J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Jun;29(6):782-787. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.782.
Phenotype Difference between Familial and Sporadic Ankylosing Spondylitis in Korean Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. elee@snu.ac.kr
- 3Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Applied Statistics, Dankook University, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 1796939
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.782
Abstract
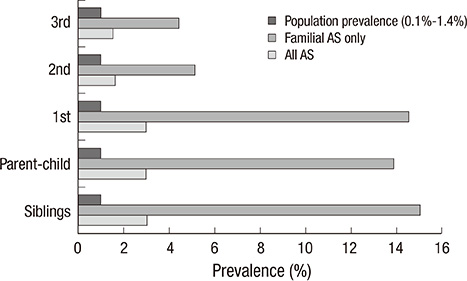
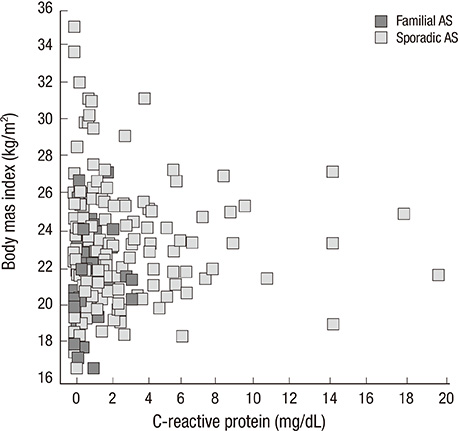
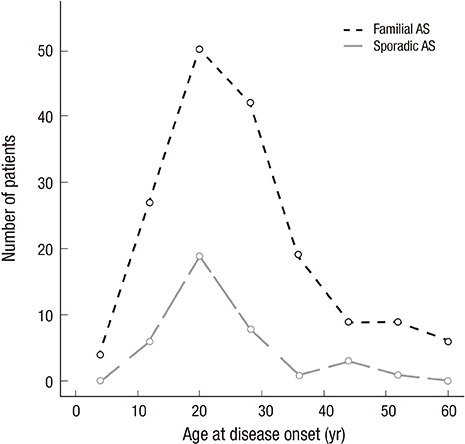
- Clustered occurrences of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in family have been noticed. We evaluated patients with AS confirmed by the modified New York criteria for familial history of AS (one or more first to third degree relatives). The clinical characteristics and the recurrence risks (number of AS patients/number of familial members) of the familial AS compared to sporadic AS were investigated. Out of a total of 204 AS patients, 38 patients (18.6%) reported that they had a familial history of AS. The recurrence risks in the familial AS patients for first, second and third degree family members were 14.5%, 5.2%, and 4.4% respectively. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (22.6+/-22.2 vs 35.4+/-34.4, P=0.029) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (1.24+/-1.7 vs 2.43+/-3.3, P=0.003) at diagnosis, body mass index (21.9+/-2.7 vs 23.7+/-3.3, P=0.002) and frequency of oligoarthritis (13.2% vs 33.7%, P=0.021) were significantly lower in the familial form. The presence of HLA-B27 (97.4% vs 83.1%, P=0.044) was significantly higher in familial AS. In conclusion, Korean familial AS patients show a lower frequency of oligoarthritis, lower BMI, lower ESR and CRP at diagnosis and higher presence of HLA-B27.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Age Factors
Arthritis, Juvenile/diagnosis/epidemiology
Blood Sedimentation
Body Mass Index
C-Reactive Protein/analysis
Demography
Family
Female
HLA-B27 Antigen/metabolism
Humans
Interviews as Topic
Male
Middle Aged
Phenotype
Recurrence
Republic of Korea
Risk Factors
Severity of Illness Index
Sex Factors
Spondylitis, Ankylosing/*diagnosis
HLA-B27 Antigen
C-Reactive Protein
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hopper JL. Disease-specific prospective family study cohorts enriched for familial risk. Epidemiol Perspect Innov. 2011; 8:2.2. O'Neill SM, Rubinstein WS, Wang C, Yoon PW, Acheson LS, Rothrock N, Starzyk EJ, Beaumont JL, Galliher JM, Ruffin MT 4th. Familial risk for common diseases in primary care: the Family Healthware Impact Trial. Am J Prev Med. 2009; 36:506–514.3. Kramer JL, Velazquez IA, Chen BE, Rosenberg PS, Struewing JP, Greene MH. Prophylactic oophorectomy reduces breast cancer penetrance during prospective, long-term follow-up of BRCA1 mutation carriers. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8629–8635.4. Hartmann LC, Schaid DJ, Woods JE, Crotty TP, Myers JL, Arnold PG, Petty PM, Sellers TA, Johnson JL, McDonnell SK, et al. Efficacy of bilateral prophylactic mastectomy in women with a family history of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:77–84.5. Brown MA, Laval SH, Brophy S, Calin A. Recurrence risk modelling of the genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000; 59:883–886.6. Brown MA, Kennedy LG, MacGregor AJ, Darke C, Duncan E, Shatford JL, Taylor A, Calin A, Wordsworth P. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: the role of genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:1823–1828.7. Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey M, James DC, Sturrock RD. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973; 1:904–907.8. Schlosstein L, Terasaki PI, Bluestone R, Pearson CM. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973; 288:704–706.9. Van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A. The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals: a comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:241–249.10. Said-Nahal R, Miceli-Richard C, Berthelot JM, Duché A, Dernis-Labous E, Le Blévec G, Saraux A, Perdriger A, Guis S, Claudepierre P, et al. The familial form of spondylarthropathy: a clinical study of 115 multiplex families: Groupe Français d'Etude Génétique des Spondylarthropathies. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1356–1365.11. Calin A, Kennedy LG, Edmunds L, Will R. Familial versus sporadic ankylosing spondylitis: two different diseases? Arthritis Rheum. 1993; 36:676–681.12. Almodóvar R, Font P, Zarco-Montejo P, Collantes E, Mulero J, Gratacós J, Juanola X, Ariza R. Phenotypic differences between familial versus sporadic ankylosing spondylitis: a cross-sectional Spanish registry of spondyloarthropathies (REGISPONSER). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011; 29:822–827.13. Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R, Huitfeldt B, Amor B, Calin A, Cats A, Dijkmans B, Olivieri I, Pasero G, et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991; 34:1218–1227.14. Chou CT, Lin KC, Wei JC, Tsai WC, Ho HH, Hwang CM, Cherng JM, Hsu CM, Yu DT. Study of undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy among first-degree relatives of ankylosing spondylitis probands. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:662–665.15. Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:361–368.16. Paardt Mv, Dijkmans B, Giltay E, van der Horst-Bruinsma I. Dutch patients with familial and sporadic ankylosing spondylitis do not differ in disease phenotype. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:2583–2584.17. De Vlam K, Vastesaeger N, Brasseur JP, Boonen A, Lenaerts J, Lesaffre E, Mielants H, Steinfeld S, Ribbens C, Leroi H, et al. Belgian patients with familial and sporadic ankylosing spondylitis differ in disease phenotype. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:S717–S718.18. Hamersma J, Cardon LR, Bradbury L, Brophy S, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Calin A, Brown MA. Is disease severity in ankylosing spondylitis genetically determined? Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:1396–1400.19. Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006; 17:4–12.20. Ottaviani S, Allanore Y, Tubach F, Forien M, Gardette A, Pasquet B, Palazzo E, Meunier M, Hayem G, Job-Deslandre C, et al. Body mass index influences the response to infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012; 14:R115.21. Miceli-Richard C, Said-Nahal R, Breban M. Impact of sex on inheritance of ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet. 2000; 355:1097–1098.22. Calin A, Brophy S, Blake D. Impact of sex on inheritance of ankylosing spondylitis: a cohort study. Lancet. 1999; 354:1687–1690.23. Brown MA, Crane AM, Wordsworth BP. Genetic aspects of susceptibility, severity, and clinical expression in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002; 14:354–360.24. Hoyle E, Laval SH, Calin A, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA. The X-chromosome and susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1353–1355.25. Joshi R, Reveille JD, Brown MA, Weisman MH, Ward MM, Gensler LS, Wordsworth BP, Evans DM, Assassi S. Is there a higher genetic load of susceptibility loci in familial ankylosing spondylitis? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:780–784.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Treatment of Cervical Cord Injury with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Case Report
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Treatment of Cervical Cord Injury in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Orthopaedic Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis