J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):527-532. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.527.
Prognosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Synchronous Brain Metastases Treated with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jilee@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Hemato-Oncolgy, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778439
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.527
Abstract
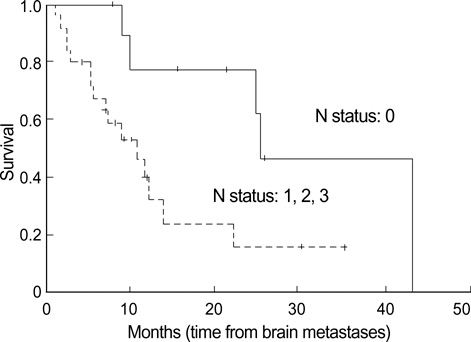
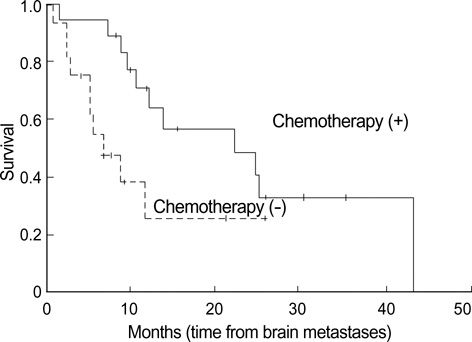
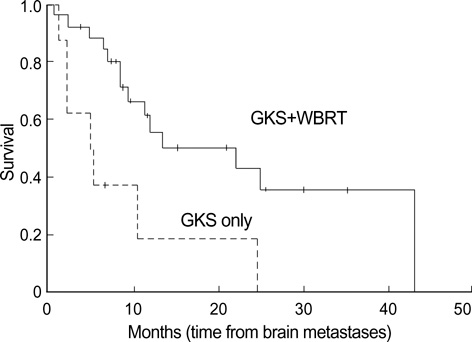
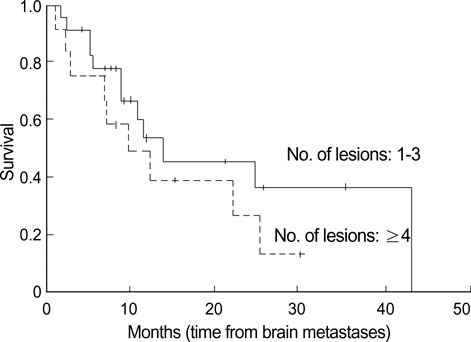
- The clinical outcome and prognostic factors of patients with synchronous brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who were treated with gamma knife radiosurgery (GKS) were analyzed. A total of 35 patients with NSCLC underwent GKS as an initial treatment for metastatic brain lesions of synchronous onset. The period of survival and various prognostic factors such as age, gender, performance status, multiplicity of the brain lesions, intracranial tumor volume, and extent of the primary tumor were analyzed. The overall median survival time for this series was 12 months (range 0.75 to 43 months) from the diagnosis. Of the 21 patients who were no longer alive at the conclusion of this study, only 7 (33.3%) died of neurological causes. Multivariate analysis of these data revealed that N stage, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), and chemotherapy were significant predictors for survival (p<0.05). Survival of patients with NSCLC and synchronous brain metastases is mainly dependent upon the progression of the systemic disease, provided that the cerebral lesions are treated adequately with local treatment modalities including radiosurgery. Application of radiosurgery as an initial treatment option and aggressive local and systemic modalities to control extracranial disease may improve survival.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peto R, Chen ZM, Boreham J. Tobacco--the growing epidemic. Nat Med. 1999. 5:15–17.
Article2. Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB. Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol. 1988. 45:741–744.
Article3. Coia LR. The role of radiation therapy in the treatment of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992. 23:229–238.
Article4. Posner JB. Diagnosis and treatment of metastases to the brain. Clin Bull. 1974. 4:47–57.5. Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ, Eijkenboom WM, Hanssens PE, Schmitz PI. Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. 43:795–803.
Article6. Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, Noordijk EM, Padberg GW, Voormolen JH, Hoekstra FH, Tans JT, Lambooij N, Metsaars JA, Wattendorff AR, Brand R, Hermans J. Treatment of single brain metastasis: radiotherapy alone or combined with neurosurgery? Ann Neurol. 1993. 33:583–590.
Article7. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Macdonald JS, Young B. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990. 322:494–500.
Article8. Kaal EC, Niel CG, Vecht CJ. Therapeutic management of brain metastasis. Lancet Neurol. 2005. 4:289–298.
Article9. Cho KT, Kim DG. Stereotactic radiosurgery fro brain metastases: Prognostic factors for survival and local control. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003. 33:333–338.10. Iwasaki A, Shirakusa T, Yoshinaga Y, Enatsu S, Yamamoto M. Evaluation of the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastasis and the role of risk score as a survival predictor. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004. 26:488–493.
Article11. Nugent JL, Bunn PA Jr, Matthews MJ, Ihde DC, Cohen MH, Gazdar A, Minna JD. CNS metastases in small cell bronchogenic carcinoma: increasing frequency and changing pattern with lengthening survival. Cancer. 1979. 44:1885–1893.12. Schuette W. Treatment of brain metastases from lung cancer: chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2004. 45:Suppl 2. S253–S257.
Article13. Mountain CF. Revisions in the International System for Staging Lung Cancer. Chest. 1997. 111:1710–1717.
Article14. Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997. 37:745–751.
Article15. Kocher M, Maarouf M, Bendel M, Voges J, Muller RP, Sturm V. Linac radiosurgery versus whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. A survival comparison based on the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004. 180:263–267.16. Amendola BE, Wolf A, Coy S, Amendola MA. Radiosurgery as palliation for brain metastases: a retrospective review of 72 patients harboring multiple lesions at presentation. J Neurosurg. 2002. 97:511–514.
Article17. Nam TK, Lee JI, Jung YJ, Im YS, An HY, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH. Gamma knife surgery for brain metastases in patients harboring four or more lesions: survival and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg. 2005. 102:Suppl. 147–150.
Article18. Yang CC, Ting J, Wu X, Markoe A. Dose volume histogram analysis of the gamma knife radiosurgery treating twenty-five metastatic intracranial tumors. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998. 70:Suppl 1. 41–49.
Article19. Serizawa T, Iuchi T, Ono J, Saeki N, Osato K, Odaki M, Ushikubo O, Hirai S, Sato M, Matsuda S. Gamma knife treatment for multiple metastatic brain tumors compared with whole-brain radiation therapy. J Neurosurg. 2000. 93:Suppl 3. 32–36.
Article20. Flannery TW, Suntharalingam M, Kwok Y, Koffman BH, Amin PP, Chin LS, Nicol B, Fowler Z, Young AB, Regine WF. Gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for synchronous versus metachronous solitary brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2003. 42:327–333.
Article21. Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet. 2004. 363:1665–1672.
Article22. Ambrogi V, Tonini G, Mineo TC. Prolonged survival after extracranial metastasectomy from synchronous resectable lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001. 8:663–666.
Article23. Bonnette P, Puyo P, Gabriel C, Giudicelli R, Regnard JF, Riquet M, Brichon PY. Surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. Chest. 2001. 119:1469–1475.
Article24. Hotta K, Kiura K, Ueoka H, Tabata M, Fujiwara K, Kozuki T, Okada T, Hisamoto A, Tanimoto M. Effect of gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839) on brain metastases in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2004. 46:255–261.
Article25. Ishida A, Kanoh K, Nishisaka T, Miyazu Y, Iwamoto Y, Kohno N, Miyazawa T. Gefitinib as a first line of therapy in non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. Intern Med. 2004. 43:718–720.
Article26. Kim DY, Lee KW, Yun T, Kim DW, Kim TY, Heo DS, Bang YJ, Kim NK. Efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy after cranial radiation in patients with brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2005. 14:207–211.