Ann Lab Med.
2012 May;32(3):206-209. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.3.206.
Contamination of X-ray Cassettes with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus in a Radiology Department
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaeseok@hallym.or.kr
- 2Hospital Infection Control Office, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1381686
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.3.206
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We performed surveillance cultures of the surfaces of X-ray cassettes to assess contamination with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
METHODS
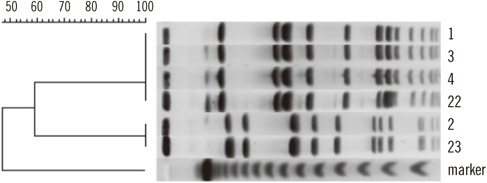
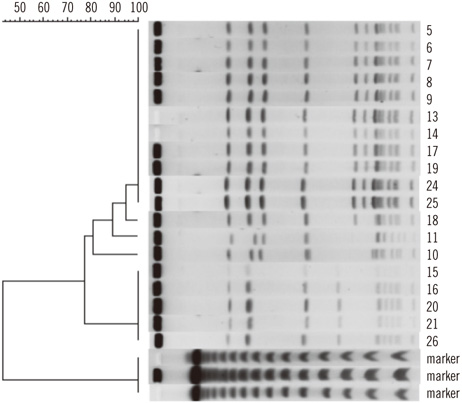
The surfaces of 37 X-ray cassettes stored in a radiology department were cultured using mannitol salt agar containing 6 microg/mL oxacillin. Suspected methicillin-resistant staphylococcal colonies were isolated and identified by biochemical testing. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis was performed to determine the clonal relationships of the contaminants.
RESULTS
Six X-ray cassettes (16.2%) were contaminated with MRSA. During the isolation procedure, we also detected 19 X-ray cassettes (51.4%) contaminated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus (MRSH), identified as yellow colonies resembling MRSA on mannitol salt agar. PFGE analysis of the MRSA and MRSH isolates revealed that most isolates of each organism were identical or closely related to each other, suggesting a common source of contamination.
CONCLUSIONS
X-ray cassettes, which are commonly in direct contact with patients, were contaminated with MRSA and MRSH. In hospital environments, contaminated X-ray cassettes may serve as fomites for methicillin-resistant staphylococci.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
Diagnostic Equipment/*microbiology
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field
Humans
Methicillin Resistance
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus/drug effects/*isolation & purification
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Oxacillin/pharmacology
Staphylococcus haemolyticus/drug effects/*isolation & purification
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boyce JM, Potter-Bynoe G, Chenevert C, King T. Environmental contamination due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: possible infection control implications. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1997. 18:622–627.2. Bures S, Fishbain JT, Uyehara CF, Parker JM, Berg BW. Computer keyboards and faucet handles as reservoirs of nosocomial pathogens in the intensive care unit. Am J Infect Control. 2000. 28:465–471.
Article3. Rampling A, Wiseman S, Davis L, Hyett AP, Walbridge AN, Payne GC, et al. Evidence that hospital hygiene is important in the control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 2001. 49:109–116.4. Oie S, Hosokawa I, Kamiya A. Contamination of room door handles by methicillin-sensitive/methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 2002. 51:140–143.5. Meyers PH. Contamination of patient-contact surfaces in radiology departments. JAMA. 1969. 209:772.
Article6. Haskin ME, McGinley JA. Hospital ecology and nosocomial infections. A systems analysis of fomites with infection potential and vectors of microbial cross contamination in hospital radiology departments. Radiol Clin North Am. 1972. 10:583–588.7. CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 15th Informational supplement. M100-S15 CLSI. 2005. Wayne: PA.8. Bannerman TL, Hancock GA, Tenover FC, Miller JM. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as a replacement for bacteriophage typing of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:551–555.9. Mulligan ME, Murray-Leisure KA, Ribner BS, Standiford HC, John JF, Korvick JA, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a consensus review of the microbiology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology with implications for prevention and management. Am J Med. 1993. 94:313–328.10. Hota B. Contamination, disinfection, and cross-colonization: are hospital surfaces reservoirs for nosocomial infection? Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:1182–1189.11. Dettenkofer M, Wenzler S, Amthor S, Antes G, Motschall E, Daschner FD. Does disinfection of environmental surfaces influence nosocomial infection rates? A systematic review. Am J Infect Control. 2004. 32:84–89.
Article12. Talon D. The role of the hospital environment in the epidemiology of multi-resistant bacteria. J Hosp Infect. 1999. 43:13–17.
Article13. Kim HJ, Lee NY, Kim S, Shin JH, Kim MN, Kim EC, et al. Characteristics of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures at nine university hospitals in Korea during 2009. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2011. 14:48–54.
Article14. Shittu A, Lin J, Morrison D, Kolawole D. Isolation and molecular characterization of multiresistant Staphylococcus sciuri and Staphylococcus haemolyticus associated with skin and soft-tissue infections. J Med Microbiol. 2004. 53:51–55.15. Nunes AP, Teixeira LM, Bastos CC, Silva MG, Ferreira RB, Fonseca LS, et al. Genomic characterization of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolated from Brazilian medical centres. J Hosp Infect. 2005. 59:19–26.16. Tabe Y, Nakamura A, Oguri T, Igari J. Molecular characterization of epidemic multiresistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolates. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. 32:177–183.17. Degener JE, Heck ME, van Leeuwen WJ, Heemskerk C, Crielaard A, Joosten P, et al. Nosocomial infection by Staphylococcus haemolyticus and typing methods for epidemiological study. J Clin Microbiol. 1994. 32:2260–2265.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- A statistical analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus
- Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus