J Korean Med Assoc.
2014 Jun;57(6):508-513. 10.5124/jkma.2014.57.6.508.
Pediatric intestinal failure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmkim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1958088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2014.57.6.508
Abstract
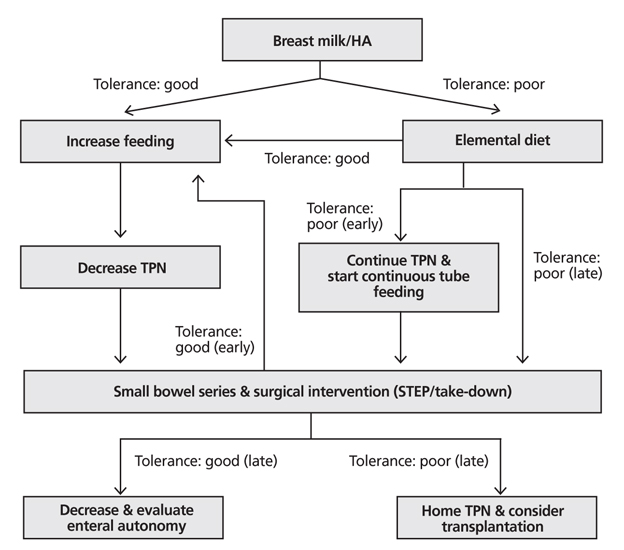
- Pediatric intestinal failure causes growth failure and mortality in children due to the inability to maintain normal nutritional balance. Short bowel syndrome is the most common cause in pediatric cases, and the residual bowel length is important for predicting long-term dependence on parenteral nutrition. Based on the possibility that the process of intestinal adaptation in children can continue throughout the first five years, enteral autonomy should be prioritized in the management of intestinal failure. Despite the lack of well-established guidelines, careful advance of enteral feeding and a multidisciplinary team approach are critical for optimizing survival outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Keefe SJ, Buchman AL, Fishbein TM, Jeejeebhoy KN, Jeppesen PB, Shaffer J. Short bowel syndrome and intestinal failure: consensus definitions and overview. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:6–10.2. Squires RH, Duggan C, Teitelbaum DH, Wales PW, Balint J, Venick R, Rhee S, Sudan D, Mercer D, Martinez JA, Carter BA, Soden J, Horslen S, Rudolph JA, Kocoshis S, Superina R, Lawlor S, Haller T, Kurs-Lasky M, Belle SH. Pediatric Intestinal Failure Consortium. Natural history of pediatric intestinal failure: initial report from the Pediatric Intestinal Failure Consortium. J Pediatr. 2012; 161:723–728.e2.
Article3. Lee MD, Kim SY, Kim WK, Kim IK, Kim SC, Kim SK, Kim JE, Kim JC, Kim HH, Park KW, Park WH, Seo JM, Song YT, Oh SM, Yoo SY, Lee DS, Lee SK, Lee SC, Chung SY, Chung SU, Jung ES, Jung PM, Cho MH, Choi KJ, Choi SO, Choi SH, Han SJ, Huh YS, Hong C, Whang EH. Index cases in pediatric surgery, 2000: national survey by the Korean association of pediatric surgeons. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2001; 7:147–156.
Article4. Kronfli R, Bradnock TJ, Sabharwal A. Intestinal atresia in association with gastroschisis: a 26-year review. Pediatr Surg Int. 2010; 26:891–894.
Article5. Andorsky DJ, Lund DP, Lillehei CW, Jaksic T, Dicanzio J, Richardson DS, Collier SB, Lo C, Duggan C. Nutritional and other postoperative management of neonates with short bowel syndrome correlates with clinical outcomes. J Pediatr. 2001; 139:27–33.
Article6. Quiros-Tejeira RE, Ament ME, Reyen L, Herzog F, Merjanian M, Olivares-Serrano N, Vargas JH. Long-term parenteral nutritional support and intestinal adaptation in children with short bowel syndrome: a 25-year experience. J Pediatr. 2004; 145:157–163.
Article7. Buchman AL, Scolapio J, Fryer J. AGA technical review on short bowel syndrome and intestinal transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:1111–1134.
Article8. Rudolph JA, Squires R. Current concepts in the medical management of pediatric intestinal failure. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010; 15:324–329.
Article9. Mazariegos GV, Superina R, Rudolph J, Cohran V, Burns RC, Bond GJ, Jaffe R, Sindhi R. Current status of pediatric intestinal failure, rehabilitation, and transplantation: summary of a colloquium. Transplantation. 2011; 92:1173–1180.
Article10. Oh SH. Short bowel syndrome and intestinal failure. In : Hong SK, editor. AMC ICU nutrition. Seoul: Koonja publication;2012. p. 248–252.11. Tomsits E, Pataki M, Tolgyesi A, Fekete G, Rischak K, Szollar L. Safety and efficacy of a lipid emulsion containing a mixture of soybean oil, medium-chain triglycerides, olive oil, and fish oil: a randomised, double-blind clinical trial in premature infants requiring parenteral nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 51:514–521.
Article12. Gura KM, Duggan CP, Collier SB, Jennings RW, Folkman J, Bistrian BR, Puder M. Reversal of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in two infants with short bowel syndrome using parenteral fish oil: implications for future management. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:e197–e201.
Article13. Wales PW, Allen N, Worthington P, George D, Compher C; the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, Teitelbaum D. ASPEN Clinical guidelines: support of pediatric patients with intestinal failure at risk of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014; 04. 02. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0148607114527772.14. Barclay AR, Beattie LM, Weaver LT, Wilson DC. Systematic review: medical and nutritional interventions for the management of intestinal failure and its resultant complications in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 33:175–184.
Article15. Goulet O, Ruemmele F. Causes and management of intestinal failure in children. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:2 Suppl 1. S16–S28.
Article16. Forchielli ML, Miller SJ. Nutritional goals and requirements. In : Merritt R, DeLegge MH, Holcombe B, Mueller C, Ochoa J, Smith KR, Schwenk WF, Guenter F, editors. The ASPEN nutrition support patient education manual. 2nd ed. Silver Spring: American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition;2008. p. 38–53.17. Cho YS. Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Indirect calorimetry in NST practice. In : Proceeding of 8th KSPEN NST Workshop; 2013 Mar 15; Seoul, Korea. Seongnam: Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition;2013.18. Lee SM. Regulations of domestic medical foods. In : Proceeding of 11st KSPEN Conference; 2012 Aug 24; Seoul, Korea. Seongnam: Korean Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition;2012.19. Ko JS. Current status of intestinal failure and intestinal transplantation. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012; 15:127–137.
Article20. Marshall JK, Gadowsky SL, Childs A, Armstrong D. Economic analysis of home vs hospital-based parenteral nutrition in Ontario, Canada. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2005; 29:266–269.
Article21. Kim KS. Strategy for activation of home total paren-teral nutrition. J Korean Soc Parent Enter Nutr. 2013; 5:96–101.
Article22. Choi S. Practical considerations in trace element supplementation via adult parenteral nutrition. J Korean Soc Parent Enter Nutr. 2013; 5:102–109.
Article23. Puder M, Valim C, Meisel JA, Le HD, de Meijer VE, Robinson EM, Zhou J, Duggan C, Gura KM. Parenteral fish oil improves outcomes in patients with parenteral nutrition-associated liver injury. Ann Surg. 2009; 250:395–402.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Intestinal Failure and Intestinal Transplantation
- Short Bowel Syndrome as the Leading Cause of Intestinal Failure in Early Life: Some Insights into the Management
- A Case of Duodenal Web Associated with Intestinal Malrotation
- The Update of Treatment for Primary Intestinal Lymphangiectasia
- Management Strategies for Patients with Chronic Intestinal Failure Who Are Potential Candidates for a Future Intestinal Transplant