Korean J Radiol.
2010 Dec;11(6):665-672. 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.6.665.
Clinical Application of Liver MR Imaging in Wilson's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, and the Institute of Radiation Medicine, SNUMRC, Seoul 110-744, Korea. kimio@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 1119230
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2010.11.6.665
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine whether there is a correlation between liver MR findings and the clinical manifestations and severity of liver dysfunction in patients with Wilson's disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two radiologists retrospectively evaluated MR images of the liver in 50 patients with Wilson's disease. The Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective study and informed consent was waived. MR images were evaluated with a focus on hepatic contour abnormalities and the presence of intrahepatic nodules. By using Fisher's exact test, MR findings were compared with clinical presentations (neurological and non-neurological) and hepatic dysfunction, which was categorized by the Child-Pugh classification system (A, B and C). Follow-up MR images were available for 17 patients.
RESULTS
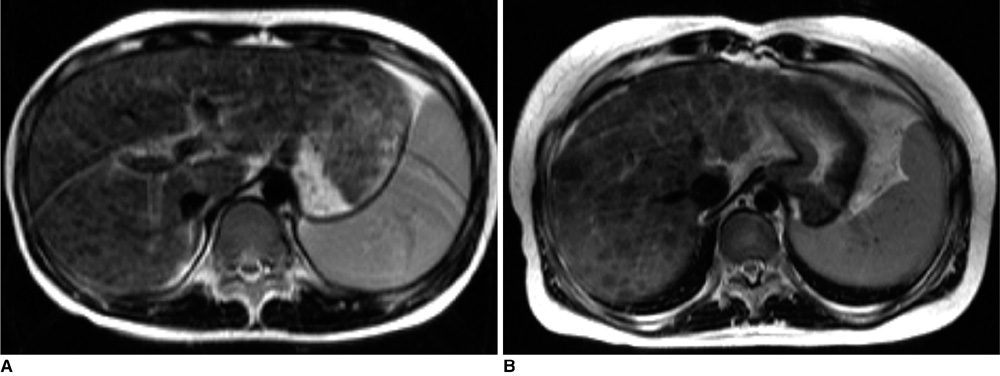
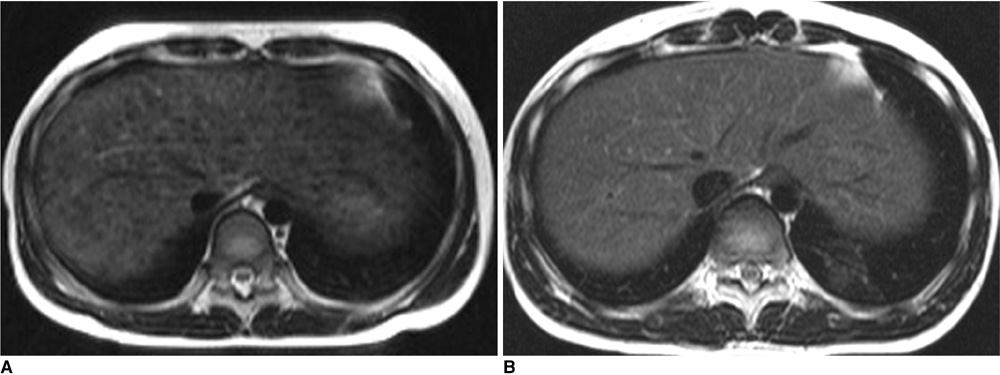
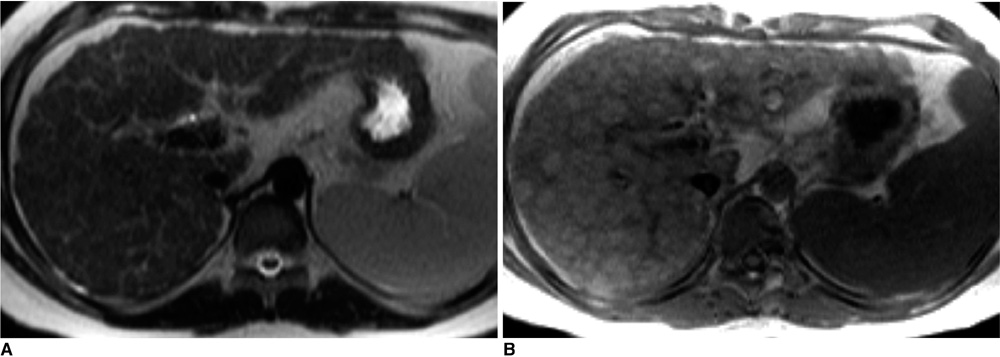
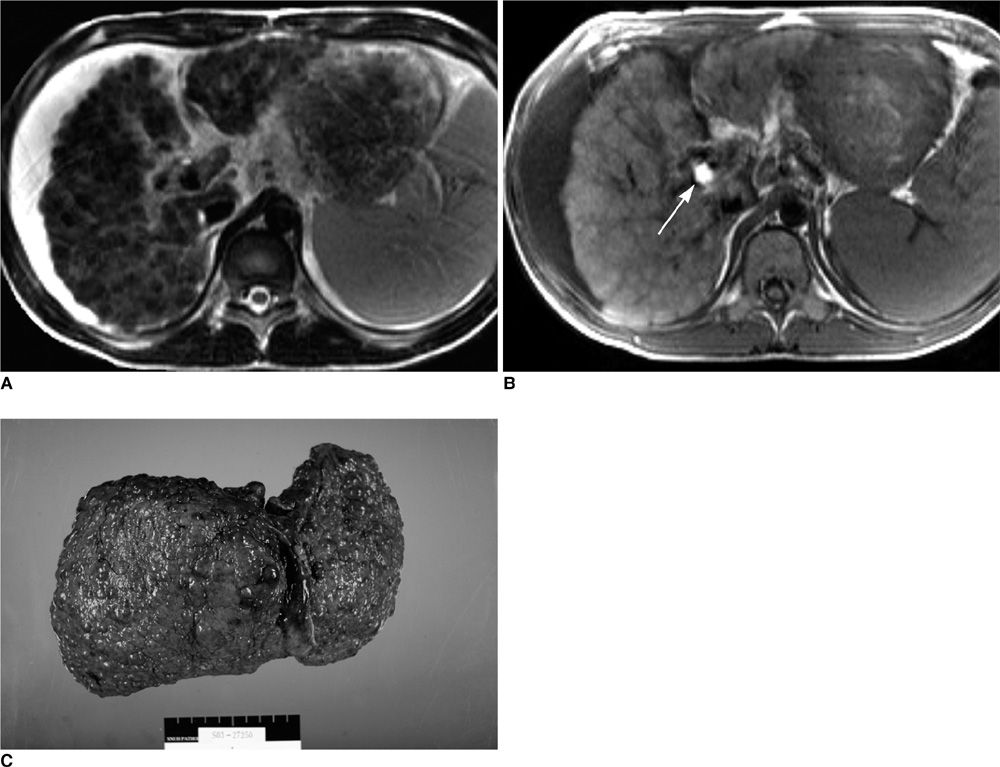
Contour abnormalities of the liver and intrahepatic nodules were observed in 31 patients (62%) and 25 patients (50%), respectively. Each MR finding showed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) among the three groups of Child-Pugh classifications (A, n = 36; B, n = 5; C, n = 9), except for splenomegaly (p = 0.243). The mean age of the patients with positive MR findings was higher than that of patients with negative MR findings. For patients with Child-Pugh class A (n = 36) with neurological presentation, intrahepatic nodules, surface nodularity, and gallbladder fossa widening were more common. Intrahepatic nodules were improved (n = 8, 47%), stationary (n = 5, 29%), or aggravated (n = 4, 24%) on follow-up MR images.
CONCLUSION
MR imaging demonstrates the contour abnormalities and parenchymal nodules of the liver in more than half of the patients with Wilson's disease, which correlates with the severity of hepatic dysfunction and clinical manifestations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Diagnosis of Wilson Disease in Young Children: Molecular Genetic Testing and a Paradigm Shift from the Laboratory Diagnosis
Jeong Kee Seo
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012;15(4):197-209. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.197.Experimental Evaluation of Accelerated T1rho Relaxation Quantification in Human Liver Using Limited Spin-Lock Times
Feng Zhao, Min Deng, Jing Yuan, Gao-Jun Teng, Anil T Ahuja, Yi-Xiang J. Wang
Korean J Radiol. 2012;13(6):736-742. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.736.
Reference
-
1. Gitlin JD. Wilson disease. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:1868–1877.2. Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, Forbes JR, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:327–337.3. Tanzi RE, Petrukhin K, Chernov I, Pellequer JL, Wasco W, Ross B, et al. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:344–350.4. Seo JK. Wilson disease: an update. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:333–363. [Korean].5. Ala A, Schilsky ML. Wilson disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and screening. Clin Liver Dis. 2004. 8:787–805.6. Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli-Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003. 23:139–142.7. Panagiotakaki E, Tzetis M, Manolaki N, Loudianos G, Papatheodorou A, Manesis E, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations for a wide spectrum of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B). Am J Med Genet A. 2004. 131:168–173.8. Cançado EL, Rocha Mde S, Barbosa ER, Scaff M, Cerri GG, Magalhães A, et al. Abdominal ultrasonography in hepatolenticular degeneration. A study of 33 patients. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 1987. 45:131–113.9. Ko S, Lee T, Ng S, Lin J, Cheng Y. Unusual liver MR findings of Wilson's disease in an asymptomatic 2-year-old girl. Abdom Imaging. 1998. 23:56–59.10. Akhan O, Akpinar E, Oto A, Köroglu M, Ozmen MN, Akata D, et al. Unusual imaging findings in Wilson's disease. Eur Radiol. 2002. 12:S66–S69.11. Chu WC, Leung TF, Chan KF, Yeung DK, Yeung TK, Cheung HM, et al. Wilson's disease with chronic active hepatitis: monitoring by in vivo 31-phosphorus MR spectroscopy before and after medical treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1339–1342.12. Kozic D, Svetel M, Petrovic I, Sener RN, Kostic VS. Regression of nodular liver lesions in Wilson's disease. Acta Radiol. 2006. 47:624–627.13. Akpinar E, Akhan O. Liver imaging findings of Wilson's disease. Eur J Radiol. 2007. 61:25–32.14. Akhan O, Akpinar E, Karcaaltincaba M, Haliloglu M, Akata D, Karaosmanoglu AD, et al. Imaging findings of liver involvement of Wilson's disease. Eur J Radiol. 2009. 69:147–155.15. Child CG, Turcotte JG. Child CG, editor. Surgery and portal hypertension. The liver and portal hypertension. 1964. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders;50–52.16. Awaya H, Mitchell DG, Kamishima T, Holland G, Ito K, Matsumoto T. Cirrhosis: modified caudate-right lobe ratio. Radiology. 2002. 224:769–774.17. Mergo PJ, Ros PR, Buetow PC, Buck JL. Diffuse disease of the liver: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1994. 14:1291–1307.18. Davies SE, Williams R, Portmann B. Hepatic morphology and histochemistry of Wilson's disease presenting as fulminant hepatic failure: a study of 11 cases. Histopathology. 1989. 15:385–394.19. Cope-Yokoyama S, Finegold MJ, Sturniolo GC, Kim K, Mescoli C, Rugge M, et al. Wilson disease: histopathological correlations with treatment on follow-up liver biopsies. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. 16:1487–1494.20. Merle U, Schaefer M, Ferenci P, Stremmel W. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and long-term outcome of Wilson's disease: a cohort study. Gut. 2007. 56:115–120.21. Ito K, Mitchell DG, Gabata T, Hussain SM. Expanded gallbladder fossa: simple MR imaging sign of cirrhosis. Radiology. 1999. 211:723–726.22. Kim TJ, Kim IO, Kim WS, Cheon JE, Moon SG, Kwon JW, et al. MR imaging of the brain in Wilson disease of childhood: findings before and after treatment with clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:1373–1378.23. Taly AB, Meenakshi-Sundaram S, Sinha S, Swamy HS, Arunodaya GR. Wilson disease: description of 282 patients evaluated over 3 decades. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007. 86:112–121.