Yonsei Med J.
2008 Dec;49(6):1041-1045. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.1041.
Successful Catheter Ablation of Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Non-coronary Aortic Sinus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Yonsei Cardiovascular Hospital and Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mhlee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1782956
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.1041
Abstract
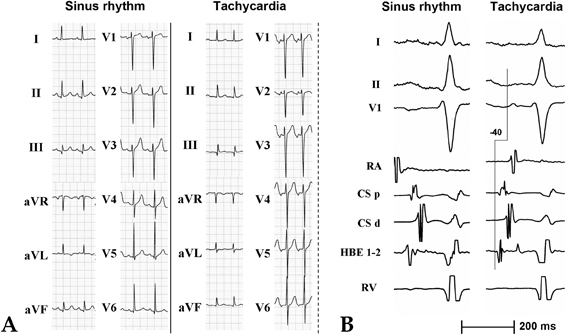
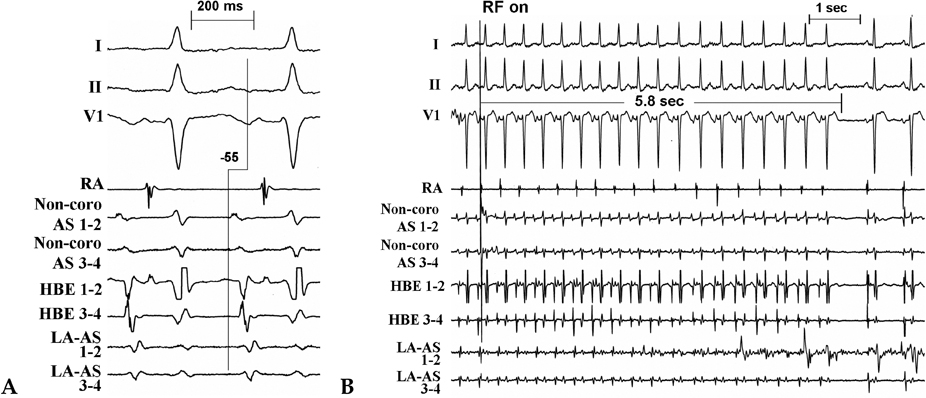
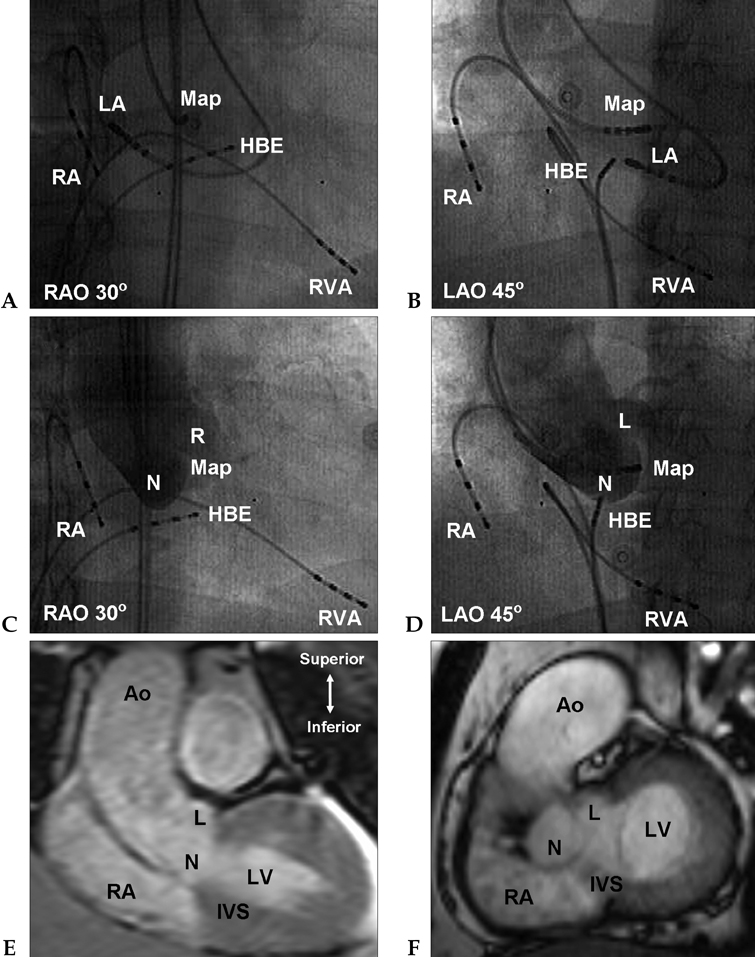
- We report a rare case of atrial tachycardia originating from the non-coronary aortic sinus. After failed radiofrequency (RF) energy applications at right His-bundle region, the complete elimination of atrial tachycardia was achieved with an RF energy application in the non-coronary aortic sinus. With the review of other papers, this report emphasizes the importance of mapping in the non-coronary aortic sinus in focal atrial tachycardia near the atrioventricular node or near the His-bundle.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Atrial Tachycardia From Noncoronary Aortic Cusp During Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation
Myung-Jin Cha, Jun Kim, Yoon Jung Park, Min Soo Cho, Hyoung-Seob Park, Soonil Kwon, Young Soo Lee, Jinhee Ahn, Hyung-Oh Choi, Jong-Sung Park, YouMi Hwang, Jin Hee Choi, Ki-Won Hwang, Yoo-Ri Kim, Seongwook Han, Seil Oh, Gi-Byoung Nam, Kee-Joon Choi, Hui-Nam Pak
Korean Circ J. 2022;52(7):513-526. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2021.0388.
Reference
-
1. Lai LP, Lin JL, Chen TF, Ko WC, Lien WP. Clinical, electrophysiological characteristics, and radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial tachycardia near the apex of Koch's triangle. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1998. 21:367–374.
Article2. Badhwar N, Kalman J, Sparks PB, Kistler PM, Attari M, Berger M, et al. Atrial tachycardia arising from the coronary sinus musculature: electrophysiological characteristics and long-term outcomes of radiofrequency ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005. 46:1921–1930.3. Connors SP, Vora A, Green MS, Tang AS. Radiofrequency ablation of atrial tachycardia originating from the triangle of Koch. Can J Cardiol. 2000. 16:39–43.4. Chen CC, Tai CT, Chiang CE, Yu WC, Lee SH, Chen YJ, et al. Atrial tachycardias originating from the atrial septum: electrophysiologic characteristics and radiofrequency ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2000. 11:744–749.
Article5. Tada H, Naito S, Miyazaki A, Oshima S, Nogami A, Taniguchi K. Successful catheter ablation of atrial tachycardia originating near the atrioventricular node from the noncoronary sinus of Valsalva. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2004. 27:1440–1443.
Article6. Ouyang F, Ma J, Ho SY, Bänsch D, Schmidt B, Ernst S, et al. Focal atrial tachycardia originating from the non-coronary arortic sinus, electrophysiological characteristics and catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. 48:122–131.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Aortomitral Junction
- Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Tachycardia
- A case of sinus node dysfunction and atrial tachycardia after the excision of a left atrial myxoma
- Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia in Two Patients with Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava
- Characteristics and Outcomes of Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Sinus Venosus during Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation