics. 1999. 103:39–46.
Article18. Mercuri E, Barnett A, Rutherford M, Guzzetta A, Haataja L, Cioni G, Cowan F, Dubowitz L. Neonatal cerebral infarction and neuromotor outcome at school age. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:95–100.
Article19. De Vries LS, Groenendaal F, van Haastert IC, Eken P, Rademaker KJ, Meiners LC. Asymmetrical myelination of the posterior limb of the internal capsule in infants with periventricular hemorrhagic infarction: an early predictor of hemiplegia. Neuropediatrics. 1999. 30:314–319.20. Perlman JM, Rollins NK, Evans D. Neonatal stroke: clinical characteristics and cerebral blood flow velocity measurements. Pediatr Neurol. 1994. 11:281–284.
Article21. Beattie LM, Butler SJ, Goudie DE. Pathways of neonatal stroke and subclavian steal syndrome. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006. 91:F204–F207.
Article22. Golomb MR, Garg BP, Carvalho KS, Johnson CS, Williams LS. Perinatal stroke and the risk of developing childhood epilepsy. J Pediatr. 2007. 151:409–413.
Article23. Carrilho I, Costa E, Barreirinho MS, Santos M, Barbot C, Barbot J. Prothrombotic study in full term neonates with arterial stroke. Haematologica. 2001. 86:E16.24. Mercuri E, Cowan F, Gupte G, Manning R, Laffan M, Rutherford M, Edwards AD, Dubowitz L, Roberts I. Prothrombotic disorders and abnormal neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with neonatal cerebral infarction. Pediatrics. 2001. 107:1400–1404.
Article25. Grabowski EF, Buonanno FS, Krishnamoorthy K. Prothrombotic risk factors in the evaluation and management of perinatal stroke. Semin Perinatol. 2007. 31:243–249.
Article26. Verdu A, Cazorla MR, Moreno JC, Casado LF. Prenatal stroke in a neonate heterozygous for factor V Leiden mutation. Brain Dev. 2005. 27:451–454.
Article27. Nelson KB. Thrombophilias, perinatal stroke, and cerebral palsy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2006. 49:875–884.
Article28. Bobrowska-Snarska D, Ostanek L, Nesterowicz B, Brzosko M. Severe neurological and obstetrical complications in a patient with antiphospholipid syndrome. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2006. 115:457–462.29. Selton D, Andre M, Hascoet JM. Interest of EEG in full-term newborns with isolated unilateral ischemic stroke. Arch Pediatr. 2005. 12:630–634.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Extremely Preterm Infants
- Case Series of Isolated Deep Gray Matter Injuries in Preterm Infants
- Neurodevelopmental Outcomes According to Brain Injury Patterns in Neonates with Postasphyxial Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
- Evaluation of the serum erythropoietin levels in neonates