Yonsei Med J.
2006 Dec;47(6):873-876. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.6.873.
MR Findings of Fulminent Leukoencephalopathy in EBV-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. slee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777179
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.6.873
Abstract
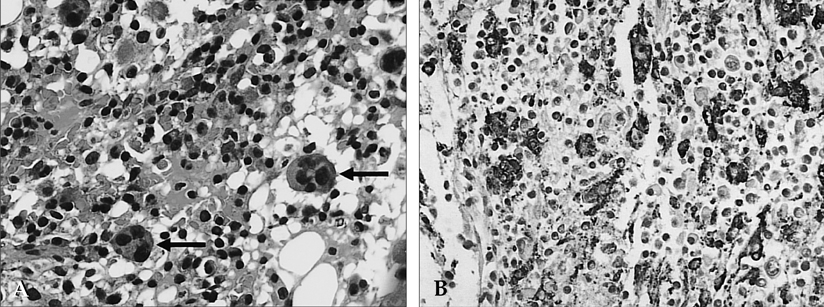
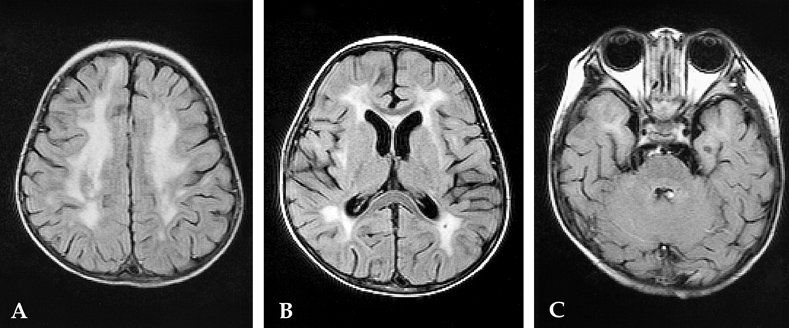
- Various manifestations of brain involvement for patients with virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome have been reported. Here, we report on the sequential magnetic resonance (MR) findings of acute demyelination of the entire brain with subsequent brain atrophy in a follow-up study of a 25-month- old boy who was admitted with fever and then diagnosed with infectious mononucleosis and EBV-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. We also review other conditions that should be included in the differential diagnosis of this disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Risdall RJ, McKenna RW, Nesbit ME, Krivit W, Balfour HH Jr, Simmons RL, et al. Virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: a benign histiocytic proliferation distinct from malignant histiocytosis. Cancer. 1979. 44:993–1002.2. Schmidt MH, Sung L, Shuckett BM. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children: abdominal US findings within 1 week of presentation. Radiology. 2004. 230:685–689.3. Forbes KP, Collie DA, Parker A. CNS involvement of virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: MR imaging appearance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:1248–1250.4. Cho HS, Park YN, Lyu CJ, Park SM, Oh SH, Yang CH, et al. EBV-elicited familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Yonsei Med J. 1997. 38:245–248.5. Horn M, Stutte HJ, Schlote W. Familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (Farquhar's disease): involvement of the central nervous system. Clin Neuropathol. 2002. 21:139–144.6. Rostasy K, Kolb R, Pohl D, Mueller H, Fels C, Moers AV, et al. CNS disease as the main manifestation of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in two children. Neuropediatrics. 2004. 35:45–49.7. Huddle DC, Rosenblum JD, Diamond CK. CT and MR findings in familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 162:1504–1505.8. Kollias SS, Ball WS Jr, Tzika AA, Harris RE. Familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: neuroradiologic evaluation with pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1994. 192:743–754.9. Fitzgerald NE, MacClain KL. Imaging characteristics of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Radiol. 2003. 33:392–401.10. Takahashi S, Oki J, Miyamoto A, Koyano S, Ito K, Azuma H, et al. Encephalopathy associated with haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following rotavirus infection. Eur J Pediatr. 1999. 158:133–137.11. Janka G, Imashuku S, Elinder G, Schneider M, Henter JI. Infection- and malignancy-associated hemophagocytic syndromes. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1998. 12:435–444.12. Henter JI, Nennesmo I. Neuropathologic findings and neurologic symptoms in twenty-three children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Pediatr. 1997. 130:358–365.13. Imashuku S. Differential diagnosis of hemophagocytic syndrome: underlying disorders and selection of the most effective treatment. Int J Hematol. 1997. 66:135–151.14. Akima M, Sumi SM. Neuropathology of familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: six cases and review of the literature. Hum Pathol. 1984. 15:161–168.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome Demonstrated by In Situ Hybridization
- A case of virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome
- CNS Involvement in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: CT and MR Findings
- Fatal Infectious Mononucleosis: A case report
- Evaluation of Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors in the Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome