Korean J Orthod.
2010 Jun;40(3):195-206. 10.4041/kjod.2010.40.3.195.
Zygoma-gear appliance for intraoral upper molar distalization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Karadeniz Technical University, Department of Orthodontics, Trabzon, Turkey. dtmehmetbayram@yahoo.com
- KMID: 1459573
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2010.40.3.195
Abstract
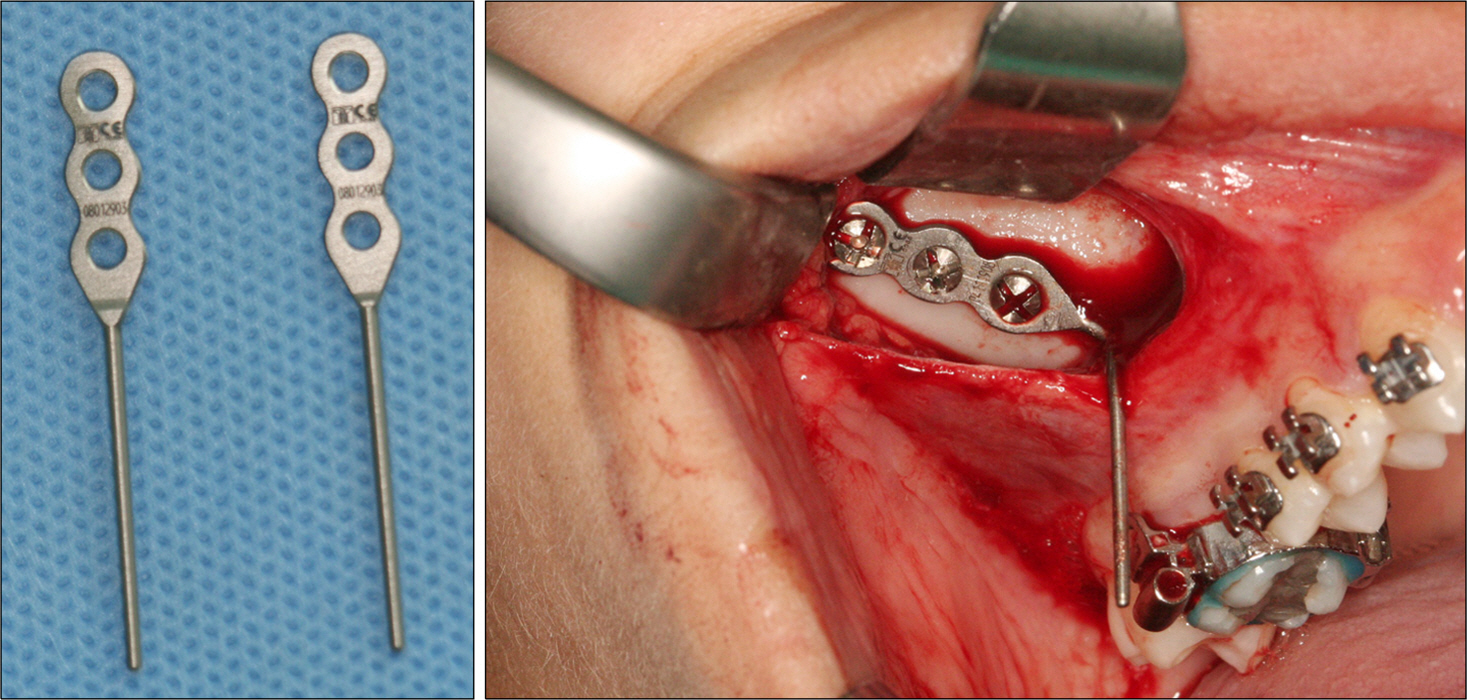
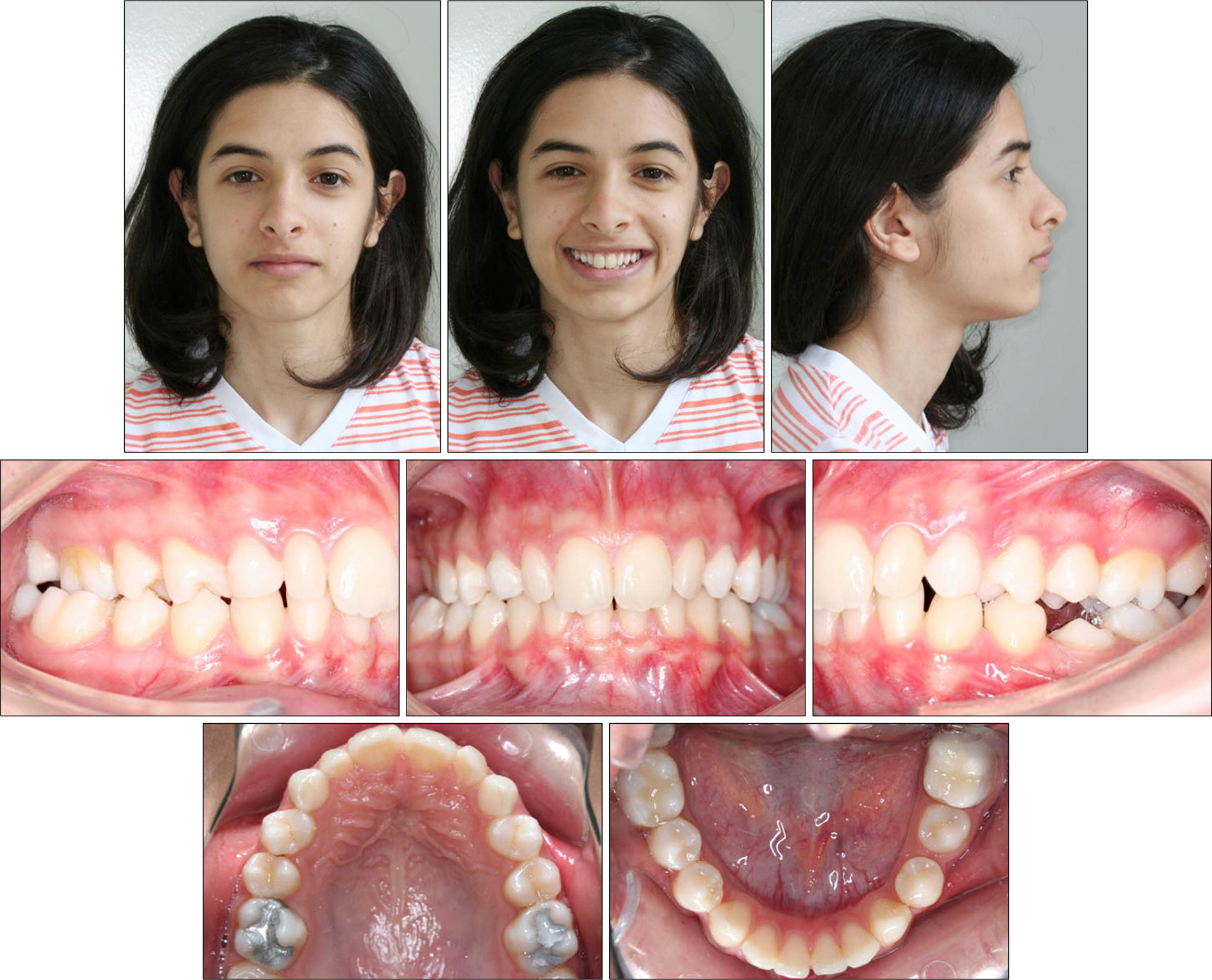
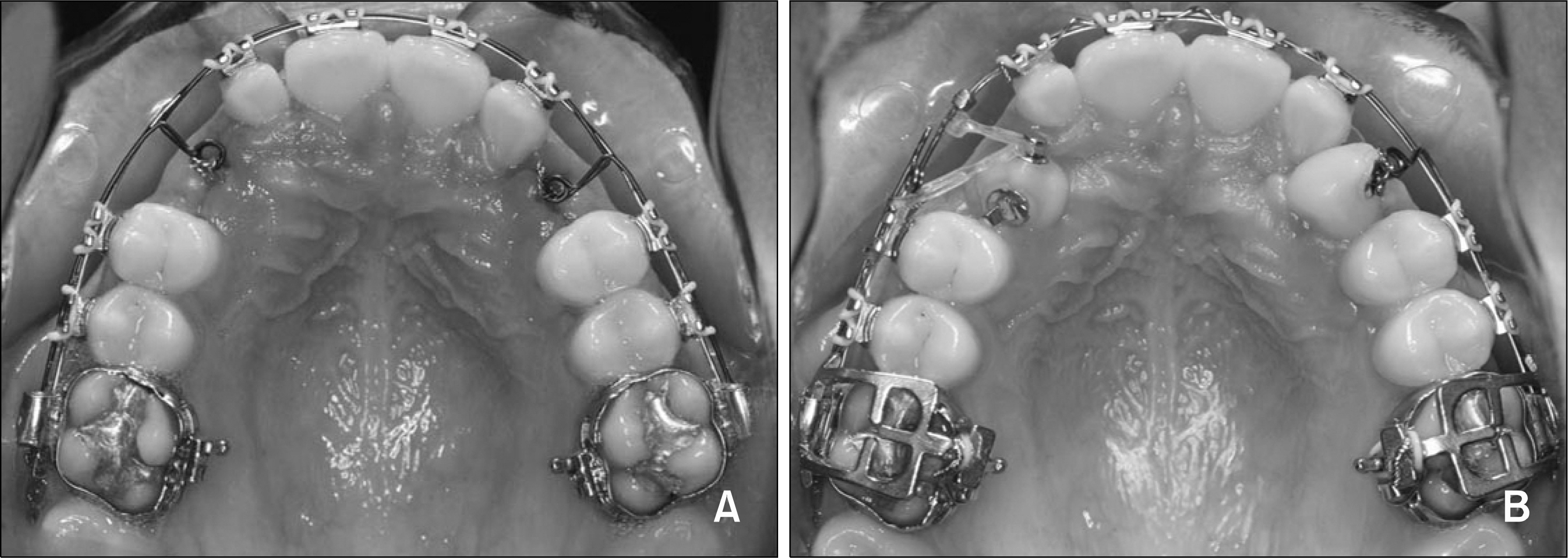
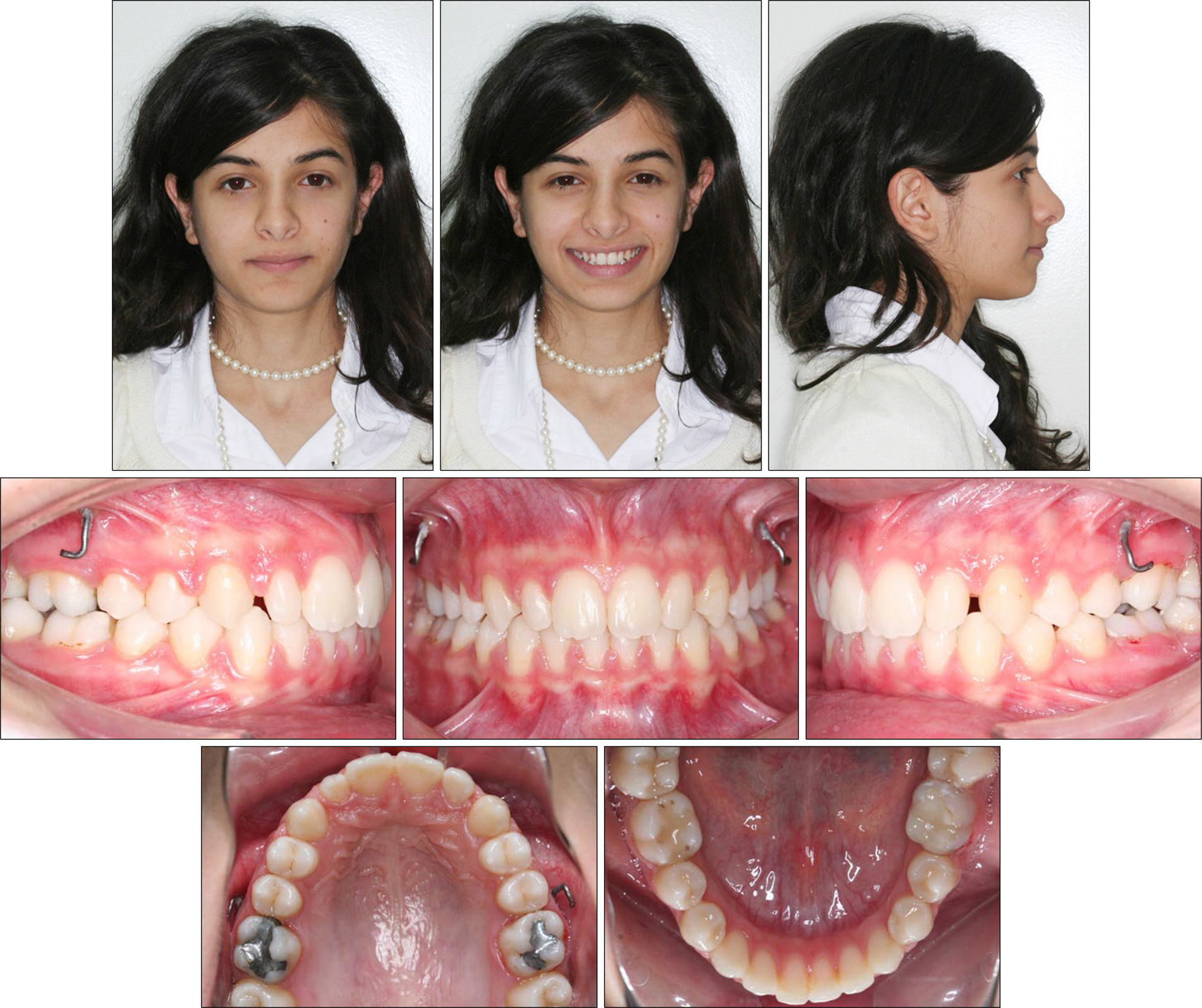
- The aim of this report is to present an intraoral upper molar distalization system supported with zygomatic anchorage plates (Zygoma-gear Appliance, ZGA). This system was used for a 16-year-old female patient with a Class II molar relationship requiring molar distalization. The system consisted of bilateral zygomatic anchorage plates, an inner-bow and heavy intraoral elastics. Distalization of the upper molars was achieved in 3 months and the treatment results were evaluated from lateral cephalometric radiographs. According to the results of the cephalometric analysis, the maxillary first molars showed a distalization of 4 mm, associated with a distal axial inclination of 4.5degrees. The results of this study show that an effective upper molar distalization without anchorage loss can be achieved in a short time using the ZGA. We suggest that this new system may be used in cases requiring molar distalization in place of extraoral appliances.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Cangialosi TJ., Meistrell ME Jr., Leung MA., Ko JY. A cephalometric appraisal of edgewise Class II nonextraction treatment with extraoral force. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988. 93:315–24.
Article2.Wilson WL., Wilson RC. Modular 3D appliances. Problem solving in edgewise, straightwire and lightwire treatment. J Clin Orthod. 1984. 18:272–81.3.Blechman AM. Magnetic force systems in orthodontics. Clinical results of a pilot study. Am J Orthod. 1985. 87:201–10.4.Hilgers JJ. The pendulum appliance for Class II non-compliance therapy. J Clin Orthod. 1992. 26:706–14.5.Byloff FK., Darendeliler MA. Distal molar movement using the pendulum appliance. Part 1: clinical and radiological evaluation. Angle Orthod. 1997. 67:249–60.6.Taner TU., Yukay F., Pehlivanoglu M., Cakirer B. A comparative analysis of maxillary tooth movement produced by cervical headgear and pend-x appliance. Angle Orthod. 2003. 73:686–91.7.Haydar S., Uner O. Comparison of Jones jig molar distalization appliance with extraoral traction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000. 117:49–53.
Article8.Carano A., Testa M. The distal jet for upper molar distali-zation. J Clin Orthod. 1996. 30:374–80.9.Keles A., Pamukcu B., Tokmak EC. Bilateral maxillary molar distalization with sliding mechanics: keles slider. World J Orthod. 2002. 3:57–66.10.Fortini A., Lupoli M., Giuntoli F., Franchi L. Dentoskeletal effects induced by rapid molar distalization with the first class appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 125:697–705.
Article11.Kärcher H., Byloff FK., Clar E. The Graz implant supported pendulum, a technical note. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2002. 30:87–90.
Article12.Keles A., Erverdi N., Sezen S. Bodily distalization of molars with absolute anchorage. Angle Orthod. 2003. 73:471–82.13.Gelgör IE., Büyükyilmaz T., Karaman AI., Dolanmaz D., Kalayci A. Intraosseous screw-supported upper molar distali-zation. Angle Orthod. 2004. 74:838–50.14.Kircelli BH., Pektas ZO., Kircelli C. Maxillary molar distalization with a bone-anchored pendulum appliance. Angle Orthod. 2006. 76:650–9.15.Kinzinger GS., Diedrich PR., Bowman SJ. Upper molar distalization with a miniscrew-supported distal jet. J Clin Orthod. 2006. 40:672–8.16.Escobar SA., Tellez PA., Moncada CA., Villegas CA., Latorre CM., Oberti G. Distalization of maxillary molars with the bone-supported pendulum: a clinical study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007. 131:545–9.
Article17.Bayram M., Nur M., Kilkis D. The frog appliance for upper molar distalization: a case report. Korean J Orthod. 2010. 40:50–60.
Article18.Kim SJ., Chun YS., Jung SH., Park SH. Three dimensional analysis of tooth movement using different types of maxillary molar distalization appliances. Korean J Orthod. 2008. 38:376–87.
Article19.De Clerck H., Geerinckx V., Siciliano S. The zygoma anchorage system. J Clin Orthod. 2002. 36:455–9.20.Sugawara J., Kanzaki R., Takahashi I., Nagasaka H., Nanda R. Distal movement of maxillary molars in nongrowing patients with the skeletal anchorage system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 129:723–33.
Article21.Kaya B., Arman A., Uckan S., Yazici AC. Comparison of the zygoma anchorage system with cervical headgear in buccal segment distalization. Eur J Orthod. 2009. 31:417–24.
Article22.Burstone CJ. Application of bioengineering to clinical orthodontics. In: Graber TM, Vanarsdall RJ editors. Orthodontics. Current principles and techniques. 3rd ed.St Louis: CV Mosby;2000. p. 259–92.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The frog appliance for upper molar distalization: a case report
- Noncompliance screw supported maxillary molar distalization in a parallel manner
- Comparison of transverse dental changes induced by the palatally applied Frog appliance and buccally applied Karad's integrated distalizing system
- Combined treatment with headgear and the Frog appliance for maxillary molar distalization: a randomized controlled trial
- C-activator treatment for distalization of maxillary molars in Class II anterior deep bite malocclusion