J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):224-228. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.224.
Surgical Resection of Recurrent Lung Cancer in Patients Following Curative Resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jkim@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hallym University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781826
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.224
Abstract
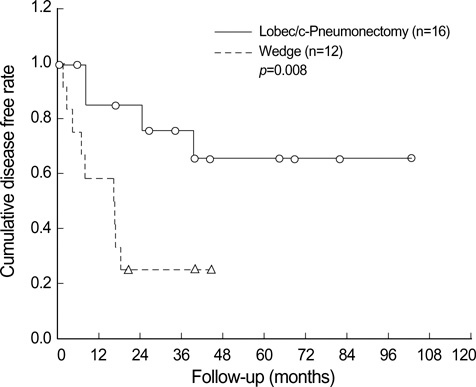
- We reviewed our experience with resection of recurrent lung cancer to evaluate the benefit and risk of the procedure. From December 1994 to December 2003, 29 consecutive patients underwent pulmonary resections for recurrent lung cancer. The mean duration from the first resection to second surgery was 25.4+/-15.1 months for the definite 2nd primary lung cancer (n=20) and 8.9+/-5.7 months for metastatic lung cancer (n=9). The procedures at the second operations were completion-pneumonectomy in 11 patients, lobectomy in 5 patients, wedge resection in 12 patients and resection and anastomosis of trachea in 1 patient. Morbidity was observed in 6 (21%) of the patients and the in-hospital mortality was two patients (7%) after the repeated lung resection. Tumor recurrence after reoperation was observed in 14 patients (48%). The actuarial 5-yr survival rate was 69% and the 5-yr disease free rate following reoperation was 44%. No significant difference was found in overall survival and disease free survival between the 2nd primary lung cancer group and the metastatic lung cancer group. The recurrence rate following reoperation was significantly different between the wedge resection group and lobectomy/completion pneumonectomy group (p=0.008), but the survival rate was not significantly different (p=0.41). Surgical intervention for recurrent lung cancers can be performed with acceptable mortality and morbidity. If tolerable, completion pneumonectomy or lobectomy is recommended for resection of recurrent lung cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Salvage Concurrent Chemo-radiation Therapy for Loco-regional Recurrence Following Curative Surgery of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Kyung Hwa Lee, Yong Chan Ahn, Hongryull Pyo, Jae Myoung Noh, Seung Gyu Park, Tae Gyu Kim, Eonju Lee, Heerim Nam, Hyebin Lee, Jong-Mu Sun, Jin Seok Ahn, Myung-Ju Ahn, Keunchil Park
Cancer Res Treat. 2019;51(2):769-776. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.366.
Reference
-
1. Angeletti CA, Mussi A, Janni A, Lucchi M, Ribechini A, Chella A, Fontanini G. Second primary lung cancer and relapse: treatment and follow-up. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1995. 9:607–611.
Article2. Antakli T, Schaefer RF, Rutherford JE, Read RC. Second primary lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995. 59:863–867.
Article3. Asaph JW, Keppel JF, Handy JR Jr, Douville EC, Tsen AC, Ott GY. Surgery for second lung cancers. Chest. 2000. 118:1621–1625.
Article4. Voltolini L, Paladini P, Luzzi L, Ghiribelli C, Bisceglie MD, Gotti G. Iterative surgical resections for local recurrent and second primary bronchogenic carcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2000. 18:529–534.
Article5. Fujimoto T, Zaboura G, Fechner S, Hillejan L, Schroder T, Marra A, Krbek T, Hinterthaner M, Greschuchna D, Stamatis G. Completion pneumonectomy: current indications, complications, and results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001. 121:484–490.
Article6. Aziz TM, Saad RA, Glasser J, Jilaihawi AN, Prakash D. The management of second primary lung cancers. A single centre experience in 15 years. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. 21:527–533.
Article7. Donington JS, Miller DL, Rowland CC, Deschamps C, Allen MS, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC. Subsequent pulmonary resection for bronchogenic carcinoma after pneumonectomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002. 74:154–159.
Article8. Regnard JF, Icard P, Magdeleinat P, Jauffret B, Fares E, Levasseur P. Completion pneumonectomy: experience in eighty patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999. 117:1095–1101.
Article9. Terzi A, Lonardoni A, Falezza G, Scanagatta P, Santo A, Furlan G, Calabro F. Completion pneumonectomy for non-small cell lung cancer: experience with 59 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. 22:30–34.
Article10. Martini N, Melamed MR. Multiple primary lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1975. 70:606–612.
Article11. Westeel V, Choma D, Clement F, Woronoff-Lemsi MC, Pugin JF, Dubiez A, Depierre A. Relevance of the intensive postoperative follow-up after surgery for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000. 70:1185–1190.12. Haberkorn U. Positron emission tomography (PET) of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2001. 34:S115–S121.
Article13. McGovern EM, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC, Payne WS. Completion pneumonectomy: indications, complications, and results. Ann Thorac Surg. 1988. 46:141–146.
Article14. Gregoire J, Deslauriers J, Guojin L, Rouleau J. Indications, risk, and results of completion pneumonectomy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993. 105:918–924.15. Okada M, Tsubota N, Yoshimura M, Miyamoto Y. Operative approach for multiple primary lung carcinomas. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998. 115:836–840.
Article16. Lung Cancer Study Group. Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1N0 non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995. 60:615–623.17. Doddoli C, Thomas P, Ghez O, Giudicelli R, Fuentes P. Surgical management of metachronous bronchial carcinoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001. 19:899–903.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Therapeutic approach to non-curative resection after endoscopic treatment in early gastric cancer
- A Case of Long Term Survival in Patient with Early Intrahepatic Recurrence and Extrahepatic Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Results of Curative Reoperation for Recurrent Cancer of the Extrahepatic Biliary Tract
- Clinical Review of Carcinomas of the Extrahepatic Bile Ducts and Gallbladders
- Lobectomy versus Sublobar Resection in Non-Lepidic Small-Sized Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer