Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Aug;56(2):83-89. 10.4166/kjg.2010.56.2.83.
Add on Lamivudine to Adefovir Monotherapy for the Treatment of Lamivudine-resistant Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. sung_woncho@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1775862
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.56.2.83
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Add on adefovir (ADV) to ongoing lamivudine (LAM) has been recommended as a standard therapy for the treatment of LAM resistance. In the past, switch to ADV monotherapy was suggested as an option for the treatment of LAM resistance, leading to frequent development of ADV resistance. However, ADV monotherapy has been still used in LAM-resistant patients because of low cost in Korea. The aims of this study were to evaluate the virologic response and virologic breakthrough during adding on LAM in LAM-resistant patients receiving ADV monotherapy.
METHODS
The study population comprised 99 patients with LAM-resistance. We divided them into 3 groups (Group 1: switch to ADV monotherapy, N=58, Group 2: add on ADV to ongoing LAM, N=25, Group 3: add on LAM to ADV monotherapy, N=16). HBV DNA levels were assessed at baseline and every 3 months during therapy. Serum HBV DNA levels were measured by bDNA assay or the COBAS TaqMantrade mark HBV test.
RESULTS
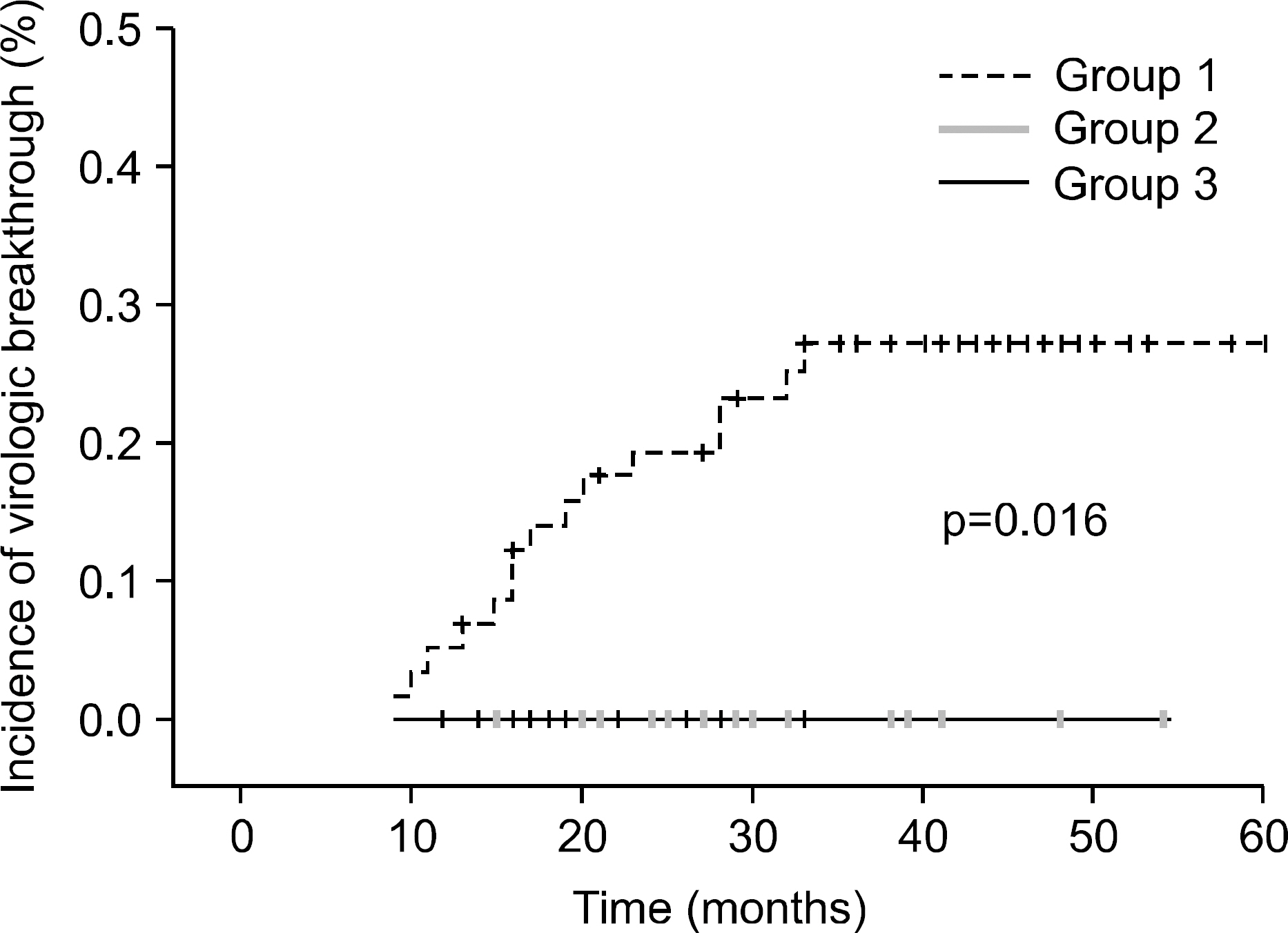
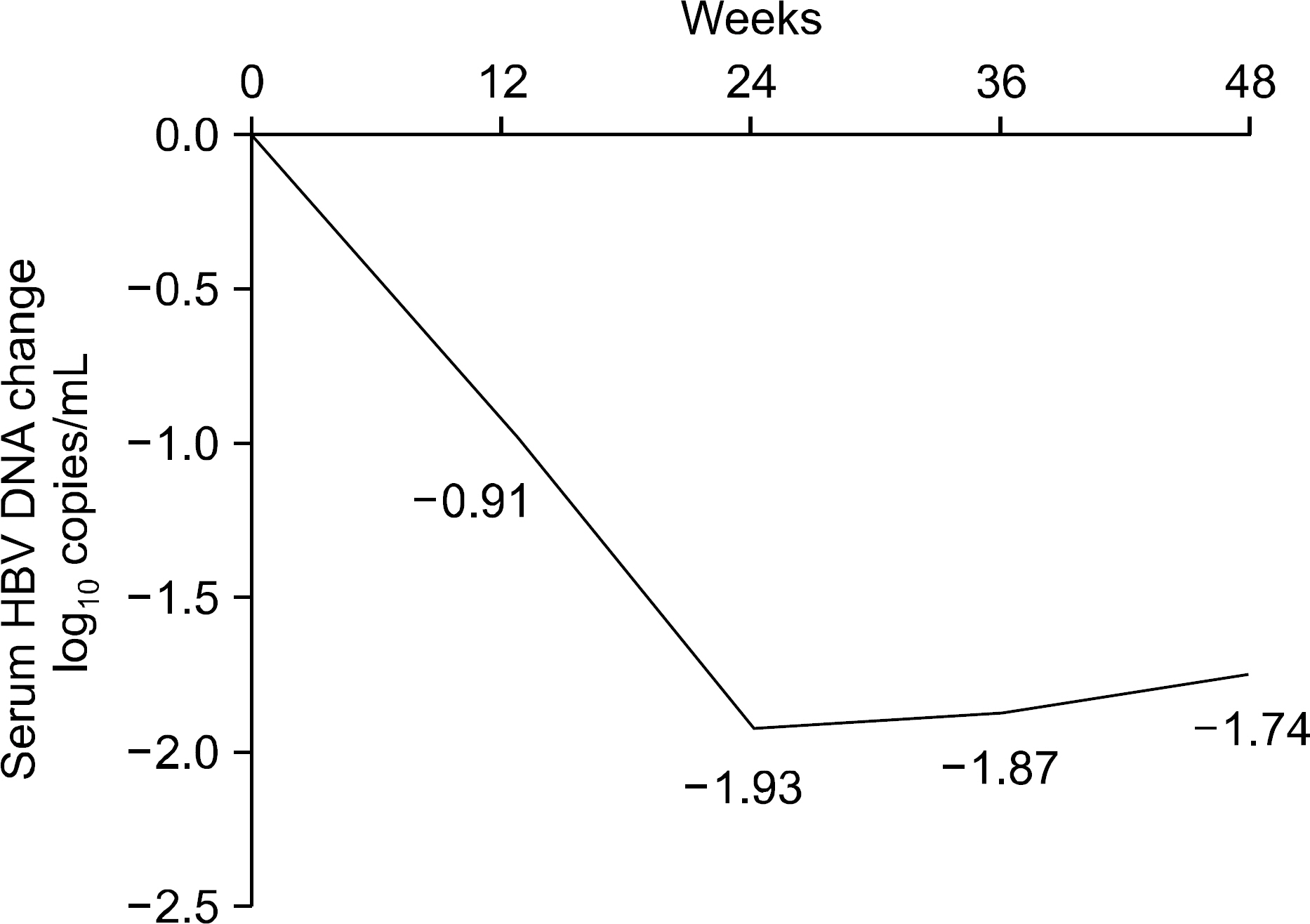
The median treatment duration for group 1, group 2, and group 3 was 42.0, 20.6, and 31.8 (18.7 mon. of ADV+13.1 mon. of LAM) months, respectively. Cumulative rate of virologic breakthrough in group 1 was 5.2%, 19.0%, and 25.9% at 12, 24, and 36 months of treatment, respectively. Virologic breakthrough was not detected in group 2 and group 3 (p=0.016, group 1 vs. group 2 or 3). In group 3, median serum HBV DNA levels were 4.22 log10 copies/mL prior to LAM administration. Median serum HBV DNA changes from baseline (log10 copies/mL) were -0.91, -1.93, -1.87 and -1.74 at week 12, 24, 36 and 48, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Later add on LAM to ADV monotherapy prevented the development of ADV resistance in patients with LAM resistance effectively, comparable to ADV add on to continuing LAM therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Perrillo RP. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B with interferon: experience in western countries. Semin Liver Dis. 1989; 9:240–248.
Article2. Lok AS, Chung HT, Liu VW, Ma OC. Longterm follow-up of chronic hepatitis B patients treated with interferon alfa. Gastroenterology. 1993; 105:1833–1838.
Article3. Wong DK, Cheung AM, O'Rourke K, Naylor CD, Detsky AS, Heathcote J. Effect of alpha-interferon treatment in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. A metaanalysis. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 119:312–323.4. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007; 45:507–539.
Article5. Lai CL, Dienstag J, Schiff E, et al. Prevalence and clinical correlates of YMDD variants during lamivudine therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:687–696.
Article6. Lok AS, Lai CL, Leung N, et al. Longterm safety of lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2003; 125:1714–1722.
Article7. Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV, Dimou E, Laras A, Papaioannou C. Efficacy of longterm lamivudine monotherapy in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2000; 32:847–851.
Article8. Chang TT, Lai CL, Chien RN, et al. Four years of lamivudine treatment in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 19:1276–1282.
Article9. Peters MG, Hann HW, Martin P, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil alone or in combination with lamivudine in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:91–101.10. Lampertico P, Viganò M, Manenti E, Iavarone M, Sablon E, Colombo M. Low resistance to adefovir combined with lamivudine: a 3-year study of 145 lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B patients. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1445–1451.
Article11. Pellicelli AM, Barbaro G, Francavilla R, et al. Adefovir and lamivudine in combination compared with adefovir monotherapy in HBeAg-negative adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and clinical or virologic resistance to lamivudine: a retrospective, multicenter, nonrandomized, open-la-bel study. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:317–323.
Article12. Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, et al. Factors associated with the virologicalresponse of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus during combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil plus lamivudine. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:368–374.13. Fung J, Lai CL, Yuen JC, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy and combination therapy with lamivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in an Asian population. Antivir Ther. 2007; 12:41–46.14. Yatsuji H, Suzuki F, Sezaki H, et al. Low risk of adefovir resistance in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir plus lamivudine combination therapy: two-year follow-up. J Hepatol. 2008; 48:923–931.
Article15. Hadziyannis S, Tassopoulos N, Chang TT, et al. Longterm adefovir dipivoxil treatment induces regression of liver fibrosis in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: results after 5 years of therapy. Hepatology. 2005; 42(suppl 1):755A.16. Yeon JE, Yoo W, Hong SP, et al. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil in lamivudine resistant chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil. Gut. 2006; 55:1488–1495.
Article17. Hong SP, Kim NK, Hwang SG, et al. Detection of hepatitis B virus YMDD variants using mass spectrometric analysis of oligonucleotide fragments. J Hepatol. 2004; 40:837–844.18. Buti M, Elefsiniotis I, Jardi R, et al. Viral genotype and baseline load predict the response to adefovir treatment in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol. 2007; 47:366–372.
Article19. Locarnini S, Qi X, Arterburn S, et al. Incidence and pre-dictors of emergence of adefovir resistant HBV during four years of adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). J Hepatol. 2005; 42(suppl 2):17.20. Reijnders JG, Leemans WF, Hansen BE, et al. On-treatment monitoring of adefovir therapy in chronic hepatitis B: virologic response can be assessed at 24 weeks. J Viral Hepat. 2009; 16:113–120.21. Kwon HC, Cheong JY, Cho SW, et al. Emergence of adefo-vir-resistant mutants after reversion to YMDD wild-type in lamivudine-resistant patients receiving adefovir monotherapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:49–54.
Article22. Rapti I, Dimou E, Mitsoula P, Hadziyannis SJ. Adding-on versus switching-to adefovir therapy in lamivudine-resistant HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007; 45:307–313.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adefovir plus lamivudine combination therapy in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B
- Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of lamivudine resistant hepatitis B mutants
- Lamivudine and adefovir combination therapy in lamivudine-resistant HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients
- Efficacy of New Anti-viral Agent in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
- Experience with Entecavir Therapy for Lamivudine-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B in Korean Children and Adolescents