J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Aug;25(8):1256-1257. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1256.
Metabolic Super Scan in 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. akaxan@nate.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 1714057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1256
Abstract
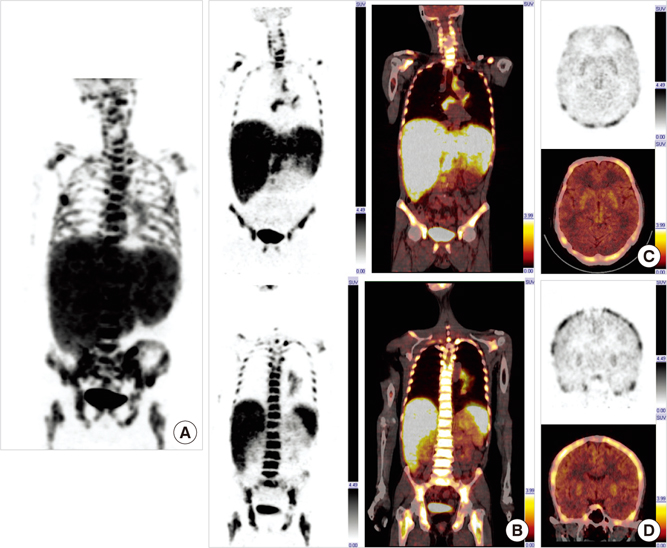
- A 50-yr-old man presented with intermittent hemoptysis and was diagnosed small cell lung cancer. 18F-FDG PET/CT for staging demonstrated extensive hypermetabolic lesions throughout the skeleton and liver. Interestingly, skeletal muscles of limbs, mediastinum, bowel, and especially brain showed very low FDG uptake. Because of some characteristics in common with super scan on skeletal scintigraphy, this case could be considered as 'metabolic super scan'.
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinoma, Small Cell/complications/radionuclide imaging
Fluorine Radioisotopes/diagnostic use
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/*diagnostic use
Hemoptysis/complications/radionuclide imaging
Humans
Liver Neoplasms/diagnosis/secondary
Lung Neoplasms/complications/radionuclide imaging
Male
Middle Aged
*Positron-Emission Tomography
Radiopharmaceuticals/*diagnostic use
Figure
Reference
-
1. Podoloff DA, Kim EE. 'Sub'-super scan-manifestation of bone narrow metastases? Clin Nucl Med. 1989. 14:597–602.2. Su HY, Liu RS, Liao SQ, Wang SJ. F-18 FDG PET superscan. Clin Nucl Med. 2006. 31:28–29.
Article3. Basu S, Nair N. Unusually elevated liver radioactivity on F-18 FDG PET in Hodgkin's disease: hepatic 'superscan'. Clin Nucl Med. 2004. 29:626–628.4. Pour MC, Simon-Corat Y, Horne T. Diffuse increased uptake on bone scan: super scan. Semin Nucl Med. 2004. 34:154–156.
Article5. Kim SE, Kim DY, Lee DS, Chung JK, Lee MC, Koh CS. Absent of faint renal uptake in bone scan etiology and significance in metastatic bone disease. Clin Nucl Med. 1991. 16:545–549.6. Manier SM, Van Nostrand D. Super bone scan. Semin Nucl Med. 1984. 14:46–47.7. Sy WM, Patel D, Faunce H. Significance of absent or faint kidney sign on bone scan. J Nucl Med. 1975. 16:454–456.8. Fujii M, Kiura K, Takigawa N, Takeda H, Tanimoto M. Super scan using positron emission tomography in lung cancer patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2007. 2:1042–1043.
Article9. Fulham MJ, Brunetti A, Aloj L, Raman R, Dwyer AJ, Di Chiro G. Decreased cerebral glucose metabolism in patients with brain tumors: an effect of corticosteroids. J Neurosurg. 1995. 83:657–664.
Article10. Gaillard WD, Zeffiro T, Fazilat S, DeCarli C, Theodore WH. Effect of valproate on cerebral metabolism and blood flow: an 18F-2-deoxyglucose and 15O water positron emission tomography study. Epilepsia. 1996. 37:515–521.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Second Primary Cancer
- Role of 18F 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Upper Gastrointestinal Malignancies
- Esophageal Leiomyoma with intense FDG uptake on 18F-FDG PET/CT
- Radiography, Bone Scan, and F-18 FDG PET/CT Imaging Findings in a Patient with Paget's Disease
- The Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Evaluation of Gastric Cancer Recurrence after Curative Gastrectomy