J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Dec;26(12):1646-1649. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1646.
Novel ELANE Gene Mutation in a Korean Girl with Severe Congenital Neutropenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Medical Center, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kyungpook National University Medical Center, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kslee@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1786025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1646
Abstract
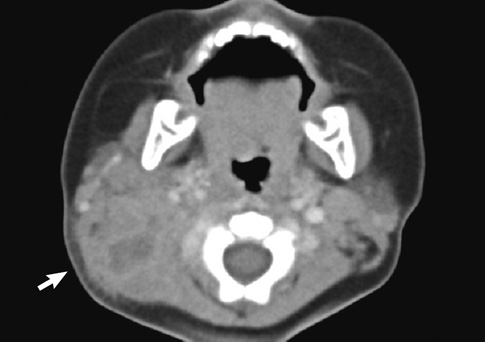
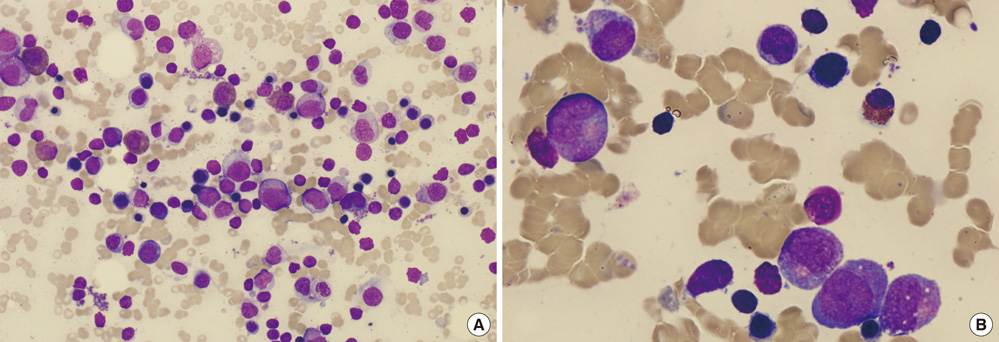
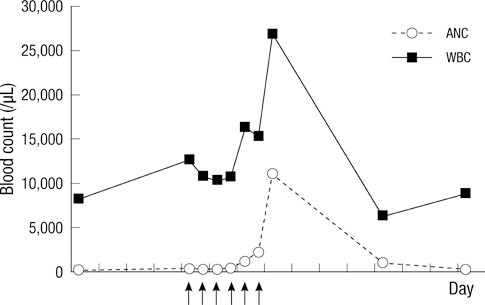
- Severe congenital neutropenia is a heterozygous group of bone marrow failure syndromes that cause lifelong infections. Mutation of the ELANE gene encoding human neutrophil elastase is the most common genetic alteration. A Korean female pediatric patient was admitted because of recurrent cervical lymphadenitis without abscess formation. She had a past history of omphalitis and isolated neutropenia at birth. The peripheral blood showed a markedly decreased absolute neutrophil count, and the bone marrow findings revealed maturation arrest of myeloid precursors at the promyelocyte to myelocyte stage. Her direct DNA sequencing analysis demonstrated an ELANE gene mutation (c.607G > C; p.Gly203Arg), but her parents were negative for it. She showed only transient response after subcutaneous 15 microg/kg/day of granulocyte colony stimulating factor administration for six consecutive days. During the follow-up observation period, she suffered from subsequent seven febrile illnesses including urinary tract infection, septicemia, and cellulitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dale DC, Cottle TE, Fier CJ, Bolyard AA, Bonilla MA, Boxer LA, Cham B, Freedman MH, Kannourakis G, Kinsey SE, Davis R, Scarlata D, Schwinzer B, Zeidler C, Welte K. Severe chronic neutropenia: treatment and follow-up of patients in the Severe Chronic Neutropenia International Registry. Am J Hematol. 2003. 72:82–93.2. James RM, Kinsey SE. The investigation and management of chronic neutropenia in children. Arch Dis Child. 2006. 91:852–858.3. Xia J, Bolyard AA, Rodger E, Stein S, Aprikyan AA, Dale DC, Link DC. Prevalence of mutations in ELANE, GFI1, HAX1, SBDS, WAS, and G6PC3 in patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Br J Haematol. 2009. 147:535–542.4. Horwitz MS, Duan Z, Korkmaz B, Lee HH, Mealiffe ME, Salipante SJ. Neutrophil elastase in cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia. Blood. 2007. 109:1817–1824.5. Bellanné-Chantelot C, Clauin S, Leblanc T, Cassinat B, Rodrigues-Lima F, Beaufils S, Vaury C, Barkaoui M, Fenneteau O, Maier-Redelsperger M, Chomienne C, Donadieu J. Mutations in the ELA2 gene correlate with more severe expression of neutropenia: a study of 81 patients from the French Neutropenia Register. Blood. 2004. 103:4119–4125.6. Dale DC, Person RE, Bolyard AA, Aprikyan AG, Bos C, Bonilla MA, Boxer LA, Kannourakis G, Zeidler C, Welte K, Benson KF, Horwitz M. Mutations in the gene encoding neutrophil elastase in congenital and cyclic neutropenia. Blood. 2000. 96:2317–2322.7. Klein C. Congenital neutropenia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009. 344–350.8. Yoo ES. Neutropenia in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:633–642.9. Lee ST, Yoon HS, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Park JH, Kim SH, Seo JJ, Im HJ. A novel mutation Ala57Val of the ELA2 gene in a Korean boy with severe congenital neutropenia. Ann Hematol. 2009. 88:593–595.10. Segal AW. How neutrophils kill microbes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. 23:197–223.11. Belaaouaj A, McCarthy R, Baumann M, Gao Z, Ley TJ, Abraham SN, Shapiro SD. Mice lacking neutrophil elastase reveal impaired host defense against gram negative bacterial sepsis. Nat Med. 1998. 4:615–618.12. Weinrauch Y, Drujan D, Shapiro SD, Weiss J, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil elastase targets virulence factors of enterobacteria. Nature. 2002. 417:91–94.13. Xia J, Link DC. Severe congenital neutropenia and the unfolded protein response. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008. 15:1–7.14. Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006. 6:173–182.15. Dale DC, Bolyard AA, Schwinzer BG, Pracht G, Bonilla MA, Boxer L, Freedman MH, Donadieu J, Kannourakis G, Alter BP, Cham BP, Winkelstein J, Kinsey S, Zeidler C, Welte K. The Severe Chronic Neutropenia International Registry: 10-year follow-up report. Support Cancer Ther. 2006. 3:220–231.16. Dale DC, Bonilla MA, Davis MW, Nakanishi AM, Hammond WP, Kurtzberg J, Wang W, Jakubowski A, Winton E, Lalezari P, Robinson W, Glaspy JA, Emerson S, Gabrilove J, Vincent M, Boxer LA. A randomized controlled phase III trial of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) for treatment of severe chronic neutropenia. Blood. 1993. 81:2496–2502.17. Rosenberg PS, Alter BP, Bolyard AA, Bonilla MA, Boxer LA, Cham B, Fier C, Freedman M, Kannourakis G, Kinsey S, Schwinzer B, Zeidler C, Welte K, Dale DC. Severe Chronic Neutropenia International Registry. The incidence of leukemia and mortality from sepsis in patients with severe congenital neutropenia receiving long-term G-CSF therapy. Blood. 2006. 107:4628–4635.18. Zeidler C, Welte K, Barak Y, Barriga F, Bolyard AA, Boxer L, Cornu G, Cowan MJ, Dale DC, Flood T, Freedman M, Gadner H, Mandel H, O'Reilly RJ, Ramenghi U, Reiter A, Skinner R, Vermylen C, Levine JE. Stem cell transplantation in patients with severe congenital neutropenia without evidence of leukemic transformation. Blood. 2000. 95:1195–1198.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Different Clinical Phenotypes in Familial Severe Congenital Neutropenia Cases with Same Mutation of the ELANE Gene
- Severe congenital neutropenia mimicking chronic idiopathic neutropenia: a case report
- Molecular Analysis of Two Cases of Severe Congenital Neutropenia
- Clinical and Laboratory Features of Severe Neutropenia Developed in Childhood
- A Case of X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia Associated with Severe Neutropenia