Resin bonding of metal brackets to glazed zirconia with a porcelain primer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Tissue Regeneration Engineering (ITREN), Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department and Research Institute of Dental Biomaterials and Bioengineering, BK21 PLUS Project, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthodontics, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. hwang@yuhs.ac
- 4The Institute of Cranio-Facial Deformity, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2130592
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2015.45.6.299
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aims of this study were to compare the shear bond strength between orthodontic metal brackets and glazed zirconia using different types of primer before applying resin cement and to determine which primer was more effective.
METHODS
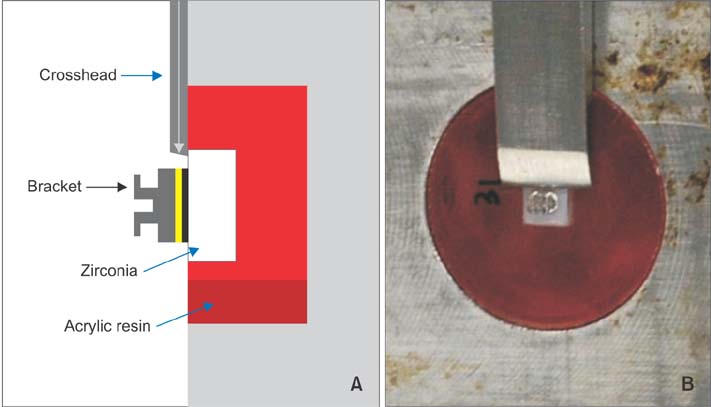
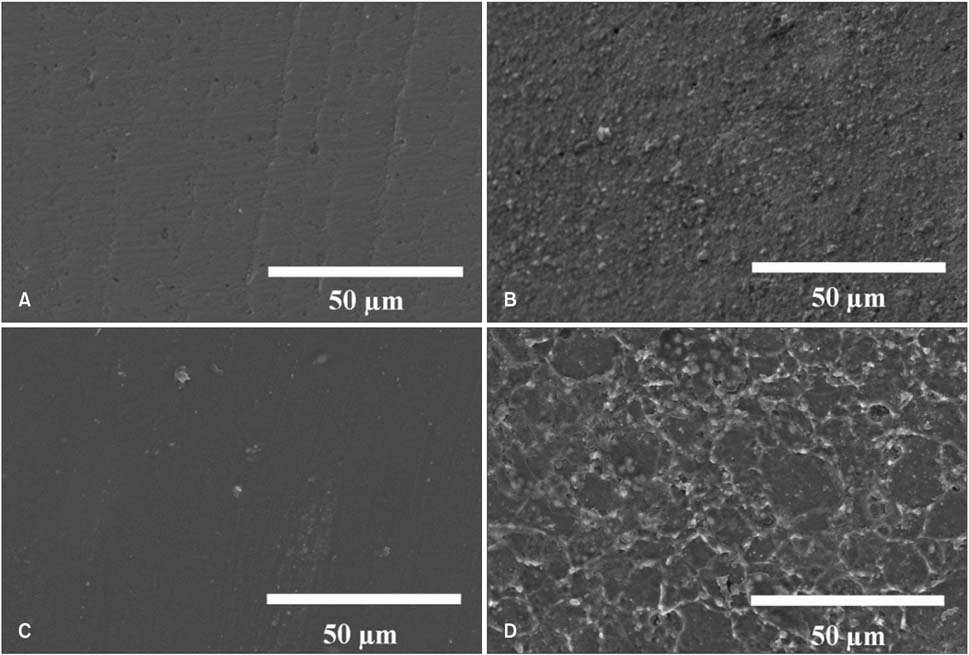
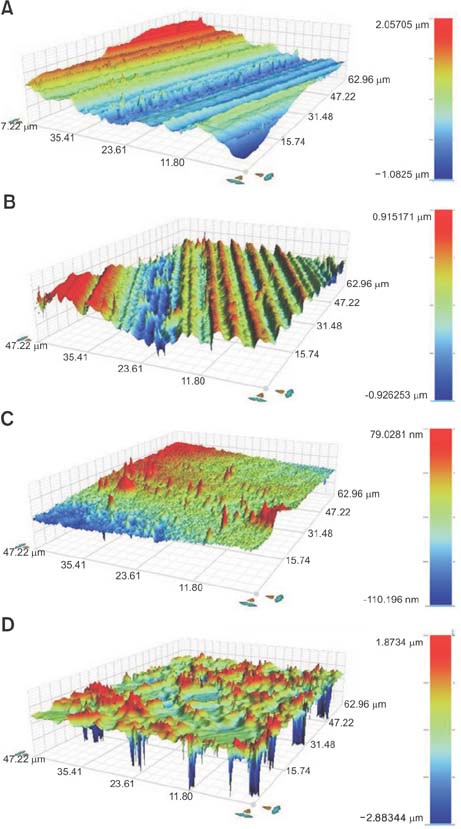
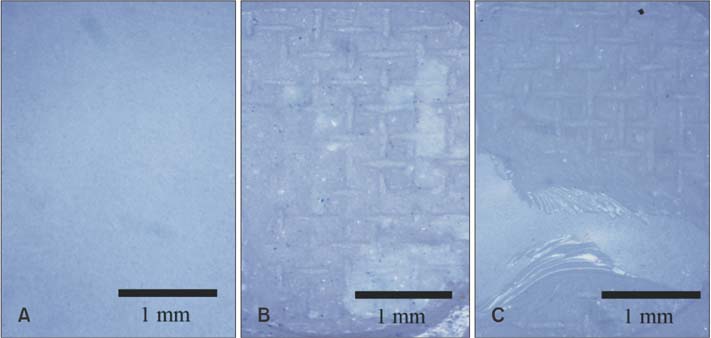
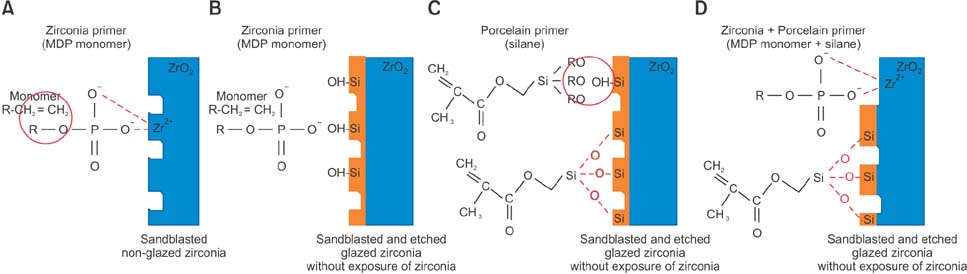
Zirconia blocks were milled and embedded in acrylic resin and randomly assigned to one of four groups: nonglazed zirconia with sandblasting and zirconia primer (NZ); glazed zirconia with sandblasting, etching, and zirconia primer (GZ); glazed zirconia with sandblasting, etching, and porcelain primer (GP); and glazed zirconia with sandblasting, etching, zirconia primer, and porcelain primer (GZP). A stainless steel metal bracket was bonded to each target surface with resin cement, and all specimens underwent thermal cycling. The shear bond strength of the specimens was measured by a universal testing machine. A scanning electron microscope, three-dimensional optical surface-profiler, and stereoscopic microscope were used to image the zirconia surfaces. The data were analyzed with one-way analyses of variance and the Fisher exact test.
RESULTS
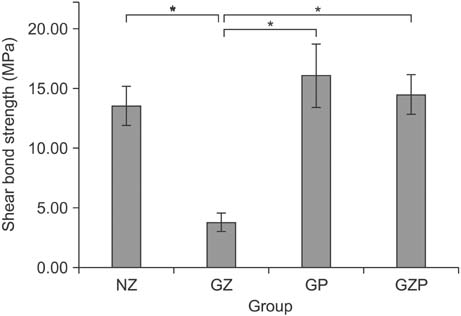
Group GZ showed significantly lower shear bond strength than did the other groups. No statistically significant differences were found among groups NZ, GP, and GZP. All specimens in group GZ showed adhesive failure between the zirconia and resin cement. In groups NZ and GP, bonding failed at the interface between the resin cement and bracket base or showed complex adhesive and cohesive failure.
CONCLUSIONS
Porcelain primer is the more appropriate choice for bonding a metal bracket to the surface of a full-contour glazed zirconia crown with resin cement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Comparison of the bonding strengths of second- and third-generation light-emitting diode light-curing units
Hee-Min Lee, Sang-Cheol Kim, Kyung-Hwa Kang, Na-Young Chang
Korean J Orthod. 2016;46(6):364-371. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.6.364.Bracket bonding to polymethylmethacrylate-based materials for computer-aided design/manufacture of temporary restorations: Influence of mechanical treatment and chemical treatment with universal adhesives
Cecilia Goracci, Mutlu Özcan, Lorenzo Franchi, Giuseppe Di Bello, Chris Louca, Alessandro Vichi
Korean J Orthod. 2019;49(6):404-412. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2019.49.6.404.Comparison of bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and a universal adhesive
Ji-Yeon Lee, Jaechan Ahn, Sang In An, Jeong-won Park
Restor Dent Endod. 2018;43(1):e7. doi: 10.5395/rde.2018.43.e7.Comparison of bond strengths of ceramic brackets bonded to zirconia surfaces using different zirconia primers and a universal adhesive
Ji-Yeon Lee, Jaechan Ahn, Sang In An, Jeong-won Park
Restor Dent Endod. 2018;43(1):. doi: 10.5395/rde.2018.43.e7.
Reference
-
1. Manicone PF, Rossi Iommetti P, Raffaelli L. An overview of zirconia ceramics: basic properties and clinical applications. J Dent. 2007; 35:819–826.
Article2. Piconi C, Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999; 20:1–25.
Article3. Cortellini D, Valenti M, Canale A. The metal-free approach to restorative treatment planning. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2006; 1:230–247.4. Bertolini Mde M, Kempen J, Lourenço EJ, Telles Dde M. The use of CAD/CAM technology to fabricate a custom ceramic implant abutment: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 111:362–366.
Article5. Keith O, Kusy RP, Whitley JQ. Zirconia brackets: an evaluation of morphology and coefficients of friction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994; 106:605–614.
Article6. Agustín-Panadero R, Román-Rodríguez JL, Ferreiroa A, Solá-Ruíz MF, Fons-Font A. Zirconia in fixed prosthesis. A literature review. J Clin Exp Dent. 2014; 6:e66–e73.
Article7. Ortorp A, Kihl ML, Carlsson GE. A 3-year retrospective and clinical follow-up study of zirconia single crowns performed in a private practice. J Dent. 2009; 37:731–736.
Article8. Miyazaki T, Nakamura T, Matsumura H, Ban S, Kobayashi T. Current status of zirconia restoration. J Prosthodont Res. 2013; 57:236–261.
Article9. Guess PC, Zavanelli RA, Silva NR, Bonfante EA, Coelho PG, Thompson VP. Monolithic CAD/CAM lithium disilicate versus veneered Y-TZP crowns: comparison of failure modes and reliability after fatigue. Int J Prosthodont. 2010; 23:434–442.10. Foxton RM, Cavalcanti AN, Nakajima M, Pilecki P, Sherriff M, Melo L, et al. Durability of resin cement bond to aluminium oxide and zirconia ceramics after air abrasion and laser treatment. J Prosthodont. 2011; 20:84–92.
Article11. Kitayama S, Nikaido T, Takahashi R, Zhu L, Ikeda M, Foxton RM, et al. Effect of primer treatment on bonding of resin cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2010; 26:426–432.
Article12. Takeuchi K, Fujishima A, Manabe A, Kuriyama S, Hotta Y, Tamaki Y, et al. Combination treatment of tribochemical treatment and phosphoric acid ester monomer of zirconia ceramics enhances the bonding durability of resin-based luting cements. Dent Mater J. 2010; 29:316–323.
Article13. Ozcan M, Vallittu PK. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the bond strength of luting cement to ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003; 19:725–731.
Article14. Borges GA, Sophr AM, de Goes MF, Sobrinho LC, Chan DC. Effect of etching and airborne particle abrasion on the microstructure of different dental ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2003; 89:479–488.
Article15. Rüttermann S, Fries L, Raab WH, Janda R. The effect of different bonding techniques on ceramic/resin shear bond strength. J Adhes Dent. 2008; 10:197–203.16. Ernst CP, Cohnen U, Stender E, Willershausen B. In vitro retentive strength of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns using different luting agents. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 93:551–558.
Article17. Xie H, Chen C, Dai W, Chen G, Zhang F. In vitro short-term bonding performance of zirconia treated with hot acid etching and primer conditioning etching and primer conditioning. Dent Mater J. 2013; 32:928–938.
Article18. Kumbuloglu O, Lassila LV, User A, Vallittu PK. Bonding of resin composite luting cements to zirconium oxide by two air-particle abrasion methods. Oper Dent. 2006; 31:248–255.
Article19. Wolfart M, Lehmann F, Wolfart S, Kern M. Durability of the resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic after using different surface conditioning methods. Dent Mater. 2007; 23:45–50.
Article20. Korkmaz FM, Bagis B, Turgut S, Ates SM, Ayaz EA. Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength of veneering ceramic to zirconia. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2015; 13:17–27.
Article21. Debnath S, Wunder SL, McCool JI, Baran GR. Silane treatment effects on glass/resin interfacial shear strengths. Dent Mater. 2003; 19:441–448.
Article22. Ando F, Komori A, Kojima I. Tensile bond strength of light-cured resin-reinforced glass ionomer cement with delayed light exposure. Odontology. 2001; 89:45–48.
Article23. Türkkahraman H, Küçükesmen HC. Porcelain surface-conditioning techniques and the shear bond strength of ceramic brackets. Eur J Orthod. 2006; 28:440–443.
Article24. Lee HS, Kim JS, Yoo SH. A comparative study of the shear bond strength and adhesive failure pattern of metal brackets bonded on natural teeth and porcelain teeth. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent. 2008; 35:195–204.25. Kocadereli I, Canay S, Akça K. Tensile bond strength of ceramic orthodontic brackets bonded to porcelain surfaces. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001; 119:617–620.
Article26. Schmage P, Nergiz I, Herrmann W, Ozcan M. Influence of various surface-conditioning methods on the bond strength of metal brackets to ceramic surfaces. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003; 123:540–546.
Article27. Qeblawi DM, Muñoz CA, Brewer JD, Monaco EA Jr. The effect of zirconia surface treatment on flexural strength and shear bond strength to a resin cement. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103:210–220.
Article28. Tsuo Y, Yoshida K, Atsuta M. Effects of alumina-blasting and adhesive primers on bonding between resin luting agent and zirconia ceramics. Dent Mater J. 2006; 25:669–674.
Article29. Yoshida K, Tsuo Y, Atsuta M. Bonding of dual-cured resin cement to zirconia ceramic using phosphate acid ester monomer and zirconate coupler. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006; 77:28–33.
Article30. Lopez JI. Retentive shear strengths of various bonding attachment bases. Am J Orthod. 1980; 77:669–678.
Article31. McCarthy MF, Hondrum SO. Mechanical and bond strength properties of light-cured and chemically cured glass ionomer cements. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994; 105:135–141.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets using various zirconia primers
- Orthodontic bracket bonding to glazed full-contour zirconia
- A comparative study on bond strength and adhesive failure pattern in bracket bonding with self-etching primer
- A study of the shear bond strength of metal brackets and ceramic brackets and the condition after debonding
- A study on the shear bond strengths of orthodontic brackets according to surface treatments and polymerizing techniques.