J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Jun;23(3):445-451. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.445.
Outcome of Immunosuppressive Therapy with Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy in Patients with Chronic Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea. hemon@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 1786883
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.445
Abstract
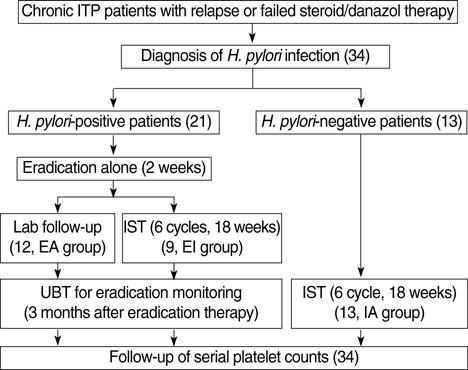
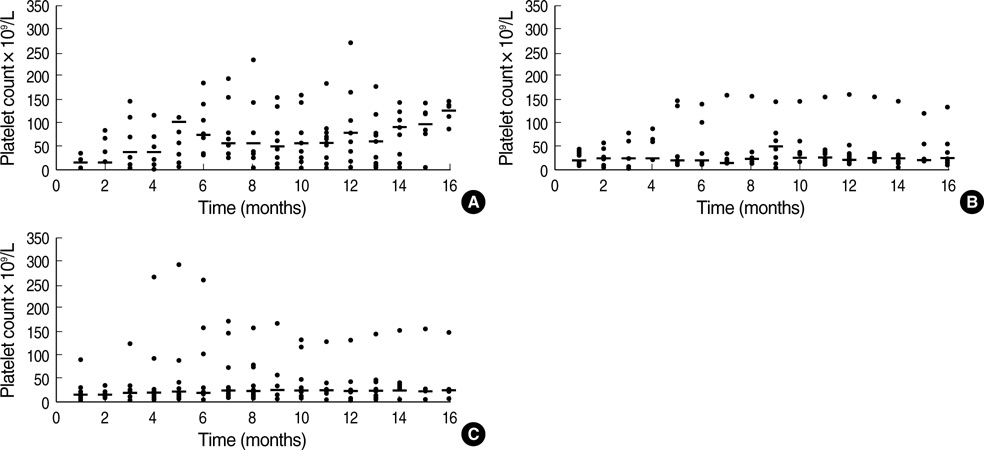
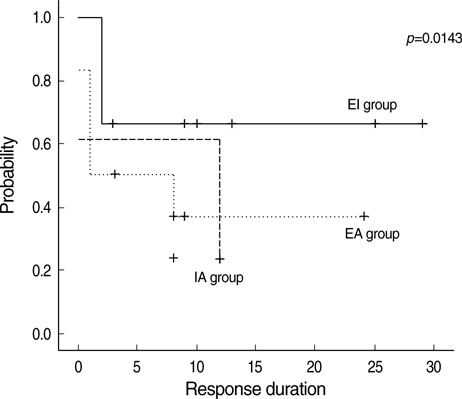
- We initiated this study to investigate whether combining Helicobacter pylori eradication with immunosuppressive therapy provides an additional benefit to patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) that has relapsed or has not responded to steroid and/or danazol therapy in patients who have H. pylori infection. Thirty- four patients with chronic ITP that had relapsed or failed to steroid and/or danazol therapy were assessed for H. pylori infection. Of the 21 confirmed cases, 12 patients were given H. pylori eradication therapy alone (EA), while 9 patients received eradication therapy combined with immunosuppressive therapy (EI). The response rate was not significantly different between patients in the EA and those in the EI group (41.7% in the EA group vs. 66.7% in the EI group, p=0.345). The median platelet count at 6 months after therapy was higher in the EI group patients (75X10(9)/L in the EI group patients vs. 18x109/L in the EA group patients, p=0.028). The median response duration was also longer in the EI group patients (9 months in the EI group patients vs. 3 months in the EA group patients, p=0.049). These results show that a significant benefit is gained by the use of H. pylori eradication combined with immunosuppressive therapy over the use of eradication therapy alone for patients with chronic ITP.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*administration & dosage
Chronic Disease
Danazol/administration & dosage
Drug Therapy, Combination
Estrogen Antagonists/administration & dosage
Female
Helicobacter Infections/complications/*drug therapy
*Helicobacter pylori
Humans
Immunosuppressive Agents/*administration & dosage
Male
Middle Aged
Purpura, Thrombocytopenic, Idiopathic/complications/*drug therapy
Steroids/administration & dosage
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karpatkin S. Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1980. 56:329–343.
Article2. McMillan R. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1981. 304:1135–1147.
Article3. Graham DY. Helicobacter pylori infection in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer and gastric cancer: A model. Gastroenterology. 1997. 113:1983–1991.
Article4. Parsonnet J, Hansen S, Rodriguez L, Gelb AB, Warnke RA, Jellum E, Orentreich N, Vogelman JH, Friedman GD. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1994. 330:1267–1271.5. Zentillin P, Savarino V, Garnero A, Accardo S, Seriolo B. Is Helicobacter pylori infection a risk factor or disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis? Gastroenterology. 1999. 116:503–504.6. De Luis DA, Valela C, de la Calle H, Canton R, de Argila CM, San Roman AL, Boixeda D. Helicobacter pylori infection is markedly increased in patients with autoimmune atrophic thyroiditis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998. 26:259–263.
Article7. Gasbarrini A, Franceschi F. Autoimmune diseases and Helicobacter pylori infection. Biomed Pharmacother. 1999. 53:223–226.
Article8. Tsang KW, Lam SK. Helicobacter pylori and extra-digestive diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. 14:844–850.9. Gasbarrini A, Franceschi F, Tartaglione R, Landolfi R, Pola P, Gasbarrini G. Regression of autoimmune thrombocytopenia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1998. 352:878.
Article10. Emilia G, Longo G, Luppi M, Gandini G, Morselli M, Ferrara L, Amarri S, Cagossi K, Torelli G. Helicobacter pylori eradication can induce platelet recovery in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2001. 97:812–814.
Article11. Veneri D, Franchini M, Gottardi M, D'Adda M, Ambrosetti A, Krampera M, Zanetti F, Pizzolo G. Efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication in raising platelet count in adult patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica. 2002. 87:1177–1179.12. Emilia G, Luppi M, Morselli M, Potenza L, D'Apollo N, Torelli G. Helicobacter pylori infection and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2002. 118:1198–1199.
Article13. Kohda K, Kuga T, Kogawa K, Kanisawa Y, Koite K, Kuroiwa G, Hirayama Y, Sato Y, Niitsu Y. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on platelet recovery in Japanese patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and secondary autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2002. 118:584–588.
Article14. Hashino S, Mori A, Suzuki S, Izumiyama K, Kahata K, Yonezumi M, Chiba K, Kondo T, Ota S, Toyashima N, Kato N, Tanaka J, Imamura M, Asaka M. Platelet recovery in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Int J Hematol. 2003. 77:188–191.
Article15. Hino M, Yamane T, Park K, Takubo T, Ohta K, Kitagawa S, Higuchi K, Arakawa T. Platelet recovery after eradication of Helicobacter pylori in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Hematol. 2003. 82:30–32.
Article16. Michel M, Cooper N, Jean C, Frissora C, Bussel JB. Does Helicobater pylori initiate or perpetuate immune thrombocytopenic purpura? Blood. 2004. 103:890–896.
Article17. Figueroa M, Gehlsen J, Hammond D, Ondreyco S, Piro L, Pomeroy T, Williams F, McMillan R. Combination chemotherapy in refractory immune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:1226–1229.
Article18. Inoue Y, Nakagawa Y, Sawanobori M, Suzuki K, Enomoto H. Combination chemotherapy (CVP) in a patient with refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Rinsho ketsueki. 1998. 39:193–197.19. Tamai Y, Takami H, Akagi T, Kawamura S, Munakata A. Combination chemotherapy in a patient with severe multiple systemic autoimmune disease. Clin Lab Haematol. 1998. 20:315–316.
Article20. Takahashi T, Yujiri T, Shinohara K, Inonue Y, Sato Y, Fujii Y, Okubo M, Zaitsu Y, Ariyoshi K, Nakamura Y, Nawata R, Oka Y, Shirai M, Tanizawa Y. Molecular mimicry by Helicobater pylori CagA protein may be involved in the pathogenesis of H. pylori-associated chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2004. 124:91–96.21. Perez-Perez GI, Bhat N, Gaensbauer J, Fraser A, Taylor DN, Kuipers EJ, Zhang L, You WC, Elaser MJ. Country-specific constancy by age in cagA proportion of Helicobacter pylori infections. Int J Cancer. 1997. 72:453–456.22. Evans DJ Jr, Evans DG. Helicobacter pylori CagA: analysis of sequence diversity in relation to phosphorylation motifs and implications for the role of CagA as a virulence factor. Helicobacter. 2001. 6:187–198.
Article23. Veneri D, Gottardi M, Guizzardi E, Zanuso C, Krampera M, Franchini M. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Helicobacter pylori infection and HLA class II alleles. Blood. 2002. 100:1926–1927.
Article24. Jarque I, Andreu R, Llopis I, De la Rubia J, Gomis F, Senent L, Jimenez C, Martin G, Martinez JA, Sanz GF, Ponce J, Sanz MA. Absence of platelet response after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2001. 115:1002–1003.
Article25. Baker GL, Kahl LE, Zee BC, Stolzer BL, Aganval AK, Medsger TA Jr. Malignancy following treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with cyclophosphamide. Am J Med. 1987. 83:1–9.
Article26. Krause JR. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: Development of acute non-lymphocytic leukemia subsequent to treatment with cyclophosphamide. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1982. 10:61–65.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: Report of 3 cases
- Resolution of Chronic Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: A Case Report
- The Effects of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy for Chronic Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Helicobacter pylori Eradication, a Gordian Knot for Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura?
- Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura