Korean J Radiol.
2007 Feb;8(1):78-81. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.1.78.
CNS Involvement in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: CT and MR Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. twchung@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 753870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.1.78
Abstract
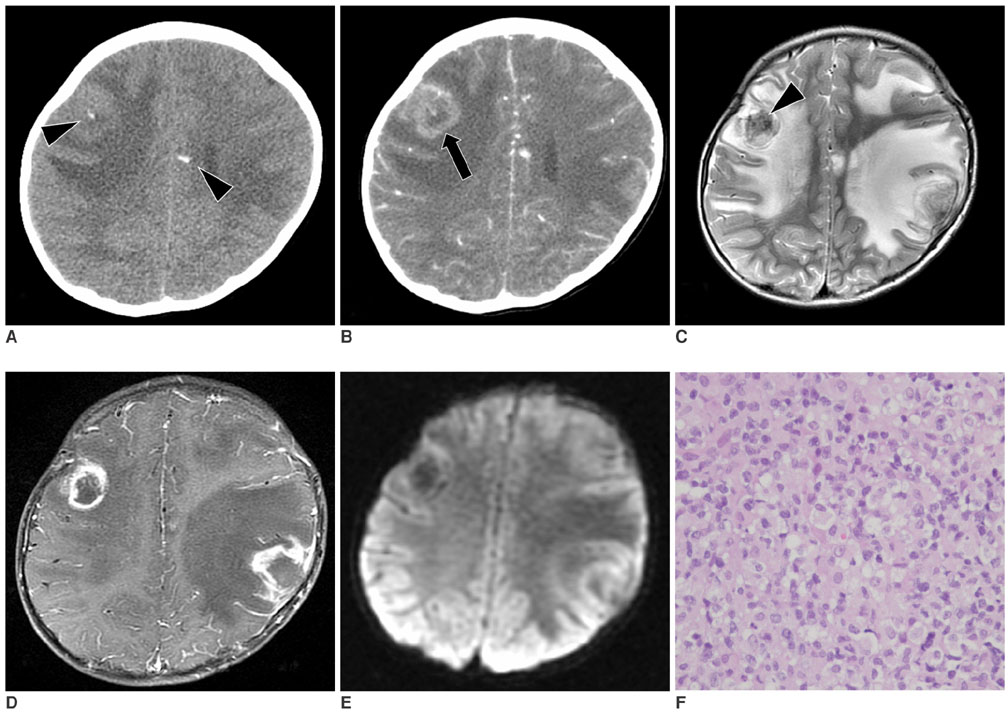
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare disorder that is characterized by proliferation of benign histiocytes, and this commonly involves the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow and central nervous system (CNS). We report here on the CT and MR imaging findings in a case of CNS HLH that showed multiple ring enhancing masses mimicking abscess or another mass on the CT and MR imaging.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Farquhar J, Claireaux A. Familial haemophagocytic reticulosis. Arch Dis Child. 1952. 27:519–525.2. Janka G, Imashuku S, Elinder G, Schneider M, Henter JI. Infection- and malignancy-associated hemophagocytic syndromes. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1998. 12:435–444.3. Henter JI, Nennesmo I. Neuropathologic findings and neurologic symptoms in twenty-three children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Pediatr. 1997. 130:358–365.4. Kieslich M, Vecchi M, Driever PH, Laverda AM, Schwabe D, Jacobi G. Acute encephalopathy as a primary manifestation of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001. 43:555–558.5. Kollias SS, Ball WS Jr, Tzika AA, Harris RE. Familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: neuroradiologic evaluation with pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1994. 192:743–754.6. Rooms L, Fitzgerald N, McClain KL. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis masquerading as child abuse: presentation of three cases and review of central nervous system findings in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatrics. 2003. 111(5 Pt 1):e636–e640.7. Munoz Ruano MM, Castillo M. Brain CT and MR imaging in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:802.8. Forbes KP, Collie DA, Parker A. CNS involvement of virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: MR imaging appearance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 21:1248–1250.9. Ozgen B, Karli-Oguz K, Sarikaya B, Tavil B, Gurgey A. Diffusion-weighted cranial MR imaging findings in a patient with hemophagocytic syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:1312–1314.10. Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, Shabana W, Breucq C, Osteaux M. Use of diffusion weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. 20:1252–1257.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hemophagocytic Syndrome Induced by Adenovirus Infection after Splenectomy
- Serial Brain MRI Findings in CNS Involvement of Familial Erythrophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Report
- Unrelated stem cell transplantation after reduced-intensity conditioning plus rituximab for Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with CNS involvement
- Central nervous system (CNS) involvement is a critical prognostic factor for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- Multiple Ecthyma Gangrenosum in a Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Patient