J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Jun;20(3):489-494. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.489.
Clinical Significance of Ki-67 Labeling Index in Pituitary Macroadenoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. neons@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1778512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.489
Abstract
- The aim of our study was to investigate the correlation of the proliferative activity of pituitary neoplasms with clinical characteristics and recurrences. Tumor specimens were obtained from 44 consecutive patients with pituitary macroadenomas who underwent surgery between July 1998 and August 2003. Specimens were immediately fixed in 10% buffered formalin and then embedded in paraffin. The Ki-67 antigen was assessed by immumohistochemical analysis using the monoclonal antibody. We investigated the correlation of the Ki-67 labeling index with the following clinical and radiological characteristics: sex, age, presence or absence visual field defect, tumor classification, maximal tumor diameter, Hardy's classification, type of tumor, invasiveness, and recurrence. Our study suggests that the clinical characteristics such as visual field defect and recurrence are correlated with the high Ki-67 labeling index. No statistical differences were observed in the Ki-67 labeling index in relation to the following characteristics: sex, age, tumor classification, maximal tumor diameter, Hardy's classification, type of tumor, and invasiveness into the sphenoid sinus or cavernous sinus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
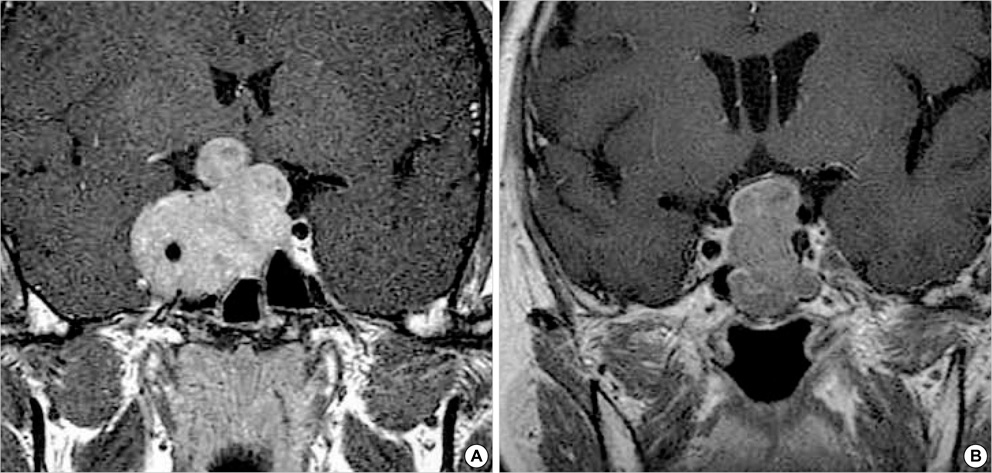
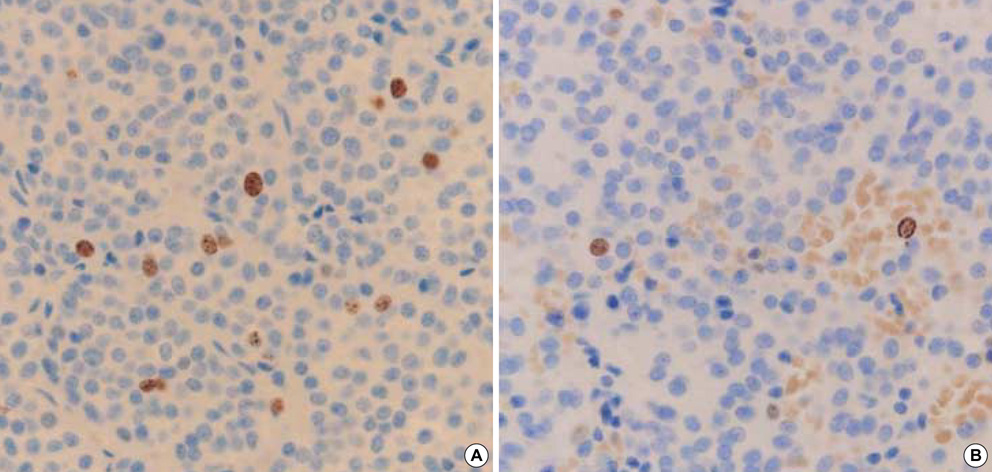
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Characteristics of Incidental Pituitary Microadenomas in 120 Korean Forensic Autopsy Cases
Jang-Hee Kim, Jung-Seok Seo, Bong-Woo Lee, Sang-Young Lee, Seok-Hoon Jeon, Kyi-Beom Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22(Suppl):S61-S65. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S61.
Reference
-
1. Pizaro CB, Oliveira MC, Coutinho LB, Ferreira NP. Measurement of Ki-67 antigen in 159 pituitary adenomas using the MIB-1 monoclonal antibody. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2004. 37:235–243.
Article2. Losa M, Franzin A, Mangili F, Terreni MR, Barzaghi R, Veglia F, Mortini P, Giovanelli M. Proliferation index of non-functioning pituitary adenomas: correlations with clinical characteristics and long-term follow-up results. Neurosugery. 2000. 47:1313–1319.
Article3. Sassolas G, Trouillas J, Treluyer C, Perrin G. Management of non-functioning pituitary adenomas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1993. 129:21–26.4. Petruson B, Jakobsson KE, Elfverson J, Bengtsson BA. Five-year follow-up of nonsecreting pituitary adenomas. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995. 121:317–322.
Article5. Shone GR, Richards SH, Hourihan MD, Hall R, Thomas JP, Scanlon MF. Non-secretary adenomas of the pituitary treated by transethmoidal sellotomy. J R Soc Med. 1991. 84:140–143.6. Comtois R, Beauregard H, Somma M, Serri O, Aris-Jilwan N, Hardy J. The clinical and endocrine outcome to transsphenoidal microsurgery of nonsecreting pituitary adenomas. Cancer. 1991. 68:860–866.
Article7. Carboni P Jr, Detta A, Hitchcork ER, Postans R. Pituitary adenoma proliferative indices and risk of recurrence. Br J Neurosurg. 1992. 6:33–40.
Article8. Cattoretti G, Becker MH, Key G, Duchrow M, Schluter C, Galle J, Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB1 and MIB3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992. 168:357–363.9. Gerdes J. Ki-67 and other proliferation markers useful for immunohistological diagnostic and prognostic evaluation in human malignancies. Seminar in Cancer Biology. 1990. 1:199–206.10. Landolt A, Shibata T, Kleihues P. Growth rate of human pituitary adenoma. J Neurosurg. 1987. 67:803–806.11. Zhao D, Tomono Y, Nose T. Expression of P27, Kip 1 and Ki-67 in pituitary adenomas: An investigation of marker of adenoma invasiveness. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1999. 141:187–192.
Article12. Kitz K, Knosp E, Koos WT, Korn A. Proliferation of pituitary adenomas. Measurement by MAb Ki-67. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991. 53:Suppl. 60–64.13. Ekramullah SM, Saitoh Y, Arita N, Ohnishi T, Hayakawa T. The correlation of Ki-67 staining indices with tumor doubling times in regrowing non-functioning pituitary adenomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996. 138:1449–1455.14. McCormick D, Chong H, Hobbs C, Datta C, Hall PA. Detection of the Ki-67 antigen in fixed and wax-embedded sections with the monoclonal antibody MIB-1. Histopathology. 1993. 22:355–360.
Article15. Knosp E, Kitz K, Perneczky A. Proliferation activity in pituitary adenomas: measurement by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Neurosurgery. 1989. 25:927–930.
Article16. Parkins CS, Darling JL, Gill SS, Revesz T, Thomas DG. Cell proliferation in serial biopsies through malignant brain tumors: measurement using Ki-67 antibody labelling. Br J Neurosurg. 1991. 5:289–298.17. Mastronardi L, Guiducci A, Spera C, Puzzilli F, Liberati F, Maira G. Ki-67 labelling index and invasiveness among anterior pituitary adenomas: analysis of 103 cases using the MIB-1 monoclonal antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1999. 52:107–111.
Article18. Kim SY, Chung SH, Kim HJ, Whang K, Han YP, Hong SK. Bcl-2 and Bax expression and Ki-67 proliferative index in astrocytic tumors: in relation to prognosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2004. 35:465–471.19. Yonezawa K, Tamaki N, Kokunai T. Clinical features and growth fractions of pituitary adenomas. Surg Neurol. 1997. 48:494–500.
Article20. Jaffrain-Rea ML, Di Stefano D, Minniti G, Esposito V, Bultrini A, Ferretti E, Santoro A, Faticanti Scucchi L, Gulino A, Cantore G. A critical reappraisal of MIB-1 labelling index significance in a large series of pituitary tumours: secreting versus non-secreting adenomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2002. 9:103–113.
Article21. Shibuya M, Saito F, Miwa T, Davis RL, Wilson CB, Hoshino T. Histochemical study of pituitary adenomas with Ki-67 and anti-DNA polymerase alpha monoclonal antibodies, bromodeoxyuridine labeling, and nucleolar organizer region counts. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 1992. 84:178–183.22. Delgrane E, Trouillas J, Maiter D, Donckier J, Tourniaire J. Sex-related difference in the growth of prolactinomas; a clinical and proliferation marker study. J Clin Endoclinol Metab. 1997. 82:2102–2107.23. Mindermann T, Wilson CB. Age-related and gender-related occurrence of pituitary adenomas. Clin Endocrinol. 1994. 41:359–364.
Article24. Yamada S, Kovacs K, Horvath E, Aiba T. Morphological study of clinically nonsecreting pituitary adenomas in patients under 40 years of age. J Neurosurg. 1991. 75:902–905.
Article25. Hardy J. Kohler PO, Ross GT, editors. Transsphenoidal surgery of hypersecreting pituitary adenomas. Diagnosis and treatment of pituitary tumors. 1973. Excerpta Medica, America Elsevier;179–194.26. Lath R, Chacko G, Chandy MJ. Determination of Ki-67 labeling index in pituitary adenomas using MIB-1 monoclonal antibody. Neurol India. 2001. 49:144–147.27. Scheithauer BW, Kovacs KT, Laws ER Jr, Randall RV. Pathology of invasive pituitary tumors with special reference to functional classification. J Neurosurg. 1986. 65:733–744.
Article28. Kim DH, Suh YL, Shin DI, Shin HJ, Kim JH. p53 expression and Ki-67 labeling index in brain tumor with special reference to tumor and histologic grade. Korean J Pathol. 1998. 32:81–87.29. Gandour-Edwards R, Kapadia SB, Janecka IP, Martinez AJ, Barnes L. Biologic markers of invasive pituitary adenomas involving the sphenoid sinus. Mod Pathol. 1995. 8:160–164.30. Thapar K, Kovacs K, Scheithauer BW, Stefaneanu L, Horvath E, Pernicone PJ, Murray D, Laws ER Jr. Proliferation activity and invasiveness among pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: An analysis using the MIB-1 antibody. Neurosurgery. 1996. 38:99–106.31. Kawamoto H, Uozumi T, Kawamoto K, Arita K, Yano T, Hirohata T. Analysis of the growth rate and cavernous sinus invasion of pituitary. Acta Neurochir. 1995. 136:37–43.32. Hus DW, Hakim F, Biller BM, de la Monte S, Zervas NT, Klibanski A, Hedley-Whyte ET. Significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen index in predicting pituitary adenoma recurrence. J Neurosurg. 1993. 78:753–761.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ki-67 Labeling Index as a Measure of Cell Proliferative Activity in Gastric Cancer and It's Significance
- Pituitary Apoplexy due to Pituitary Adenoma Infarction
- Correlation of Clinical Stage and Presumptive Prognostic Factors in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Uterine leiomyosarcoma in a wild rat (Rattus norvegicus): usefulness of Ki-67 labeling index for diagnosis
- Proliferative Markers of Breast Cancer