J Vet Sci.
2014 Jun;15(2):317-325. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.317.
Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay to detect shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in cattle
- Affiliations
-
- 1BK21 PLUS Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, Research Institute for Veterinary Science and College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. chose@snu.ac.kr
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Medical Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1784654
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.317
Abstract
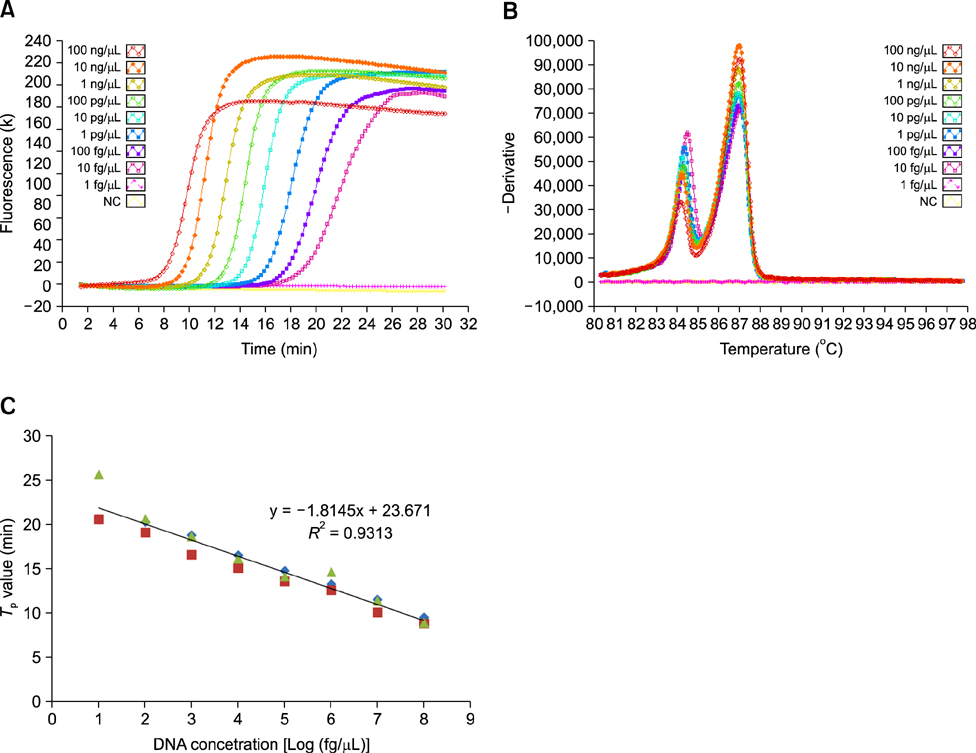
- A multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP) assay was developed for simultaneous detection of the stx1 and stx2 genes and applied for detection of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in cattle farm samples. Two target genes were distinguished based on T m values of 85.03 +/- 0.54degrees C for stx1 and 87.47 +/- 0.35degrees C for stx2. The mLAMP assay was specific (100% inclusivity and exclusivity), sensitive (with a detection limit as low as 10 fg/microL), and quantifiable (R 2 = 0.9313). The efficacy and sensitivity were measured to evaluate applicability of the mLAMP assay to cattle farm samples. A total of 12 (12/253; 4.7%) and 17 (17/253; 6.7%) STEC O157, and 11 (11/236; 4.7%) non-O157 STEC strains were isolated from cattle farm samples by conventional selective culture, immunomagnetic separation, and PCR-based culture methods, respectively. The coinciding multiplex PCR and mLAMP results for the types of shiga toxin revealed the value of the mLAMP assay in terms of accuracy and rapidity for characterizing shiga toxin genes. Furthermore, the high detection rate of specific genes from enrichment broth samples indicates the potential utility of this assay as a screening method for detecting STEC in cattle farm samples.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Cattle
Cattle Diseases/epidemiology/microbiology
Escherichia coli Infections/epidemiology/microbiology/*veterinary
Feces/microbiology
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction/veterinary
Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques/*veterinary
Shiga Toxin 1/*genetics/isolation & purification
Shiga Toxin 2/*genetics/isolation & purification
Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli/*genetics/isolation & purification
Shiga Toxin 1
Shiga Toxin 2
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aoi Y, Hosogai M, Tsuneda S. Real-time quantitative LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA) as a simple method for monitoring ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Biotechnol. 2006; 125:484–491.
Article2. Chen S, Ge B. Development of a toxR-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus. BMC Microbiol. 2010; 10:41.
Article3. Cho S, Diez-Gonzalez F, Fossler CP, Wells SJ, Hedberg CW, Kaneene JB, Ruegg PL, Warnick LD, Bender JB. Prevalence of shiga toxin-encoding bacteria and shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from dairy farms and county fairs. Vet Microbiol. 2006; 118:289–298.
Article4. Davis MA, Rice DH, Sheng H, Hancock DD, Besser TE, Cobbold R, Hovde CJ. Comparison of cultures from rectoanal-junction mucosal swabs and feces for detection of Escherichia coli O157 in dairy heifers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006; 72:3766–3770.
Article5. Dey BP, Lattuada CP. Detection, Isolation and Identification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from Meat Products and Carcass and Environmental Sponges. Microbiology Laboratory Guidebook. 3rd ed. Omaha: USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service;2013. MLG 5.06 (Revision .07).6. Feng P, Weagant SD, Jinneman K. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Bacteriological Analytical Manual. 8th ed. Silver Spring: US Food and Drug Administration;2013. Chapt. 4 (Revision A).7. Hara-Kudo Y, Nemoto J, Ohtsuka K, Segawa Y, Takatori K, Kojima T, Ikedo M. Sensitive and rapid detection of Vero toxin-producing Escherichia coli using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56:398–406.
Article8. Hsu TH, Gwo JC, Lin KH. Rapid sex identification of papaya (Carica papaya) using multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP). Planta. 2012; 236:1239–1246.
Article9. Huy NT, Hang le TT, Boamah D, Lan NT, Van Thanh P, Watanabe K, Huong VT, Kikuchi M, Ariyoshi K, Morita K, Hirayama K. Development of a single-tube loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of four pathogens of bacterial meningitis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012; 337:25–30.
Article10. Iseki H, Alhassan A, Ohta N, Thekisoe OM, Yokoyama N, Inoue N, Nambota A, Yasuda J, Igarashi I. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP) method for the simultaneous detection of bovine Babesia parasites. J Microbiol Methods. 2007; 71:281–287.
Article11. Jiang R, Long B, Zeng G, Wang D, Fan H, Wu X. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detecting enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7: a comparison with PCR. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012; 32:1026–1030.12. Kouguchi Y, Fujiwara T, Teramoto M, Kuramoto M. Homogenous, real-time duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification using a single fluorophore-labeled primer and an intercalator dye: its application to the simultaneous detection of Shiga toxin genes 1 and 2 in Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli isolates. Mol Cell Probes. 2010; 24:190–195.
Article13. Maruyama F, Kenzaka T, Yamaguchi N, Tani K, Nasu M. Detection of bacteria carrying the stx2 gene by in situ loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003; 69:5023–5028.
Article14. Mechie SC, Chapman PA, Siddons CA. A fifteen month study of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in a dairy herd. Epidemiol Infect. 1997; 118:17–25.15. Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes. 2002; 16:223–229.
Article16. Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000; 28:E63.
Article17. Paton JC, Paton AW. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998; 11:450–479.
Article18. Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Widdowson MA, Roy SL, Jones JL, Griffin PM. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States-major pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:7–15.
Article19. Shao Y, Zhu S, Jin C, Chen F. Development of multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification-RFLP (mLAMP-RFLP) to detect Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. in milk. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011; 148:75–79.
Article20. Su C, Brandt LJ. Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 123:698–714.21. Thorpe CM. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 38:1298–1303.22. Trevena WB, Willshaw GA, Cheasty T, Domingue G, Wray C. Transmission of Vero cytotoxin producing Escherichia coli O157 infection from farm animals to humans in Cornwall and west Devon. Commun Dis Public Health. 1999; 2:263–268.23. Wang F, Jiang L, Ge B. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for detecting shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in ground beef and human stools. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:91–97.
Article24. Wang F, Jiang L, Yang Q, Prinyawiwatkul W, Ge B. Rapid and specific detection of Escherichia coli serogroups O26, O45, O103, O111, O121, O145, and O157 in ground beef, beef trim, and produce by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012; 78:2727–2736.
Article25. Zhao X, Li Y, Wang L, You L, Xu Z, Li L, He X, Liu Y, Wang J, Yang L. Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection Escherichia coli O157 strains from food samples. Mol Biol Rep. 2010; 37:2183–2188.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli by Colony Hybridization with stx-specific Oligonucleotide
- Detection of Escherichia coli O157 and Escherichia coli O157:H7 by the immunomagnetic separation technique and stx1 and stx2 genes by multiplex PCR in slaughtered cattle in Samsun Province, Turkey
- Shiga Toxin: Emerging Producer Strains, Prophylactic Approaches, and Application in Cancer Therapy
- Two cases of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Associated with Escherichia coli O114
- Rapid Molecular Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7