J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Dec;21(6):979-982. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.979.
Lack of Toll-like Receptor 4 and 2 Polymorphisms in Korean Patients with Bacteremia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 146-92 Dogok-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Korea. Imfell@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 3AIDS Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713104
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.979
Abstract
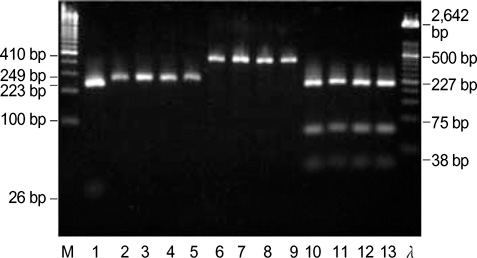
- Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are pattern-recognition receptors that are important in innate immune responses to bacterial infection. The purpose of this study is to describe the prevalence of TLRs genetic variations in the bacteremic patients in Korea. A total of 154 patients with bacteremia and 179 healthy volunteers were included. The Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile allele of the TLR4 gene and Arg753Gln and Arg677Trp allele of the TLR2 gene were tested by PCR-RFLP. The DNA sequences were determined to confirm the PCR-RFLP results. Contrary to the expectation, no genetic polymorphisms were detected in both groups of this study, suggesting that it is very rare in Korean.
MeSH Terms
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4/blood/*genetics
Toll-Like Receptor 2/blood/*genetics
Risk Factors
Risk Assessment/*methods
Prevalence
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide/genetics
Middle Aged
Male
Korea/epidemiology
Humans
Genetic Screening/methods
Genetic Predisposition to Disease/epidemiology/genetics
Female
DNA Mutational Analysis
Biological Markers/blood
Bacteremia/blood/*epidemiology/*genetics
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rarity of TLR4 Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile Polymorphisms in the Korean Population
Yeun Sun Kim, You Jin Hwang, Sung Yong Kim, Sun Mee Yang, Ki Young Lee, Ie Byung Park
Yonsei Med J. 2008;49(1):58-62. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.58.
Reference
-
1. Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996. 86:973–983.2. Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning CJ. Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:17406–17409.
Article3. Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 1999. 11:443–451.
Article4. Hirschfeld M, Kirschning CJ, Schwandner R, Wesche H, Weis JH, Wooten RM, Weis JJ. Cutting edge: inflammatory signaling by Borrellia burgdorferi lipoproteins is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol. 1999. 163:2382–2386.5. Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in TLR4 gene. Science. 1998. 282:2085–2088.
Article6. Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 2001. 410:1099–1103.
Article7. Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000. 408:740–745.
Article8. Vasselon T, Detmers PA. Toll receptors: a central element in innate immune responses. Infect Immun. 2002. 70:1033–1041.
Article9. Zhang D, Zhang G, Hayden MS, Greenblatt MB, Bussey C, Flavell RA, Ghost S. A Toll-like receptor that prevents infection by uropathogenic bacteria. Science. 2004. 303:1522–1526.
Article10. Yarovinsky F, Zhang D, Andersen JF, Bannenberg GL, Serhan CN, Hayden MS, Hieny S, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA, Ghosh S, Sher A. TLR11 activation of dendritic cells by a protozoan profilin-like protein. Science. 2005. 308:1626–1629.
Article11. Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC, Zabner J, Kline JN, Jones M, Frees K, Watt JL, Schwartz DA. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet. 2000. 25:187–191.
Article12. Lorenz E, Mira JP, Frees KL, Schwartz DA. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with gram-negative septic shock. Arch Intern Med. 2002. 162:1028–1032.
Article13. Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Akira S. Cutting edge: TLR2-deficient an MyD88-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Staphylococcus infection. J Immunol. 2000. 165:5392–5396.14. Echchannaoui H, Frei K, Schnell C, Leib SL, Zimmerli W, Landmann R. Toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis because of reduced bacterial clearing and enhanced inflammation. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:798–806.15. Wooten RM, Ma Y, Yoder RA, Brown JP, Weis JH, Zachary JF, Kirschning CJ, Weis JJ. Toll-like receptor 2 is required for innate, but not acquired, host defense to Borrelia burgdoferi. J Immunol. 2002. 168:348–355.16. Lin MT, Albertson TE. Genomic polymorphisms in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2004. 32:569–579.
Article17. Lorenz E, Frees KL, Schwartz DA. Determination of the TLR4 genotype using allele-specific PCR. Biotechniques. 2001. 31:22–24.
Article18. Angus DC, Burgner D, Wunderink R, Mira JP, Gerlach H, Wiedermann CJ, Vincent JL. The PIRO concept: P is for predisposition. Crit Care. 2003. 7:248–251.19. Agnese DM, Calvano JE, Hahm SJ, Coyle SM, Corbett SA, Calvano SE, Lowry SF. Human Toll-like receptor 4 mutations but not CD14 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of gram-negative infections. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:1522–1525.
Article20. Morre SA, Murillo LS, Bruggeman CA, Pena AS. The role that the functional Asp299Gly polymorphism in the Toll-like receptor 4 gene plays in susceptibility to Chlamydia trachomatis-associated tubal infertility. J Infect Dis. 2003. 187:341–342.21. Svanborg C, Fréndeus B, Godaly G, Hang L, Hedlund M, Wachtler C. Toll-like receptor signaling and chemokine receptor expression influence the severity of urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis. 2001. 183:Suppl 1. S61–S65.
Article22. Read RC, Pullin J, Gregory S, Borrow R, Kaczmarski EB, di Giovine FS, Dower SK, Cannings C, Wilson AG. A functional polymorphism of Toll-like receptor 4 is not associated with likelihood or severity of meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 2002. 184:640–642.
Article23. Feterowski C, Emanuilidis K, Miethke T, Gerauer K, Rump M, Ulm K, Holzmann B, Weighardt H. Effects of functional Toll-like receptor 4 mutations on the immune response to human and experimental sepsis. Immunology. 2003. 109:426–431.24. Morre SA, Murillo LS, Spaargaren J, Fennema HS, Pena AS. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism in susceptibility to Candida albicans infection. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:1377–1379.25. Okayama N, Fujimura K, Suehiro Y, Hamanaka Y, Fujiwara M, Matsubara T, Maekawa T, Hazama S, Oka M, Nohara H, Kayano K, Okita K, Hinoda Y. Simple genotype analysis of the Asp299Gly polymorphism of the Toll-like receptor-4 gene that is associated with lipopolysaccharide hyporesponsiveness. J Clin Lab Anal. 2002. 16:56–58.26. Lorenz E, Mira JP, Cornish KL, Arbour NC, Schwartz DA. A novel polymorphism in the toll-like receptor 2 gene and its potential association with staphylococcal infection. Infect Immun. 2000. 68:6398–6401.
Article27. Schröder NW, Hermann C, Hamann L, Gobel UB, Hartung T, Schumann RR. High frequency of polymorphism Arg753Gln of the Toll-like receptor-2 gene detected by a novel allele-specific PCR. J Mol Med. 2003. 81:368–372.
Article28. Kang TJ, Chae GT. Detection of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) mutation in the lepromatous leprosy patients. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2001. 31:53–58.
Article29. Ingalls RR, Lien E, Golenbock DT. Membrane-associated proteins of a lipopolysaccharide-deficient mutant of Neisseria meningitides activate the inflammatory response through Toll-like receptor 2. Infect Immun. 2001. 69:2230–2236.30. Mira JP, Cariou A, Grall F, Delclaux C, Losser MR, Heshmati F, Cheval C, Monchi M, Teboul JL, Riche F, Leleu G, Arbibe L, Mignon A, Delpech M, Dhainaut JF. Association of TNF2, a TNF-α promoter polymorphism, with septic shock susceptibility and mortality: a multicenter study. JAMA. 1999. 282:561–568.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association between Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 9 Gene and Outcomes after Ischemic Stroke
- Nucleic Acid Recognition and Signaling by Toll-like Receptor 9: Compartment-dependent Regulation
- Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist and obesity associated kidney disease: Where should we go from here?
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Toll-Like Receptor 7 and Toll-Like Receptor 9 in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Patients from Central China
- Bacterial 23S Ribosomal RNA, a Ligand for Toll-like Receptor 13