J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Apr;22(2):347-351. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.347.
The Effect of 2 Hz and 100 Hz Electrical Stimulation of Acupoint on Ankle Sprain in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tshahm@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 1713199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.347
Abstract
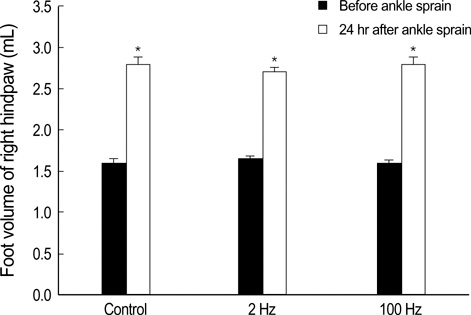
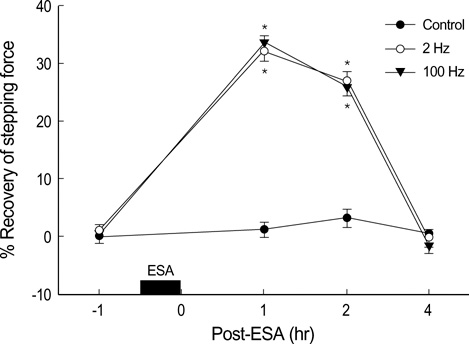
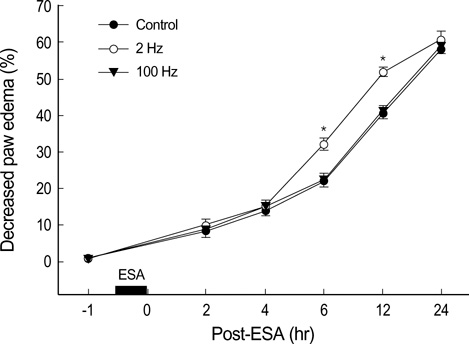
- The electrical stimulation of acupoint (ESA) releases several endogenous neuropeptides, which play important roles in management of pain and inflammation. ESA with low and high frequencies has been shown to release different neuropepides, suggesting its various therapeutic effects. Pain and edema are major problems for ankle sprain. However, there have been few reports on the effects of ESA for ankle sprain. We aimed to investigate that ESA can reduce pain and edema resulting from ankle sprain, and whether there is a difference in therapeutic effects between low and high frequency ESA. To induce ankle sprain in Sprague-Dawley rats, the ankle of right hindpaw was overextended in direction of simultaneous inversion and plantar flexion. Stepping force and edema in the paw of the sprained ankle were measured by electronic balance and plethysmometer, respectively. In both 2 and 100 Hz ESA groups, stepping force was increased significantly in similar degrees (p<0.05). Only 2 Hz ESA produced the significant rapid decrease in ankle edema. This study demonstrates that ESA of 2 Hz and 100 Hz shows comparable analgesic effects, but only 2 Hz ESA can facilitate the reduction of edema caused by ankle sprain.
MeSH Terms
-
Treatment Outcome
Sprains and Strains/diagnosis/etiology/*physiopathology/*prevention & control
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Rats
Male
Electroacupuncture/*methods
Edema/diagnosis/etiology/physiopathology/prevention & control
Arthralgia/diagnosis/etiology/physiopathology/*prevention & control
Ankle Injuries/complications/diagnosis/*physiopathology/*therapy
Animals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deluze C, Bosia L, Zirbs A, Chantraine A, Vischer TL. Electroacupuncture in fibromyalgia: results of a controlled trial. Brit Med J. 1992. 305:1249–1252.
Article2. Zhang RX, Lao L, Wang X, Fan A, Wang L, Ren K, Berman BM. Electroacupuncture attenuates inflammation in a rat model. J Altern Complement Med. 2005. 11:135–142.
Article3. Koo ST, Park YI, Lim KS, Chung K, Chung JM. Acupuncture analgesia in a new rat model of ankle sprain pain. Pain. 2002. 99:423–431.
Article4. Naeser MA, Alexander MP, Stiassny-Eder D, Lannin LN, Bachman D. Acupuncture in the treatment of hand paresis in chronic and acute stroke patients-improvement observed in all cases. Clin Rehabil. 1994. 8:127–141.5. Moon SK, Whang YK, Park SU, Ko CN, Kim YS, Bae HS, Cho KH. Antispastic effect of electroacupuncture and moxibustion in stroke patients. Am J Chin Med. 2003. 31:467–474.
Article6. Wang JQ, Mao L, Han JS. Comparison of the antinociceptive effects induced by electroacupuncture and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in the rat. Int J Neurosci. 1992. 65:117–129.
Article7. Chen XH, Han JS. Analgesia induced by electroacupuncture of different frequencies is mediated by different types of opioid receptors: another cross-tolerance study. Behav Brain Res. 1992. 47:143–149.
Article8. Han Z, Jiang YH, Wan Y, Wang Y, Chang JK, Han JS. Endomorphine-1 mediates 2 Hz but not 100 Hz electroacupuncture analgesia in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1999. 274:75–78.9. Lee JH, Beitz AJ. The distribution of brain-stem and spinal cord nuclei associated with different frequencies of electroacupuncture analgesia. Pain. 1993. 52:11–28.10. Zang WT, Jin Z, Cui GH, Zang KL, Zang L, Zeng YW, Luo F, Chen ACN, Han JS. Relations between brain network activation and analgesic effect induced by low vs. high frequency electrical acupoint stimulation in different subjects: functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain Res. 2003. 982:168–178.11. Liao JM, Lin CF, Ting H, Chang CC, Lin YJ, Lin TB. Electroacupuncture at Hoku elicits dual effect on autonomic nervous system in anesthetized rats. Neurosci Res. 2002. 42:15–20.
Article12. Stener-Victorin E, Kobayashi R, Kurosawa M. Ovarian blood flow responses to electro-acupuncture stimulation at different frequencies and intensities in anaesthetized rats. Auton Neurosci. 2003. 108:50–56.
Article13. Liu SH, Jason WJ. Lateral ankle sprains and instability problems. Clin Sports Med. 1994. 13:793–809.
Article14. Renstrom PA, Konradsen L. Ankle ligament injuries. Br J Sports Med. 1997. 31:11–20.
Article15. Ekman EF, Fiechtner JJ, Levy S, Fort JG. Efficacy of celecoxib versus ibuprofen in treatment of acute pain: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial in acute ankle sprain. Am J Orthop. 2002. 31:445–451.16. Aghababian RV. Comparison of diflunisal and acetaminophen with codeine in the management of grade 2 ankle sprain. Clin Ther. 1986. 8:520–526.17. Zhang YQ, Ji GC, Wu GC, Zhao ZQ. Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists and electroacupuncture synergetically inhibit carrageenan-induced behavioral hyperalgesia and spinal fos expression in rats. Pain. 2002. 99:525–535.
Article18. Hwang BG, Min BI, Kim JH, Na HS, Park DS. Effects of electroacupuncture on the mechanical allodynia in the rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 2002. 320:49–52.
Article19. Lao L, Zhang RX, Zhang G, Wang X, Berman BM, Ren K. A parametric study of electroacupuncture on persistent hyperalgesia and Fos protein expression in rats. Brain Res. 2004. 10:18–29.
Article20. Lin JG, Lo MW, Wen YR, Hsieh CL, Tsai SK, Sun WZ. The effect of high and low frequency electroacupuncture in pain after lower abdominal surgery. Pain. 2002. 99:509–514.
Article21. Huang C, Hu ZP, Long H, Shi YS, Han JS, Wan Y. Attenuation of mechanical but not thermal hyperalgesia by electroacupuncture with the involvement of opioids in rat model of chronic inflammatory pain. Brain Res Bull. 2004. 63:99–103.
Article22. Otsuki T, Agatsuma Y, Jokura H, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Yoshimoto T. Monosodium urate test: a new analgesic test by crystal-induced monoarthritis in rats. J Neurosci Methods. 1990. 33:229–231.
Article23. Min SS, Han JS, Kim YI, Na HS, Yoon YW, Hong SK, Han HC. A novel method for convenient assessment of arthritic pain in voluntarily walking rats. Neurosci Lett. 2001. 308:95–98.
Article24. Lao L, Zhang G, Wei F, Berman BM, Ren K. Electro-acupuncture attenuates behavioral hyperalgesia and selectively reduces spinal fos protein expression in rats with persistent inflammation. J Pain. 2001. 2:111–117.
Article25. Ceccherelli F, Gagliardi G, Ruzzante L, Giron G. Acupuncture modulation of capsaicin-induced inflammation: effect of intraperitoneal and local administration of naloxone in rats. A blind controlled study. J Altern Complement Med. 2002. 8:341–349.26. Lee JH, Choi YH, Choi BT. The anti-inflammatory effects of 2 Hz electroacupuncture with different intensities on acute carrageenan-induced inflammation in the rat paw. Int J Mol Med. 2005. 16:99–102.
Article27. Aoki E, Kasahara T, Hagiwara H, Sunaga M, Hisamitsu N, Hisamitsu T. Electroacupuncture and moxibustion influence lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha production macrophages. In Vivo. 2005. 19:495–500.28. Joris A, Costello A, Dubner R, Hargreaves KM. Opiates suppress carrageenan-induced edema and hyperthermia at doses that inhibit hyperalgesia. Pain. 1990. 43:95–103.
Article29. Cheng R, Mckibbin L, Roy B, Pomeranz B. Electroacupuncture elevates blood cortisol levels in naïve horses: sham treatment has no effect. Int J Neurosci. 1980. 10:95–97.30. Pan B, Castro-Lopes JM, Coimbra A. Activation of anterior lobe corticotrophs by electroacupuncture or noxious stimulation in the anaesthetized rats, as shown by colocalization of Fos protein with ACTH and β-endorphin and increased hormone release. Brain Res Bull. 1996. 40:175–182.31. Zhang SP, Zhang JS, Yung KK, Zhang HQ. Non-opioid-dependent anti-inflammatory effects of low frequency electroacupuncture. Brain Res Bull. 2004. 62:327–334.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Simultaneous Electroacupuncture on Ankle Sprain Pain in Rats
- Effective Acupoint of Electroacupuncture on Ankle-sprained Pain in Rats
- The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Spasticity in Hemiplegic Patients
- Effect of electrical stimulation of the vestibular system on vestibuloocular reflex and c-Fos expression in the medial vestibular nuclei of unilateral labyrinthectomized rats
- Effects of electrical stimulation of the vestibular system on neuronal activity of the ipsilateral medial vestibular nuclei following unilateral labyrinthectomy in rats