Infect Chemother.
2009 Oct;41(5):301-304. 10.3947/ic.2009.41.5.301.
A Case of Escherichia Coli Empyema Preceded by Acute Pyelonephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. kysun@dmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1473658
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2009.41.5.301
Abstract
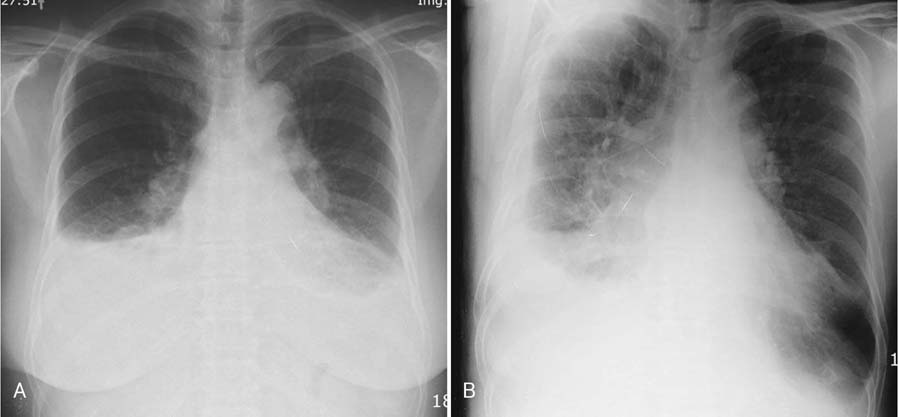
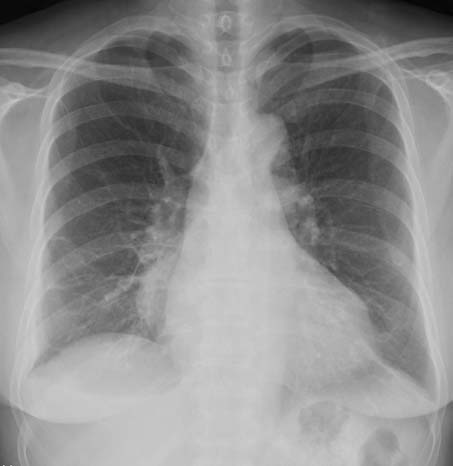
- We experienced a case of acute pyelonephritis which progressed to Escherichia coli bacteremia and later complicated by empyema in a 65-year-old female. She was successfully treated with intravenous antibiotic therapy and percutaneous drainage of empyema.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cassivi SD, McKellar SH. Bope ET, Rakel RE, editors. Pleural effusion and empyema thoracis. Conn's Current Therapy. 2008. 60th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;248.2. Hernández Pérez JM, Rodráguez Suárez PM, Freixinet Gilart J. Pleural empyema secondary to pyonephrosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008. 44:285.
Article3. Berkman N, Liss H, Kramer MR. Pyelonephritis as a cause of pleural effusion. Respiration. 1996. 63:384–386.
Article4. Chapman SJ, Davies RJ. The management of pleural space infections. Respirology. 2004. 9:4–11.
Article5. De Hoyos A, Sunderasen S. Thoracic empyema. Surg Clin N Am. 2002. 82:643–671.
Article6. Rahman NM, Chapman SJ, Davies RJ. The approach to the patient with a parapneumonic effusion. Clin Chest Med. 2006. 27:253–266.
Article7. Molnar TF. Current surgical treatment of thoracic empyema in adults. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007. 32:22–30.
Article8. Nicolle LE. Urinary Tract Infection. Traditional pharmacologic therapies. Am J Med. 2002. 8:113 Suppl 1A. 35S–44S.
Article9. Nesbit RM, Dick VS. Pulmonary complications of acute renal and perirenal suppuration. Am J Roentgenol. 1940. 44:161–169.10. Wang IK, Chuang FR, Chang HY, Lin CL, Yang CT. Acute pyelonephritis associated with transudative pleural effusion in a middle-aged woman without urinary tract obstruction. Med Princ Pract. 2006. 15:309–311.
Article11. Stark DD, Shanes JG, Baron RL, Koch DD. Biochemical features of urinothorax. Arch Intern Med. 1982. 142:1509–1511.
Article12. Miller KS, Wooten S, Sahn SA. Urinothorax: a cause of low pH transudative pleural effusions. Am J Med. 1988. 85:448–449.
Article13. Baron RL, Stark DD, McClennan BL, Shanes JG, Davis GL, Koch DD. Intrathoracic extension of retroperitoneal urine collections. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981. 137:37–41.
Article14. Kim DK, Nam SY, Lee CG, Kim DW, Moon JS, Kim YS, Hur TG. A case of Escherichia coli Empyema preceded by gastroenteritis. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007. 17:74–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case ofEscherichia Coli Empyema Preceded by Gastroenteritis
- A Case Report of Sepsis by Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase Producing Escherichia Coli
- Subcapsular hematoma as a complication of acute pyelonephritis: a case report
- A Case of Huge Infected Adrenal Pseudocyst associated with Acute Pyelonephritis and E. coli Bacteremia
- Escherichia Coli Subdural Empyema Following Subdural Hygroma in Elderly Patient