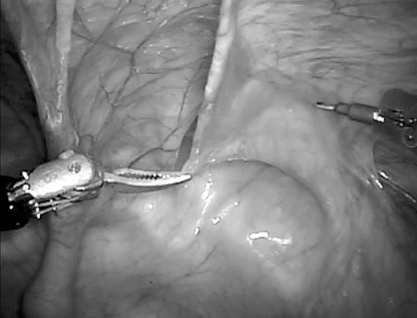
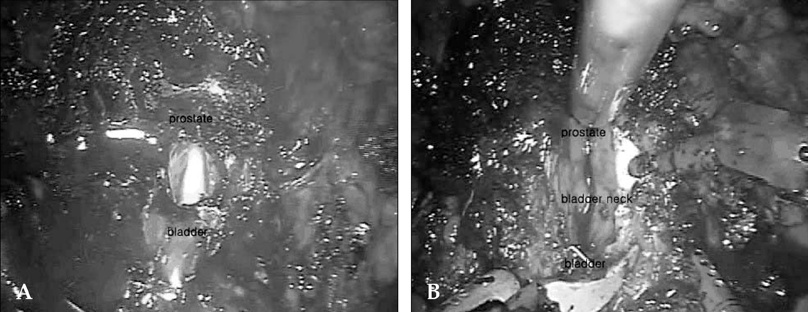
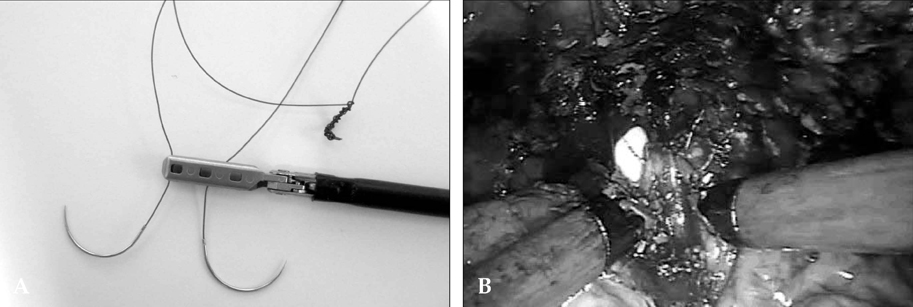
Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: Four Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urologic Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khrha@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.341
Abstract
- The role of the da Vinci(TM) robot is being defined in minimally invasive urologic surgery. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (rLRP) has emerged as a feasible treatment option for patients with organ-confined prostate cancer. We performed the first four rLRPs on four prostate cancer patients in the Republic of Korea. This is a report of its techniques and outcomes. In all four cases, the surgery was successfully completed with a mean operative time of 392.5 minutes. The mean estimated blood loss was 312.5mL, and catheterization lasted 14 to 21 days. There were no major intraoperative or postoperative complications. The mean hospital stay was 11 days. The rLRP is a safe and feasible approach. It will become one of the standard options for the management of localized prostate cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Yonsei Experience in Robotic Urologic Surgery - Application in Various Urological Procedures
Sung Yul Park, Wooju Jeong, Young Deuk Choi, Byung Ha Chung, Sung Joon Hong, Koon Ho Rha
Yonsei Med J. 2008;49(6):897-900. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.897.Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy has lower biochemical recurrence than laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Seon Heui Lee, Hyun Ju Seo, Na Rae Lee, Soo Kyung Son, Dae Keun Kim, Koon Ho Rha
Investig Clin Urol. 2017;58(3):152-163. doi: 10.4111/icu.2017.58.3.152.Efficacy and Safety of Robotic Procedures Performed Using the da Vinci Robotic Surgical System at a Single Institute in Korea: Experience with 10000 Cases
Dong Hoon Koh, Won Sik Jang, Jae Won Park, Won Sik Ham, Woong Kyu Han, Koon Ho Rha, Young Deuk Choi
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(8):975-981. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.975.
Reference
-
1. Walsh PC. Anatomic radical prostatectomy: evolution of the surgical technique. J Urol. 1998. 160(6 Pt 2):2418–2424.2. Schuessler WW, Schulam PG, Clayman RV, Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: initial short-term experience. Urology. 1997. 50:854–857.
Article3. Abbou CC, Salomon L, Hoznek A, Antiphon P, Cicco A, Saint F, et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: preliminary results. Urology. 2000. 55:630–634.
Article4. Rassweiler J, Sentker L, Seemann O, Hatzinger M, Rumpelt HJ. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with the Heilbronn technique: an analysis of the first 180 cases. J Urol. 2001. 166:2101–2108.
Article5. Guillonneau B, el-Fettouh H, Baumert H, Cathelineau X, Doublet JD, Fromont G, et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: oncological evaluation after 1,000 cases a Montsouris Institute. J Urol. 2003. 169:1261–1266.
Article6. Gill IS, Zippe CD. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: technique. Urol Clin North Am. 2001. 28:423–436.
Article7. Hemal AK, Srinivas M, Charles AR. Ergonomic problems associated with laparoscopy. J Endourol. 2001. 15:499–503.
Article8. Menon M, Kaul S, Bhandari A, Shrivastava A, Tewari A, Hemal A. Potency following robotic radical prostatectomy: a questionnaire based analysis of outcomes after conventional nerve sparing and prostatic fascial sparing techniques. J Urol. 2005. 174:2291–2296.
Article9. Kaul S, Bhandari A, Hemal A, Savera A, Shrivastava A, Menon M. Robotic radical prostatectomy with preservation of the prostatic fascia: a feasible study. Urology. 2005. 66:1261–1265.
Article10. Menon M, Hemal AK, Tewari A, Shrivastava A, Bhandari A. The technique of apical dissection of the prostate and urethrovesical anastomosis in robotic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2004. 93:715–719.
Article11. Yohannes P, Rotariu P, Pinto P, Smith AD, Lee BR. Comparison of robotic versus laparoscopic skills: is there a difference in the learning curve? Urology. 2002. 60:39–45.
Article12. Menon M. Robotic radical retropubic prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2003. 91:175–176.
Article13. Tewari A, Srivasatava A, Menon M; Members of the VIP Team. A prospective comparison of radical retropubic and robot-assisted prostatectomy: experience in one institution. BJU Int. 2003. 92:205–210.
Article14. Menon M, Shrivastava A, Sarle R, Hemal A, Tewari A. Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: a single-team experience of 100 cases. J Endourol. 2003. 17:785–790.
Article15. Tewari A, Peabody JO, Fischer M, Sarle R, Vallancien G, Delmas V, et al. An operative and anatomic study to help in nerve sparing during laparoscopic and robotic radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:444–454.
Article16. Ahlering TE, Skarecky D, Lee D, Clayman RV. Successful transfer of open surgical skills to a laparoscopic environment using a robotic interface: initial experience with laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2003. 170:1738–1741.
Article17. Perer E, Lee DI, Ahlering T, Clayman RV. Robotic revelation: laparoscopic radical prostatectomy by a nonlaparoscopic surgeon. J Am Coll Surg. 2003. 197:693–696.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- A Case of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy in Primary Small Cell Prostate Cancer
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Floating Hem-o-Lok Clips in the Bladder without Stone Formation after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Two Different Surgical Approaches for Prostatic Stromal Sarcoma: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy and Open Radical Cysto-Prostatectomy With Ileal Conduit