J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Feb;26(2):243-249. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.243.
The Correlation between Thyrotropin and Dyslipidemia in a Population-based Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shengyang, P.R. China. shanzhongyan@hotmail.com
- 2The Endocrine Institute of China Medical University, The Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Endocrine diseases. Shenyang, P.R. China.
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, The People's Hospital of Liaoning Province. Shenyang, P.R. China.
- KMID: 1782113
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.243
Abstract
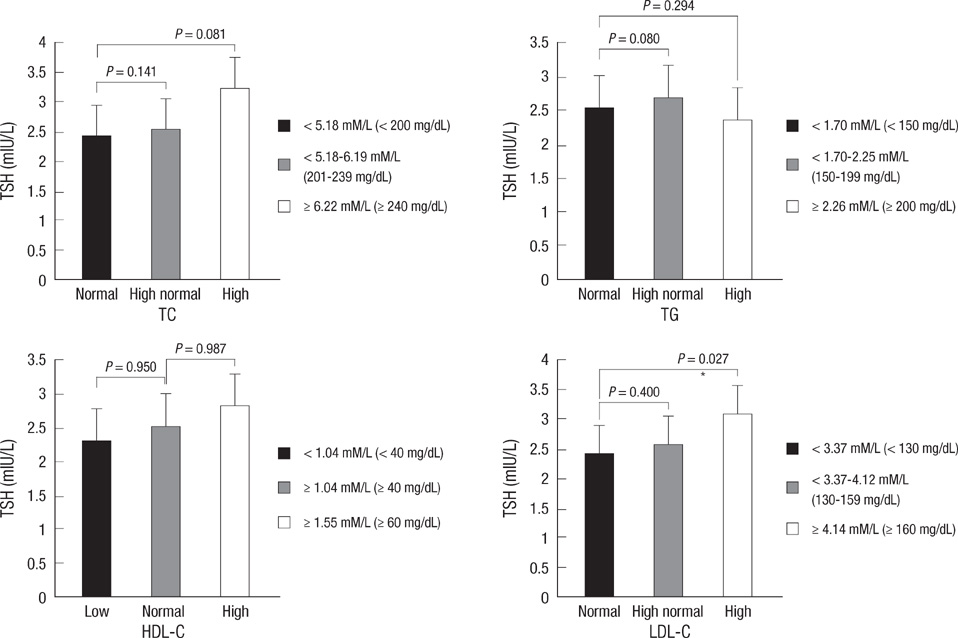
- This study investigated the relationship between serum thyrotrophin levels and dyslipidemia in subclinical hypothyroid and euthyroid subjects. A total of 110 subjects with subclinical hypothyroidism and 1,240 euthyroid subjects enrolled in this study. Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism had significantly lower high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels than those who were euthyroid. The lipid profiles were each categorized and mean thyrotrophin levels were higher in subjects in the dyslipidemia subclasses than subjects in the normal subclasses. Thyrotrophin was positively associated with serum triglyceride and negatively associated with serum HDL-C in women. Thyrotrophin was also positively associated with total cholesterol (TC) in the overweight population along with TC and LDL-C in overweight women. In the euthyroid population, thyrotrophin was positively associated with TC in the overweight population. In conclusion, serum thyrotrophin was correlated with dyslipidemia in subclinical hypothyroid and euthyroid subjects; the correlation was independent of insulin sensitivity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Klein I, Ojamaa K. Thyroid hormone and the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:501–509.2. Biondi B, Palmieri EA, Lombardi G, Fazio S. Effects of subclinical thyroid dysfunction on the heart. Ann Intern Med. 2002. 137:904–914.3. Biondi B. Cardiovascular effects of mild hypothyroidism. Thyroid. 2007. 17:625–630.4. Feldt-Rasmussen U. Is the treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism beneficial? Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009. 5:86–87.5. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988. 37:1595–1607.6. Mykkänen L, Haffner SM, Rönnemaa T, Bergman RN, Laakso M. Low insulin sensitivity is associated with clustering of cardiovascular disease risk factors. Am J Epidemiol. 1997. 146:315–321.7. Genest J Jr, Cohn JS. Clustering of cardiovascular risk factors: targeting high-risk individuals. Am J Cardiol. 1995. 76:8A–20A.8. Pallas D, Koutras DA, Adamopoulos P, Marafelia P, Souvatzoglou A, Piperingos G, Moulopoulos SD. Increased mean serum thyrotropin in apparently euthyroid hypercholesterolemic patients: does it mean occult hypothyroidism? J Endocrinol Invest. 1991. 14:743–746.9. Bakker SJ, ter Maaten JC, Popp-Snijders C, Slaets JP, Heine RJ, Gans RO. The relationship between thyrotropin and low density lipoprotein cholesterol is modified by insulin sensitivity in healthy euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1206–1211.10. Michalopoulou G, Alevizaki M, Piperingos G, Mitsibounas D, Mantzos E, Adamopoulos P, Koutras DA. High serum cholesterol levels in persons with 'high-normal' TSH levels: should one extend the definition of subclinical hypothyroidism? Eur J Endocrinol. 1998. 138:141–145.11. Chubb SA, Davis WA, Davis TM. Interactions among thyroid function, insulin sensitivity, and serum lipid concentrations: the Fremantle diabetes study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90:5317–5320.12. Liu D, Jiang F, Shan Z, Wang B, Wang J, Lai Y, Chen Y, Li M, Liu H, Li C, Xue H, Li N, Yu J, Shi L, Bai X, Hou X, Zhu L, Lu L, Wang S, Xing Q, Teng W. A cross-sectional survey of relationship between serum TSH level and blood pressure. J Hum Hypertens. 2010. 24:134–138.13. Duntas LH. Thyroid disease and lipids. Thyroid. 2002. 12:287–293.14. Benvenga S, Robbins J. Enhancement of thyroxine entry into low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-competent fibroblasts by LDL: an additional mode of entry of thyroxine into cells. Endocrinology. 1990. 126:933–941.15. Althaus BU, Staub JJ, Ryff-De Lèche A, Oberhänsli A, Stähelin HB. LDL/HDL-changes in subclinical hypothyroidism: possible risk factors for coronary heart disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1988. 28:157–163.16. Canaris GJ, Manowitz NR, Mayor G, Ridgway EC. The Colorado thyroid disease prevalence study. Arch Intern Med. 2000. 160:526–534.17. Efstathiadou Z, Bitsis S, Milionis HJ, Kukuvitis A, Bairaktari ET, Elisaf MS, Tsatsoulis A. Lipid profile in subclinical hypothyroidism: is L-thyroxine substitution beneficial? Eur J Endocrinol. 2001. 145:705–710.18. Gullu S, Sav H, Kamel N. Effects of levothyroxine treatment on biochemical and hemostasis parameters in patients with hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005. 152:355–361.19. Roos A, Bakker SJ, Links TP, Gans RO, Wolffenbuttel BH. Thyroid function is associated with components of the metabolic syndrome in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 92:491–496.20. Ruhla S, Weickert MO, Arafat AM, Osterhoff M, Isken F, Spranger J, Schöfl C, Pfeiffer AF, Möhlig M. A high normal TSH is associated with the metabolic syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010. 72:696–701.21. Kumar HK, Yadav RK, Prajapati J, Reddy CV, Raghunath M, Modi KD. Association between thyroid hormones, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Saudi Med J. 2009. 30:907–911.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody
- Molecular biologic research in the thyrotropin releasing hormone
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Clinical Significance of Measuring Thyrotropin Recepter Antibody
- Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview