Yonsei Med J.
2007 Dec;48(6):927-933. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.927.
Lamivudine Therapy for Korean Children with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kschung58@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1786205
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.927
Abstract
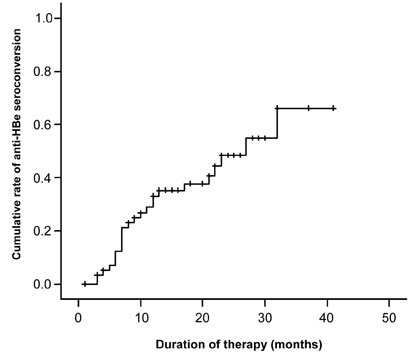
- PURPOSE: Lamivudine is known to be very effective in suppressing hepatitis B virus replication and virus induced necroinflammation. The aim of this study was to evaluate lamivudine therapy efficacy, predictive factors, breakthrough, prevalence of YMDD mutation, and relapse rate in Korean children with chronic hepatitis B. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between August 1999 and February 2005, 60 children on lamivudine therapy for chronic hepatitis B were enrolled. Treatment response was defined as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) normalization, and HBeAg and HBV-DNA disappearance. RESULTS: Seroconversion rates of HBeAg and HBV-DNA were 42% and 53%, respectively, and ALT normalization rate was 88%. Seroconversion rates of HBeAg (60.0%) and anti-HBe (60.0%) were higher in patients younger than 6 years. Seroconversion rate of HBV-DNA (68.4%) and normalization rate of serum ALT (94.7%) were highest in patients between 6 and 12 years. Seroconversion rates of all HBV markers were lowest in patients older than 12 years. Predicted 3 year cumulative seroconversion rates, were 70%, 68% for HBeAg, HBV-DNA, respectively. These were calculated by Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional hazard regression model showed that pre-treatment ALT was a positive predictive factor for seroconversion of HBeAg and HBV-DNA. Breakthrough phenomenon was noted in 6 patients, and 3 had a YMDD mutation. CONCLUSION: Lamivudine therapy had a significant effect on HBeAg seroconversion and HBV-DNA disappearance, and ALT normalization for Korean children with chronic hepatitis B.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Age Factors
Alanine Transaminase/blood
Anti-HIV Agents/therapeutic use
*Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Child
Cohort Studies
DNA, Viral/blood
Female
Hepatitis B e Antigens/blood
Hepatitis B virus/*drug effects/genetics/immunology
Hepatitis B, Chronic/blood/*drug therapy/ethnology
Humans
Korea
Lamivudine/*therapeutic use
Male
Sex Factors
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Strategy to Overcome Drug Resistance That Develops during Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B in Children
Suk Jin Hong, Byung-Ho Choe
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012;15(2):63-73. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2012.15.2.63.Therapeutic Efficacy of Lamivudine in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Hepatitis B
Yujung Choi, Kil Seoung Bae, Ki Hwan Kim, Dae Kyun Koh, Jong-Hyun Kim
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2018;25(2):72-81. doi: 10.14776/piv.2018.25.e2.
Reference
-
1. Yuen MF, Hui CK, Cheng CC, Wu CH, Lai YP, Lai CL. Long term follow-up of interferon alfa treatment in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: The effect on hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion and the development of cirrhosis-related complications. Hepatology. 2001. 34:139–145.
Article2. Choi HJ, Kim YS, Park KS, Lee SI, Moon YM, Kang JK, et al. Clinical study on distribution of hepatitis B virus markers in Korean population. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1983. 15:163–171.3. Jeong IS, Chung KS. The therapeutic effect of interferon-alpha treatment in children with chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Pediatr. 1997. 40:955–964.4. Chang JY, Jeong SJ, Kim SK, Son BK, Hong YJ, Hong KS. Positive rate of HBsAg in school children in Incheon area. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003. 10:153–158.
Article5. Mansour TS, Jin H, Wang W, Hooker EU, Ashman C, Cammack N, et al. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus and anti-hepatitis-B virus activities and toxicities of the enatiomers of 2'-deoxy-3'-oxa-4'-thiocytidine and their 5-fluoro analogues in vitro. J Med Chem. 1995. 38:1–4.
Article6. Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai AI, et al. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:61–68.
Article7. Honkoop P, Niesters HG, de Man RA, Osterhaus AD, Schalm SW. Lamivudine resistance in immunocompetent chronic hepatitis B. Incidence and patterns. J Hepatol. 1997. 26:1393–1395.8. Chayama K, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi M, Tsubota A, Hashimoto M, et al. Emergence and takeover of YMDD motif mutant hepatitis B virus during long term lamivudine therapy and re-takeover by wild type after cessation of therapy. Hepatology. 1998. 27:1711–1716.
Article9. Allen MI, Gauthier J, DesLauriers M, Bourne EJ, Carrick KM, Baldanti F, et al. Two sensitive PCR-based methods for detection of hepatitis B virus variants associated with reduced susceptibility to lamivudine. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:3338–3347.
Article10. Cha CH, Sohn YH, Jang SS, Lee HJ, Lee KJ, Shin ES, et al. Genotype analysis of hepatitis B virus isolated from Korean hepatitis patients. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:352–356.11. Chung JY, Han TH, Hwang ES, Ko JS, Seo JK. Prevalence and genotype of transfusion-transmitted virus in children with hepatitis and normal control. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 8:202–212.
Article12. Bae SH, Yoon SK, Jang JW, Kim CW, Nam SW, Choi JY, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype C prevails among chronic carriers of the virus in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:816–820.
Article13. Kim JH, Koh DK, Hur JK, Kang JH, Nainan OV, Margolis HS. The incidence rate of hepatitis B virus surface gene variants in Korean children with immunoprophylaxis failure of perinatal infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2005. 11:320–328.14. Dienstag JL, Schiff ER, Wright TL, Perrillo RP, Hann HW, Goodman Z, et al. Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1256–1263.
Article15. Schalm SW, Heathcote J, Cianciara J, Farrell G, Sherman M, Willems B, et al. Lamivudine and alpha interferon combination treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: a randomised trial. Gut. 2000. 46:562–568.
Article16. Sokal EM, Mizerski J, Badia IB, Areias JA, Schwarz KB, Little NR, et al. Long-term lamivudine therapy for children with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2006. 43:225–232.
Article17. Jonas MM, Mizerski J, Badia IB, Areias JA, Schwarz KB, Little NR, et al. Clinical trial of lamivudine in children with chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:1706–1713.
Article18. Ozgenç F, Arikan C, Sertoz RY, Nart D, Aydogdu S, Yagci RY. Effect of long-term lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected children. Antivir Ther. 2004. 9:729–732.
Article19. Liberek A, Szaflarska-Poplawska A, Korzon M, Luczak G, Góra-Gebka M, Loś-Rycharska E, et al. Lamivudine therapy for children with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:2412–2416.
Article20. Alexander G, Baba CS, Chetri K, Negi TS, Ghoudhuri G. High rates of early HBeAg seroconversion and relapse in Indian patients of chronic hepatitis B treated with lamivudine: results of an open labeled trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2005. 5:29.
Article21. Hartman C, Berkowitz D, Shouval D, Eshach-Adiv O, Hino B, Rimon N, et al. Lamivudine treatment for chronic hepatitis B infection in children unresponsive to interferon. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:224–229.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B in Korean children
- Lamivudine therapy for type B chronic hepatitis in Korea
- The Efficacy of Lamivudine in Korean Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Lamivudine and interferon combination therapy in chronic type B hepatitis
- Lamivudine and interferon combination therapy in chronic type B hepatitis