J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Sep;27(9):1120-1123. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1120.
Ceftiaxone-Induced Neurotoxicity: Case Report, Pharmacokinetic Considerations, and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. uptoyousm@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1782150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1120
Abstract
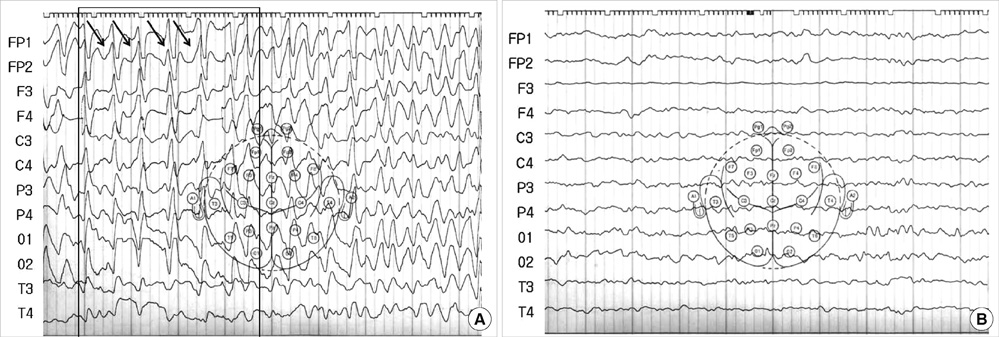
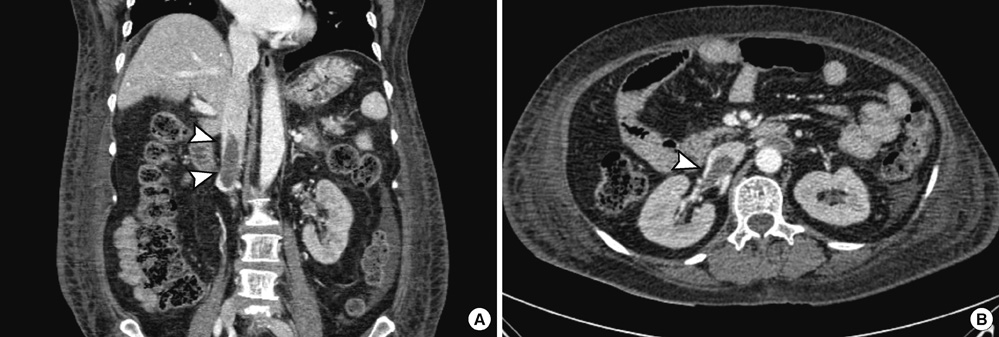
- Ceftriaxone is widely used in patients for the treatment of serious gram-negative infections. Ceftriaxone can induce some potential side effects, including neurotoxicity, however, nonconvulsive status epilepticus has rarely been reported. We report a case of acute reversible neurotoxicity associated with ceftriaxone. A 65-yr-old woman with chronic kidney disease developed altered consciousness during ceftriaxone treatment for urinary tract infection. The electroencephalogram demonstrated continuous bursts of generalized, high-voltage, 1 to 2 Hz sharp wave activity. Neurologic symptoms disappeared following withdrawal of ceftriaxone. The possibility of ceftriaxone-induced neurotoxicity should be considered in patients developing neurological impairment during ceftriaxone use, and the discontinuation of the drug could lead to complete neurological improvement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Anticoagulants/therapeutic use
Ceftriaxone/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Electroencephalography
Female
Humans
Nervous System Diseases/*etiology
Renal Dialysis
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic/pathology
Seizures/etiology
Thrombosis/diagnosis/drug therapy
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Urinalysis
Urinary Tract Infections/diagnosis/drug therapy
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Anticoagulants
Ceftriaxone
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rockowitz J, Tunkel AR. Bacterial meningitis. Practical guidelines for management. Drugs. 1995. 50:838–853.2. Weisfelt M, de Gans J, van de Beek D. Bacterial meningitis: a review of effective pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007. 8:1493–1504.3. Patel IH, Sugihara JG, Weinfeld RE, Wong EG, Siemsen AW, Berman SJ. Ceftriaxone pharmacokinetics in patients with various degrees of renal impairment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984. 25:438–442.4. Martinez-Rodriguez JE, Barriga FJ, Santamaria J, Iranzo A, Pareja JA, Revilla M, dela Rosa CR. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus associated with cephalosporins in patients with renal failure. Am J Med. 2001. 111:115–119.5. Sato Y, Morita H, Wakasugi H, Iijima S, Kawashima E, Wakayama Y, Yoshimura A. Reversible chreoathetosis after the administration of ceftriaxone sodium in patients with end-stage renal disease. Am J Med Sci. 2010. 340:382–384.6. Roncon-Albuquerque R Jr, Pires I, Martins R, Real R, Sousa G, von Hafe P. Ceftriaxone-induced acute reversible encephalopathy in a patient treated for a urinary tract infection. Neth J Med. 2009. 67:72–75.7. Grill MF, Maganti R. Cephalosporin-induced neurotoxicity: clinical manifestations, potential pathogenic mechanisms, and the role of electroencephalographic monitoring. Ann Pharmacother. 2008. 42:1843–1850.8. Lam S, Gomolin IH. Cefepime neurotoxicity: case report, pharmacokinetic considerations, and literature review. Pharmacotherapy. 2006. 26:1169–1174.9. Kim SY, Lee IS, Park SL, Lee J. Cefepime neurotoxicity in patients with renal insufficiency. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012. 36:159–162.10. Johnson H, Walker A. Intraventricular penicillin: a note of warning. JAMA. 1945. 127:217–219.11. De Sarro A, Ammendola D, Zappala M, Grasso S, De Sarro GB. Relationship between structure and convulsant properties of some beta-lactam antibiotics following intracerebroventricular microinjection in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995. 39:232–237.12. Wallace KL. Antibiotics-induced convulsions. Crit Care Clin. 1997. 13:741–762.13. Alkharfy KM, Kellum JA, Frye RF, Matzke GR. Effect of ceftazidime on systemic cytokine concentrations in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. 44:3217–3219.14. Schliamser SE, Cars O, Norrby R. Neurotoxicity of beta-lactam antibiotics: predisposing factors and pathogenesis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991. 27:405–425.15. Calandra G, Lydick E, Carrigan J, Weiss L, Guess H. Factors predisposing to seizures in seriously ill infected patients receiving antibiotics: experience with imipenem/cilastatin. Am J Med. 1988. 84:911–918.16. Cohen D, Appel GB, Scully B, Neu HC. Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in patients with renal failure and in those undergoing hemodialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983. 24:529–532.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Narrative review: the evidence for neurotoxicity ofdental local anesthetics
- Two Cases of Metronidazole-Induced Neurotoxicity Lacking of Clinico-Radiological Correlation
- A Case of Neurotoxicity Induced by Valaciclovir in a Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patient
- Neurotoxicity of local anesthetics in dentistry
- Methamphetamine-Induced Neuronal Damage: Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammation