Ewha Med J.
2021 Oct;44(4):103-110. 10.12771/emj.2021.44.4.103.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2521817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2021.44.4.103
Abstract
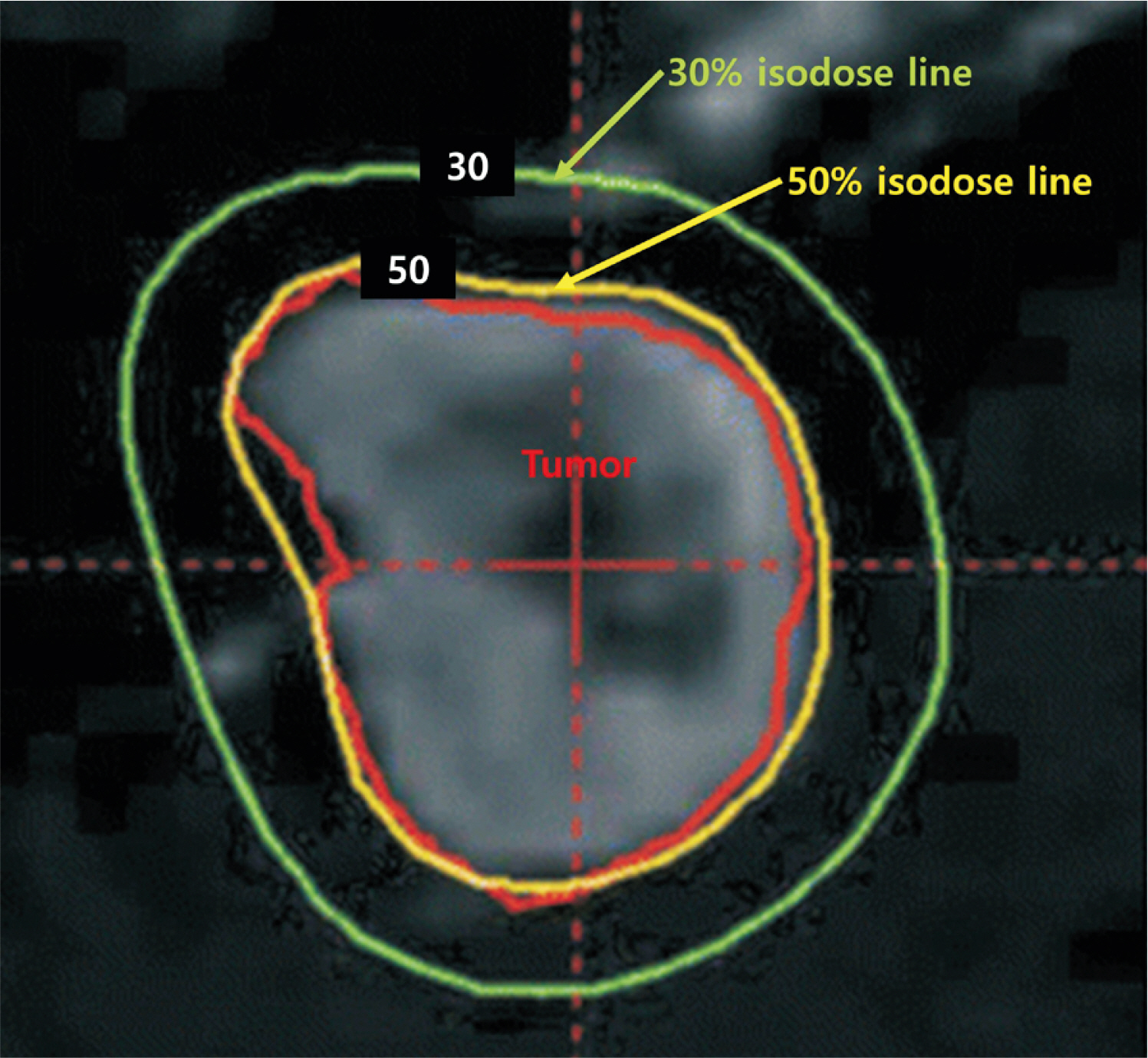
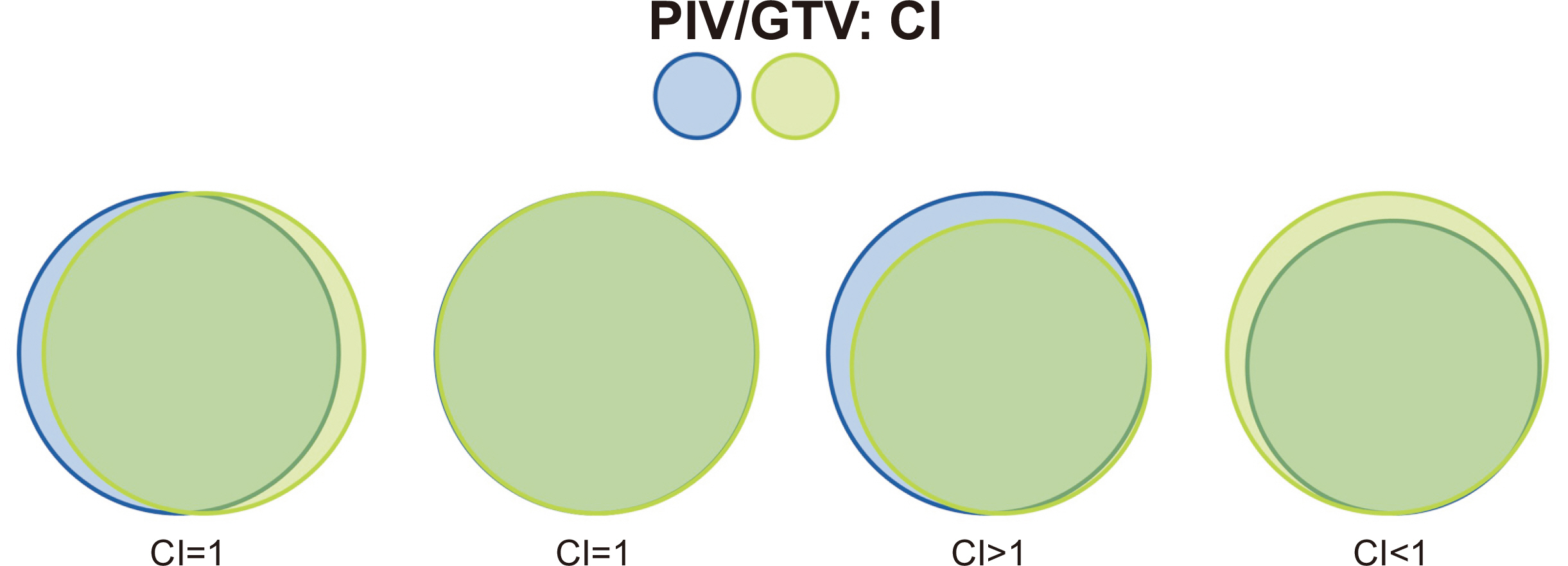
- Brain metastases are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with systemic cancer and are among the most common intracranial tumors in adults. Its incidence increases as cancer therapies improve, and patients live longer, providing new challenges to the multidisciplinary teams that manage these patients. The contemporary neurosurgical treatment of intracranial metastases has become gradually more complex as the available therapeutic options increase. For the past 50 years, wholebrain radiotherapy and systemic corticosteroids have been considered as the standard of care for patients with brain metastases. However, in recent years, stereotactic radiosurgery is spotlighted as an alternative therapeutic modality for these patients because of its relatively short, convenient, and non-invasive treatment course. Stereotactic radiosurgery is a radiation therapy technique in which multiple focused radiation beams intersect over a target, which results in the delivery of highly conformal, high-dose of radiation to the target and minimal radiation to surrounding normal parenchyma. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of stereotactic radiosurgery as a treatment modality for patients with brain metastases.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumor: What Should We Think a Little More about?
Na Rae Yang
Ewha Med J. 2022;45(1):25-27. doi: 10.12771/emj.2022.45.1.25.
Reference
-
1. Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY. 2012; Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep. 14:48–54. DOI: 10.1007/s11912-011-0203-y. PMID: 22012633.
Article2. Weissman DE. 1988; Glucocorticoid treatment for brain metastases and epidural spinal cord compression: a review. J Clin Oncol. 6:543–551. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.3.543. PMID: 3280744.
Article3. Brown PD, Pugh S, Laack NN, Wefel JS, Khuntia D, Meyers C, et al. 2013; Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro Oncol. 15:1429–1437. DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/not114. PMID: 23956241. PMCID: PMC3779047.
Article4. Chao JH, Phillips R, Nickson JJ. 1954; Roentgen-ray therapy of cerebral metastases. Cancer. 7:682–689. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(195407)7:4<682::AID-CNCR2820070409>3.0.CO;2-S.
Article5. Chu FC, Hilaris BB. 1961; Value of radiation theray in the management of intracranial metastases. Cancer. 14:577–581. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(199005/06)14:3<577::AID-CNCR2820140318>3.0.CO;2-F.6. Mulvenna P, Nankivell M, Barton R, Faivre-Finn C, Wilson P, McColl E, et al. 2016; Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomized trial. Lancet. 388:2004–2014. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30825-X.7. Pinkham MB, Sanghera P, Wall GK, Dawson BD, Whitfield GA. 2015; Neurocognitive effects following cranial irradiation for brain metastases. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 27:630–639. DOI: 10.1016/j.clon.2015.06.005. PMID: 26119727.
Article8. Wu A, Lindner G, Maitz AH, Kalend AM, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, et al. 1990; Physics of gamma knife approach on convergent beams in stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 18:941–949. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(90)90421-F.
Article9. Sturm V, Kober B, Hover KH, Schlegel W, Boesecke R, Pastyr O, et al. 1987; Stereotactic percutaneous single dose irradiation of brain metastases with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 13:279–282. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(87)90140-4.
Article10. Hartgerink D, Swinnen A, Roberge D, Nichol A, Zygmanski P, Yin FF, et al. 2019; LINAC based stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: guidance for clinical implementation. Acta Oncol. 58:1275–1282. DOI: 10.1080/0284186X.2019.1633016. PMID: 31257960.
Article11. Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE. 2004; Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol. 22:2865–2872. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149. PMID: 15254054.
Article12. Tabouret E, Chinot O, Metellus P, Tallet A, Viens P, Goncalves A. 2012; Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: an overview. Anticancer Res. 32:4655–4662.13. Percy AK, Elveback LR, Okazaki H, Kurland LT. 1972; Neoplasms of the central nervous system. Epidemiologic considerations. Neurology. 22:40–48. DOI: 10.1212/WNL.22.1.40. PMID: 5061838.14. Posner JB, Chernik NL. 1978; Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol. 19:579–592.15. Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. 1983; Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma: autopsy study. Cancer. 52:2349–2354. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831215)52:12<2349::AID-CNCR2820521231>3.0.CO;2-B.
Article16. Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK, Luo X, Suh J, Roberge D, et al. 2010; Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:655–661. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.025. PMID: 19942357.
Article17. Berghoff AS, Schur S, Fureder LM, Gatterbauer B, Dieckmann K, Widhalm G, et al. 2016; Descriptive statistical analysis of a real life cohort of 2419 patients with brain metastases of solid cancers. ESMO Open. 1:e000024. DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2015-000024. PMID: 27843591. PMCID: PMC5070252.
Article18. Nieder C, Spanne O, Mehta MP, Grosu AL, Geinitz H. 2011; Presentation, patterns of care, and survival in patients with brain metastases: what has changed in the last 20 years? Cancer. 117:2505–2512. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.25707. PMID: 24048799.19. Brown PD, Asher AL, Ballman KV, Farace E, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, et al. 2015; NCCTG N0574 (Alliance): A phase III randomized trial of whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in addition to radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 33(18_suppl):LBA4. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2015.33.18_suppl.lba4.
Article20. Toyokawa G, Seto T, Takenoyama M, Ichinose Y. 2015; Insights into brain metastasis in patients with ALK+ lung cancer: is the brain truly a sanctuary? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 34:797–805. DOI: 10.1007/s10555-015-9592-y. PMID: 26342831. PMCID: PMC4661196.
Article21. Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, et al. 1997; Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 37:745–751. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(96)00619-0.
Article22. Noordijk EM, Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, Padberg GW, Voormolen JH, Hoekstra FH, et al. 1994; The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 29:711–717. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)90558-4.
Article23. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. 1990; A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 322:494–500. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199002223220802. PMID: 2405271.
Article24. Mintz AH, Kestle J, Rathbone MP, Gaspar L, Hugenholtz H, Fisher B, et al. 1996; A randomized trial to assess the efficacy of surgery in addition to radiotherapy in patients with a single cerebral metastasis. Cancer. 78:1470–1476. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19961001)78:7<1470::AID-CNCR14>3.0.CO;2-X.
Article25. Hatiboglu MA, Akdur K, Sawaya R. 2020; Neurosurgical management of patients with brain metastasis. Neurosurg Rev. 43:483–495. DOI: 10.1007/s10143-018-1013-6. PMID: 30058049.
Article26. Soffietti R, Ruda R, Trevisan E. 2008; Brain metastases: current management and new developments. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:676–684. DOI: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e32831186fe. PMID: 18841050.
Article27. Yu C, Chen JC, Apuzzo ML, O'Day S, Giannotta SL, Weber JS, et al. 2002; Metastatic melanoma to the brain: prognostic factors after gamma knife radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 52:1277–1287. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(01)02772-9.
Article28. Goyal LK, Suh JH, Reddy CA, Barnett GH. 2000; The role of whole brain radiotherapy and stereotactic radiosurgery on brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:1007–1012. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00536-8.
Article29. Leibel SA, Sheline GE. 1987; Radiation therapy for neoplasms of the brain. J Neurosurg. 66:1–22. DOI: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.1.0001. PMID: 3023563.
Article30. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Goodman ML, Shaw EG, et al. 1994; A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 28:797–802. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)90098-1.
Article31. Li B, Yu J, Suntharalingam M, Kennedy AS, Amin PP, Chen Z, et al. 2000; Comparison of three treatment options for single brain metastasis from lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 90:37–45. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(20000220)90:1<37::AID-IJC5>3.0.CO;2-7.
Article32. Hatiboglu MA, Chang EL, Suki D, Sawaya R, Wildrick DM, Weinberg JS. 2011; Outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with brainstem metastases undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 69:796–806. DOI: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e31821d31de. PMID: 21508879.
Article33. Chang EL, Selek U, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd, Maor MH, Allen PK, Mahajan A, et al. 2005; Outcome variation among "radioresistant" brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 56:936–945.34. Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, et al. 2000; Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:291–298. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00507-6.
Article35. Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, et al. 2004; Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet. 363:1665–1672. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8.
Article36. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ, et al. 1998; Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA. 280:1485–1489. DOI: 10.1001/jama.280.17.1485. PMID: 9809728.
Article37. Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. 2006; Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 295:2483–2491. DOI: 10.1001/jama.295.21.2483. PMID: 16757720.38. Nabors LB, Portnow J, Ahluwalia M, Baehring J, Brem H, Brem S, et al. 2020; Central nervous system cancers, version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 18:1537–1570. DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0052. PMID: 33152694.
Article39. Linskey ME, Andrews DW, Asher AL, Burri SH, Kondziolka D, Robinson PD, et al. 2010; The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol. 96:45–68. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-009-0073-4. PMID: 19960227. PMCID: PMC2808519.
Article40. Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, et al. 2009; Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:1037–1044. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3.
Article41. Knisely JP, Yamamoto M, Gross CP, Castrucci WA, Jokura H, Chiang VL. Radiosurgery alone for 5 or more brain metastases: expert opinion survey. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113 Suppl:84–89. DOI: 10.3171/2010.8.GKS10999. PMID: 21121790.
Article42. Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Sato Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, et al. 2017; A multi-institutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901 study update): irradiation-related complications and long-term maintenance of mini-mental state examination scores. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 99:31–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.037. PMID: 28816158.
Article43. Subbiah IM, Lei X, Weinberg JS, Sulman EP, Chavez-MacGregor M, Tripathy D, et al. 2015; Validation and development of a modified breast graded prognostic assessment as a tool for survival in patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 33:2239–2245. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.8517. PMID: 25987700. PMCID: PMC5098846.
Article44. Minniti G, Capone L, Nardiello B, El Gawhary R, Raza G, Scaringi C, et al. 2020; Neurological outcome and memory performance in patients with 10 or more brain metastases treated with frameless linear accelerator (LINAC)-based stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol. 148:47–55. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-020-03442-7. PMID: 32100230.
Article45. Kim M, Cho KR, Choi JW, Kong DS, Seol HJ, Nam DH, et al. 2020; Two-staged gamma knife radiosurgery for treatment of numerous (>10) brain metastases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 195:105847. DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105847. PMID: 32371318.46. Brennan C, Yang TJ, Hilden P, Zhang Z, Chan K, Yamada Y, et al. 2014; A phase 2 trial of stereotactic radiosurgery boost after surgical resection for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88:130–136. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.09.051. PMID: 24331659. PMCID: PMC5736310.
Article47. Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A, Lo SS, Danielson BL, Gaspar LE, et al. 2012; Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): an American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2:210–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.004. PMID: 25925626. PMCID: PMC3808749.
Article48. Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC, et al. 2017; Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC•3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1049–1060. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2.
Article49. Choi CY, Chang SD, Gibbs IC, Adler JR, Harsh GR 4th, Lieberson RE, et al. 2012; Stereotactic radiosurgery of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases: prospective evaluation of target margin on tumor control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 84:336–342. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.009. PMID: 22652105.
Article50. Patel KR, Burri SH, Asher AL, Crocker IR, Fraser RW, Zhang C, et al. 2016; Comparing preoperative with postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for resectable brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. Neurosurgery. 79:279–285. DOI: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000001096. PMID: 26528673.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases
- Comparative Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Multisession Radiosurgery to Single Dose Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors
- How to use Leksell GammaPlan
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery after Stereotactic Aspiration for Large Cystic Brain Metastases
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme using Yeungnam Localization Device :Technical note and Clinical trial