Yonsei Med J.
2013 Mar;54(2):295-300. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.295.
Hemodynamic Instability during Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting-Relationship of Calcified Plaque and Its Characteristics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea. neurosheen@gmail.com
- KMID: 1503888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.295
Abstract
- PURPOSE
During carotid angioplasty and stenting (CAS), hemodynamic instability (HDI) can occur, possibly causing post-procedural ischemic complications. The goal of this study was to investigate the risk factors of HDI focusing on characteristics of plaque.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty nine CAS patients were retrospectively evaluated for HDI. Prolonged HDI that lasted over 30 minutes was analyzed in relation to characteristics of calcified plaque.
RESULTS
Nineteen (48.7%) patients had HDI. Ten of the 19 had both bradycardia and hypotension, and nine had only bradycardia. All bradycardia was treated well with a transcutaneous temporary cardiac pacemaker. But eight patients presented with prolonged hypotension in spite of recovery of bradycardia. Calcified plaque was a related factor associated with HDI (odds ratio, 8.571; 95% confidence interval, 1.321-55.62; p=0.024). Extensive and eccentric type calcified plaques were associated with prolonged hypotension (p=0.04, and p=0.028, respectively).
CONCLUSION
The calcification of plaque is a predictable factor of HDI during CAS, and its extensive and eccentric calcified plaques may be related to prolonged HDI.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Angioplasty/*adverse effects
Bradycardia/complications
Carotid Arteries/*surgery
Carotid Stenosis/*physiopathology
Female
*Hemodynamics
Humans
Hypotension/complications
Intraoperative Complications/*etiology/radiography
Intraoperative Period
Logistic Models
Male
Middle Aged
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Stents
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
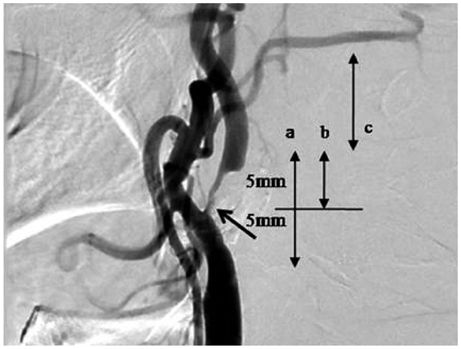
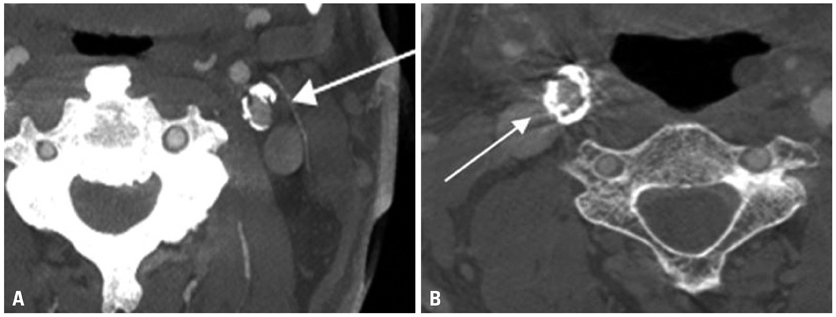
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Prediction of Prolonged Hemodynamic Instability During Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting
Jong Kook Rhim, Jin Pyeong Jeon, Jeong Jin Park, Hyuk Jai Choi, Young Dae Cho, Seung Hun Sheen, Kyung-Sool Jang
Neurointervention. 2016;11(2):120-126. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.120.Protected versus Unprotected Carotid Artery Stenting : Meta-Analysis of the Current Literature
Young Dae Cho, Sung-Eun Kim, Jeong Wook Lim, Hyuk Jai Choi, Yong Jun Cho, Jin Pyeong Jeon
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(4):458-466. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2017.0202.001.
Reference
-
1. Dietz A, Berkefeld J, Theron JG, Schmitz-Rixen T, Zanella FE, Turowski B, et al. Endovascular treatment of symptomatic carotid stenosis using stent placement: long-term follow-up of patients with a balanced surgical risk/benefit ratio. Stroke. 2001. 32:1855–1859.
Article2. Brown MM, Venables G, Clifton A, Gaines P, Taylor RS. Carotid endarterectomy vs carotid angioplasty. Lancet. 1997. 349:880–881.
Article3. Brooks WH, McClure RR, Jones MR, Coleman TL, Breathitt L. Carotid angioplasty and stenting versus carotid endarterectomy for treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a randomized trial in a community hospital. Neurosurgery. 2004. 54:318–324.
Article4. Schulz UG, Rothwell PM. Sex differences in carotid bifurcation anatomy and the distribution of atherosclerotic plaque. Stroke. 2001. 32:1525–1531.
Article5. Cayne NS, Faries PL, Trocciola SM, Saltzberg SS, Dayal RD, Clair D, et al. Carotid angioplasty and stent-induced bradycardia and hypotension: impact of prophylactic atropine administration and prior carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 2005. 41:956–961.
Article6. Dangas G, Laird JR Jr, Satler LF, Mehran R, Mintz GS, Larrain G, et al. Postprocedural hypotension after carotid artery stent placement: predictors and short- and long-term clinical outcomes. Radiology. 2000. 215:677–683.
Article7. Harrop JS, Sharan AD, Benitez RP, Armonda R, Thomas J, Rosenwasser RH. Prevention of carotid angioplasty-induced bradycardia and hypotension with temporary venous pacemakers. Neurosurgery. 2001. 49:814–820.
Article8. Howell M, Krajcer Z, Dougherty K, Strickman N, Skolkin M, Toombs B, et al. Correlation of periprocedural systolic blood pressure changes with neurological events in high-risk carotid stent patients. J Endovasc Ther. 2002. 9:810–816.
Article9. Mlekusch W, Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Nachtmann T, Lang W, Ahmadi R, et al. Hypotension and bradycardia after elective carotid stenting: frequency and risk factors. J Endovasc Ther. 2003. 10:851–859.
Article10. Pappadà G, Beghi E, Marina R, Agostoni E, Cesana C, Legnani F, et al. Hemodynamic instability after extracranial carotid stenting. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006. 148:639–645.
Article11. Qureshi AI, Luft AR, Sharma M, Janardhan V, Lopes DK, Khan J, et al. Frequency and determinants of postprocedural hemodynamic instability after carotid angioplasty and stenting. Stroke. 1999. 30:2086–2093.
Article12. Nonaka T, Oka S, Miyata K, Mikami T, Koyanagi I, Houkin K, et al. Prediction of prolonged postprocedural hypotension after carotid artery stenting. Neurosurgery. 2005. 57:472–477.13. Cieri E, De Rango P, Maccaroni MR, Spaccatini A, Caso V, Cao P. Is haemodynamic depression during carotid stenting a predictor of peri-procedural complications? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2008. 35:399–404.
Article14. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N Engl J Med. 1991. 325:445–453.15. Uwatoko T, Toyoda K, Inoue T, Yasumori K, Hirai Y, Makihara N, et al. Carotid artery calcification on multislice detector-row computed tomography. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007. 24:20–26.
Article16. Nandalur KR, Baskurt E, Hagspiel KD, Finch M, Phillips CD, Bollampally SR, et al. Carotid artery calcification on CT may independently predict stroke risk. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:547–552.
Article17. Im SH, Han MH, Kim SH, Kwon BJ. Transcutaneous temporary cardiac pacing in carotid stenting: noninvasive prevention of angioplasty-induced bradycardia and hypotension. J Endovasc Ther. 2008. 15:110–116.
Article18. Chalmers J, Pilowsky P. Brainstem and bulbospinal neurotransmitter systems in the control of blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1991. 9:675–694.
Article19. Mangin L, Medigue C, Merle JC, Macquin-Mavier I, Duvaldestin P, Monti A, et al. Cardiac autonomic control during balloon carotid angioplasty and stenting. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003. 81:944–951.
Article20. Leisch F, Kerschner K, Hofman R, Bibl D, Engleder C, Bergmann H. [Carotid stenting: acute results and complications]. Z Kardiol. 1999. 88:661–668.21. Morrish W, Grahovac S, Douen A, Cheung G, Hu W, Farb R, et al. Intracranial hemorrhage after stenting and angioplasty of extracranial carotid stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:1911–1916.22. Taha MM, Toma N, Sakaida H, Hori K, Maeda M, Asakura F, et al. Periprocedural hemodynamic instability with carotid angioplasty and stenting. Surg Neurol. 2008. 70:279–285.
Article23. Wong JH, Findlay JM, Suarez-Almazor ME. Hemodynamic instability after carotid endarterectomy: risk factors and associations with operative complications. Neurosurgery. 1997. 41:35–41.
Article24. Mendelsohn FO, Weissman NJ, Lederman RJ, Crowley JJ, Gray JL, Phillips HR, et al. Acute hemodynamic changes during carotid artery stenting. Am J Cardiol. 1998. 82:1077–1081.
Article25. Fadel PJ. Arterial baroreflex control of the peripheral vasculature in humans: rest and exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008. 40:2055–2062.26. Fadel PJ, Ogoh S, Keller DM, Raven PB. Recent insights into carotid baroreflex function in humans using the variable pressure neck chamber. Exp Physiol. 2003. 88:671–680.
Article27. Setacci F, Sirignano P, de Donato G, Chisci E, Galzerano G, Iacoponi F, et al. Carotid highly-calcified de novo stenosis and cutting-balloon angioplasty: a tool to prevent haemodynamic depression? J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2009. 50:357–364.28. Jin SC, Kwon OK, Oh CW, Jung C, Han MG, Bae HJ, et al. A technical strategy for carotid artery stenting: suboptimal prestent balloon angioplasty without poststenting balloon dilatation. Neurosurgery. 2010. 67:1438–1442.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prolonged Hemodynamic Depression After Bilateral Carotid Angioplasty and Stent Insertion
- Prediction of Prolonged Hemodynamic Instability During Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting
- A Case of Transseptal Approach to Carotid Artery Stenting in Right Internal Carotid Stenosis
- Anesthetic Management of Patients during Carotid Balloon Angioplasty and Stenting: A case report
- Massive Cerebral Microemboli after Protected Carotid Artery Angioplasty and Stenting Using a Distal Filter Embolic Protection Device for a Vulnerable Plaque with a Lipid Rich Necrotic Core and Intraplaque Hemorrhage: A Case Report