Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Nov;73(5):273-277. 10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.273.
A Case of Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. humanmd04@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2050680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.273
Abstract
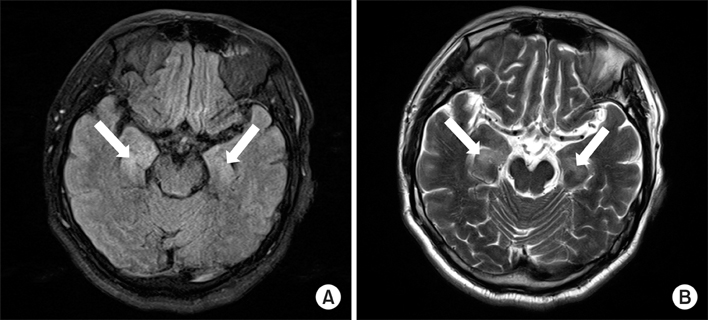
- Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis (PLE) is a rare syndrome characterized by memory impairment, affective and behavioral disturbances and seizures. Among many different neoplasms known to cause PLE, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most frequently reported. The pathogenesis is not fully understood but is believed to be autoimmune-related. We experienced a patient with typical clinical features of PLE. A 67-year-old man presented with seizure and disorientation. Brain magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated high signal intensity in the bilateral amygdala and hippocampus in flair and T2-weighted images suggestive of limbic encephalitis. Cerebrospinal fluid tapping revealed no evidence of malignant cells or infection. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography showed a lung mass with pleural effusion and a consequent biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of PLE associated with SCLC. The patient was subsequently treated with chemotherapy and neurologic symptoms gradually improved.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Paraneoplastic Brainstem Encephalitis Associated with Anti-Hu Antibody
Jee Eun Yoon, Kyung Bok Lee, Ji-Sun Kim, Moo-young Ahn, Hakjae Roh
J Neurocrit Care. 2015;8(2):126-129. doi: 10.18700/jnc.2015.8.2.126.
Reference
-
1. Gultekin SH, Rosenfeld MR, Voltz R, Eichen J, Posner JB, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis neurological symptoms, immunological findings and tumour association in 50 patients. Brain. 2000. 123(Pt 7):1481–1494.2. Darnell RB, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic syndromes involving the nervous system. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:1543–1554.3. Dalmau J, Rosenfeld MR. Paraneoplastic syndromes of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 2008. 7:327–340.4. Graus F, Delattre JY, Antoine JC, Dalmau J, Giometto B, Grisold W, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004. 75:1135–1140.5. Alamowitch S, Graus F, Uchuya M, Reñé R, Bescansa E, Delattre JY. Limbic encephalitis and small cell lung cancer: clinical and immunological features. Brain. 1997. 120(Pt 6):923–928.6. Graus F, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Neurol. 2007. 20:732–737.7. Sillevis Smitt P, Grefkens J, de Leeuw B, van den Bent M, van Putten W, Hooijkaas H, et al. Survival and outcome in 73 anti-Hu positive patients with paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy. J Neurol. 2002. 249:745–753.8. Dalmau J, Graus F, Villarejo A, Posner JB, Blumenthal D, Thiessen B, et al. Clinical analysis of anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis. Brain. 2004. 127(Pt 8):1831–1844.9. Cakirer S. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: case report. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2002. 26:55–58.10. Lawn ND, Westmoreland BF, Kiely MJ, Lennon VA, Vernino S. Clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and electroencephalographic findings in paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003. 78:1363–1368.11. Bakheit AM, Kennedy PG, Behan PO. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: clinico-pathological correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990. 53:1084–1088.12. Kobayakawa Y, Tateishi T, Kawamura N, Doi H, Ohyagi Y, Kira J. A case of immune-mediated encephalopathy showing refractory epilepsy and extensive brain MRI lesions associated with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2010. 50:92–97.13. Vedeler CA, Antoine JC, Giometto B, Graus F, Grisold W, Hart IK, et al. Management of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2006. 13:682–690.14. Bowyer S, Webb S, Millward M, Jasas K, Blacker D, Nowak A. Small cell lung cancer presenting with paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2011. 7:180–184.15. Cho TY, Kim YJ, Lee BI, Huh K. A case of limbic encephalitis associated with small cell lung cancer about diagnostic MRI findings. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1994. 12:338–342.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Limbic Encephalitis Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer: About Diagnostic MRI Findings
- Anti-Ma2-Associated Encephalitis with Axonal Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy
- A Case of Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis Associated with Immature Ovarian Teratoma
- A Case of Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis Associated with Primary Adenocarcinoma of Lung
- A Case of Immature Ovarian Teratoma Combined with Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis