Korean J Radiol.
2012 Aug;13(4):443-449. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.443.
Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Isotropic Ankle Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Three-Dimensional Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin Echo versus Three-Dimensional Isotropic Fast Field Echo Sequences
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul 135-710, Korea. ycyoon@skku.edu
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-872, Korea.
- KMID: 1383856
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.443
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
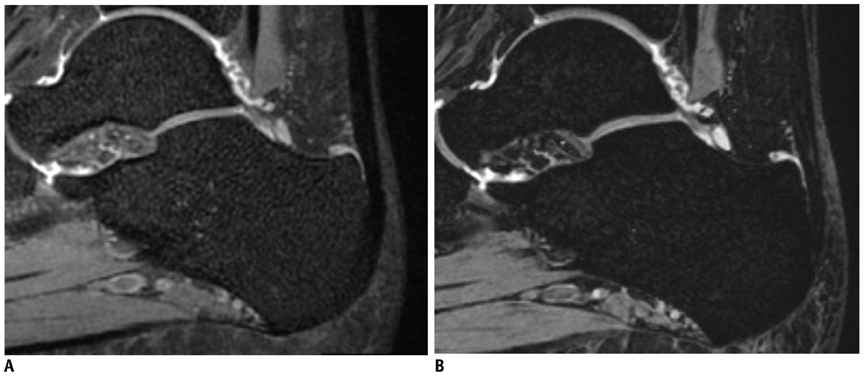
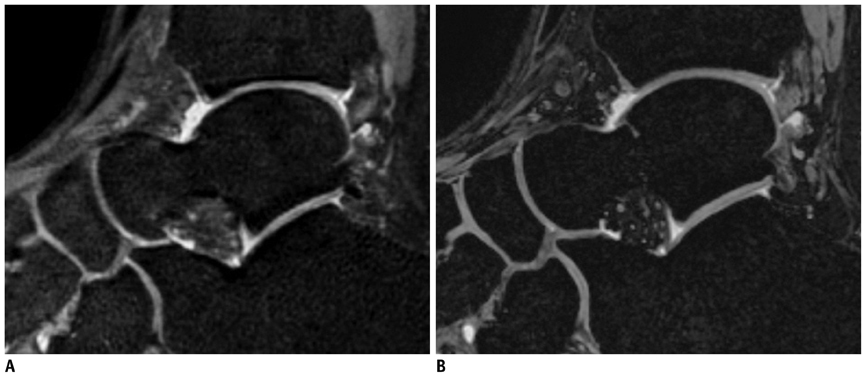
To compare the image quality of volume isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition (VISTA) imaging method with that of the three-dimensional (3D) isotropic fast field echo (FFE) imaging method applied for ankle joint imaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
MR imaging of the ankles of 10 healthy volunteers was performed with VISTA and 3D FFE sequences by using a 3.0 T machine. Two radiologists retrospectively assessed the tissue contrast between fluid and cartilage (F-C), and fluid and the Achilles tendon (F-T) with use of a 4-point scale. For a quantitative analysis, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was obtained by imaging phantom, and the contrast ratios (CRs) were calculated between F-T and F-C. Statistical analyses for differences in grades of tissue contrast and CRs were performed.
RESULTS
VISTA had significantly superior grades in tissue contrast of F-T (p = 0.001). Results of 3D FFE had superior grades in tissue contrast of F-C, but these result were not statistically significant (p = 0.157). VISTA had significantly superior CRs in F-T (p = 0.002), and 3D FFE had superior CRs in F-C (p = 0.003). The SNR of VISTA was higher than that of 3D FFE (49.24 vs. 15.94).
CONCLUSION
VISTA demonstrates superior tissue contrast between fluid and the Achiles tendon in terms of quantitative and qualitative analysis, while 3D FFE shows superior tissue contrast between fluid and cartilage in terms of quantitative analysis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gold GE, Chen CA, Koo S, Hargreaves BA, Bangerter NK. Recent advances in MRI of articular cartilage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 193:628–638.2. Stevens KJ, Busse RF, Han E, Brau AC, Beatty PJ, Beaulieu CF, et al. Ankle: isotropic MR imaging with 3D-FSE-cube--initial experience in healthy volunteers. Radiology. 2008. 249:1026–1033.3. Jung JY, Yoon YC, Kwon JW, Ahn JH, Choe BK. Diagnosis of internal derangement of the knee at 3.0-T MR imaging: 3D isotropic intermediate-weighted versus 2D sequences. Radiology. 2009. 253:780–787.4. Notohamiprodjo M, Horng A, Pietschmann MF, Müller PE, Horger W, Park J, et al. MRI of the knee at 3T: first clinical results with an isotropic PDfs-weighted 3D-TSE-sequence. Invest Radiol. 2009. 44:585–597.5. Gold GE, Busse RF, Beehler C, Han E, Brau AC, Beatty PJ, et al. Isotropic MRI of the knee with 3D fast spin-echo extended echo-train acquisition (XETA): initial experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 188:1287–1293.6. McCauley TR, Disler DG. Magnetic resonance imaging of articular cartilage of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001. 9:2–8.7. Recht MP, Piraino DW, Paletta GA, Schils JP, Belhobek GH. Accuracy of fat-suppressed three-dimensional spoiled gradient-echo FLASH MR imaging in the detection of patellofemoral articular cartilage abnormalities. Radiology. 1996. 198:209–212.8. Disler DG. Fat-suppressed three-dimensional spoiled gradient-recalled MR imaging: assessment of articular and physeal hyaline cartilage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 169:1117–1123.9. Kim HJ, Lee SH, Kang CH, Ryu JA, Shin MJ, Cho KJ, et al. Evaluation of the chondromalacia patella using a microscopy coil: comparison of the two-dimensional fast spin echo techniques and the three-dimensional fast field echo techniques. Korean J Radiol. 2011. 12:78–88.10. Gückel C, Jundt G, Schnabel K, Gächter A. Spin-echo and 3D gradient-echo imaging of the knee joint: a clinical and histopathological comparison. Eur J Radiol. 1995. 21:25–33.11. Reeder JD, Matz SO, Becker L, Andelman SM. MR imaging of the knee in the sagittal projection: comparison of three-dimensional gradient-echo and spin-echo sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989. 153:537–540.12. Gold GE, Suh B, Sawyer-Glover A, Beaulieu C. Musculoskeletal MRI at 3.0 T: initial clinical experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1479–1486.13. Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007. 26:375–385.14. Li CQ, Chen W, Beatty PJ, Brau AC, Hargreaves BA, Busse RF, et al. SNR quantification with phased-array coils and parallel imaging for 3d-fSE. 2010. In : 19th annual meeting & exhibition, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine; Stockholm. 552.15. Held P, Seitz J, Fründ R, Nitz W, Lenhart M, Geissler A. Comparison of two-dimensional gradient echo, turbo spin echo and two-dimensional turbo gradient spin echo sequences in MRI of the cervical spinal cord anatomy. Eur J Radiol. 2001. 38:64–71.16. Turetschek K, Wunderbaldinger P, Bankier AA, Zontsich T, Graf O, Mallek R, et al. Double inversion recovery imaging of the brain: initial experience and comparison with fluid attenuated inversion recovery imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1998. 16:127–135.17. Willinek WA, Bayer T, Gieseke J, von Falkenhausen M, Sommer T, Hoogeveen R, et al. High spatial resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the supraaortic arteries using the quadrature body coil at 3.0T: a feasibility study. Eur Radiol. 2007. 17:618–625.18. Nelles M, König RS, Gieseke J, Guerand-van Battum MM, Kukuk GM, Schild HH, et al. Dual-source parallel RF transmission for clinical MR imaging of the spine at 3.0 T: intraindividual comparison with conventional single-source transmission. Radiology. 2010. 257:743–753.19. Gudbjartsson H, Patz S. The Rician distribution of noisy MRI data. Magn Reson Med. 1995. 34:910–914.20. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977. 33:159–174.21. Disler DG, Recht MP, McCauley TR. MR imaging of articular cartilage. Skeletal Radiol. 2000. 29:367–377.22. McCauley TR, Disler DG. MR imaging of articular cartilage. Radiology. 1998. 209:629–640.23. Yoshioka H, Alley M, Steines D, Stevens K, Rubesova E, Genovese M, et al. Imaging of the articular cartilage in osteoarthritis of the knee joint: 3D spatial-spectral spoiled gradient-echo vs. fat-suppressed 3D spoiled gradient-echo MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2003. 18:66–71.24. Gay SB, Chen NC, Burch JJ, Gleason TR, Sagman AM. Multiplanar reconstruction in magnetic resonance evaluation of the knee. Comparison with film magnetic resonance interpretation. Invest Radiol. 1993. 28:142–145.25. Wieslander SB, Rappeport ED, Lausten GS, Thomsen HS. Multiplanar reconstruction in MR imaging of the knee. Comparison with standard sagittal and coronal images. Acta Radiol. 1998. 39:116–119.26. Duc SR, Pfirrmann CW, Koch PP, Zanetti M, Hodler J. Internal knee derangement assessed with 3-minute three-dimensional isovoxel true FISP MR sequence: preliminary study. Radiology. 2008. 246:526–535.27. Carlson J, Crooks L, Ortendahl D, Kramer DM, Kaufman L. Signal-to-noise ratio and section thickness in two-dimensional versus three-dimensional Fourier transform MR imaging. Radiology. 1988. 166:266–270.28. Weiger M, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P. 2D SENSE for faster 3D MRI. MAGMA. 2002. 14:10–19.29. Noll DC, Nishimura DG, Macovski A. Homodyne detection in magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1991. 10:154–163.30. Kijowski R, Davis KW, Woods MA, Lindstrom MJ, De Smet AA, Gold GE, et al. Knee joint: comprehensive assessment with 3D isotropic resolution fast spin-echo MR imaging--diagnostic performance compared with that of conventional MR imaging at 3.0 T. Radiology. 2009. 252:486–449.31. Ristow O, Steinbach L, Sabo G, Krug R, Huber M, Rauscher I, et al. Isotropic 3D fast spin-echo imaging versus standard 2D imaging at 3.0 T of the knee--image quality and diagnostic performance. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:1263–1272.32. Schick F. Simultaneous highly selective MR water and fat imaging using a simple new type of spectral-spatial excitation. Magn Reson Med. 1998. 40:194–202.33. Peng Q, McColl RW, Wang J, Weatherall PT. Novel rapid fat suppression strategy with spectrally selective pulses. Magn Reson Med. 2005. 54:1569–1574.34. Gold GE, Hargreaves BA, Reeder SB, Block WF, Kijowski R, Vasanawala SS, et al. Balanced SSFP imaging of the musculoskeletal system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007. 25:270–278.35. Duc SR, Pfirrmann CW, Schmid MR, Zanetti M, Koch PP, Kalberer F, et al. Articular cartilage defects detected with 3D water-excitation true FISP: prospective comparison with sequences commonly used for knee imaging. Radiology. 2007. 245:216–223.36. Duc SR, Koch P, Schmid MR, Horger W, Hodler J, Pfirrmann CW. Diagnosis of articular cartilage abnormalities of the knee: prospective clinical evaluation of a 3D water-excitation true FISP sequence. Radiology. 2007. 243:475–482.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessment of the Location of the Peroneus Longus Tendon in the Cuboid Groove Using 3D Isotropic Fast Spin-Echo MRI
- Quantitative Assessment and Ligament Traceability of Volume Isotropic Turbo Spin Echo Acquisition (VISTA) Ankle Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Fat Suppression versus without Fat Suppression
- Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus Conventional 2D Sequences at 3T
- Comparison of Three-Dimensional Isotropic and Two-Dimensional Conventional Indirect MR Arthrography for the Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears
- Diagnosis of Nerve Root Compromise of the Lumbar Spine: Evaluation of the Performance of Three-dimensional Isotropic T2-weighted Turbo Spin-Echo SPACE Sequence at 3T