Yonsei Med J.
2009 Oct;50(5):644-649. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.644.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Subtypes Prevalence in Central China
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China. zhaofeicute@yahoo.com.cn
- 2WANG Zhe Henan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Zhengzhou, China.
- KMID: 1103817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.644
Abstract
- PURPOSE
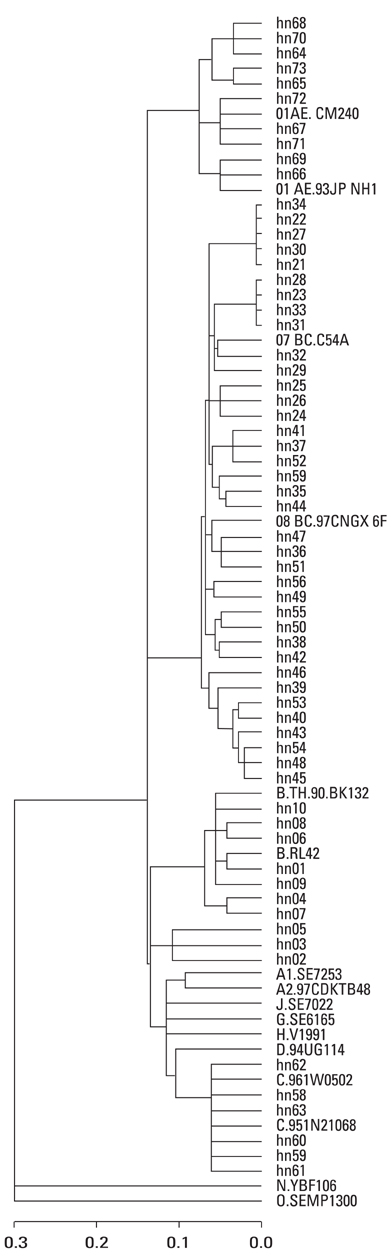
To study the epidemic characteristics, transmission sources and routes of various subtypes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and sequence variations in Henan, central China. To provide theoretical foundation for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) prevention strategy in this region where the primary HIV transmission route was through former paid blood donation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: HIV-1 gene env and gag were amplified by nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from uncultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from 1,287 HIV-1 confirmed samples in Henan. RESULTS: Among 1,287 samples, 5 HIV-1 strains were found including subtypes B' (95.9%), C (0.47%) and recombinant subtypes CRF 07_BC (1.09%), CRF 08_BC (1.79%) and CRF 01_AE (0.78%). Phylogenetic tree analysis found that 1,234 Henan subtype B' were closely related to those commonly found in Thailand, and were distantly related to other international subtypes. The dominant strain in former blood plasma donors (FPDs) was subtype B', and the dominant strains in sexual transmission were subtype B' and BC. Among HIV patients who were most likely infected through routes other than paid blood donation, the percentage of non-B' subtypes was much higher than those of FPD. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that the prevailing strain of HIV-1 in Henan is subtype B', similar to the B' subtype found in Thailand. In addition, for the first time we found subtypes C and recombinant subtypes CRF07_BC, CRF08_BC and CRF01_AE in this region. Indicating that the subtype feature of HIV-1 became more complicated than before in central China.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lorenzo E, Herrera RJ, Lai S, Fischl MA, Hill MD. The Tat and C2-V3 envelope Genes in the molecular epidemiology of human immunode-ficiency virus-1. Virology. 1996. 221:310–317.2. Hu D, Dondero TJ, Mastro TD, Gayle HD. Wonnser GP, editor. Global and molecular epidemiology of HIV. AIDS and other manifestations of HIV infection. 1998. Philadelphia: Lipponcott-Raven Publishers;27–40.3. Chen JianPing, Shao YiMing. The Nomenclature and Taxonomy of HIV. Foreign Medical Sciences (Section of Virology). 2001. 8:161–163.4. Leitner T. Myers G, Korber B, Foley B, Jeang KT, Mellors JW, Wain-Hobson S, editors. Genetic subtypes of HIV-1. Human retrovirus and AIDS: a compilation of nucleic acids and amino acid sequences. 1996. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory;III28.5. Kalish ML, Baldwin A, Raktham S, Wasi C, Luo CC, Schochetman G, et al. The evolving molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 envelope subtypes in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand: implications for HIV vaccine trials. AIDS. 1995. 9:851–857.6. Wu H, Wang B, Fang R, Lu YB, Qian DM, Zeng Y. Variation trend of the tetrapeptide on the tip of V3 loop of 62 HIV-1 strains isolated in IDU of Yunnan from 1990 to 1997. Chin J Microbiol Immunol (Chin). 2000. 20:462–464.7. Cui WG, Xing H, Wang Z, Huang HL, Li H, Ma PF, et al. Study on subtype and sequence of the C2-V3 region of env gene among HIV-1 strains in m v-lin Henan province. China J AIDS/STD (Chin). 2004. 10:403–406.8. Han WG, Su L, Wan Z, Shao YM, Wang CJ, Li H. Genomic subtypes of m V-lin Henan province. Chin J Infect Dis (Chin). 1999. 17:253–255.9. Graf M, Shao Y, Zhao Q, Seidl T, Köstler J, Wolf H, et al. Cloning and characterization of a virtually full-length HIV type 1 genome from a subtype B'-Thai strain representing the most prevalent B-clade isolate in China. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998. 14:285–288.
Article10. Kaufman J, Jing J. China and AIDS--the time to act is now. Science. 2002. 296:2339–2340.
Article11. Simon F, Mauclère P, Roques P, Loussert-Ajaka I, Müller-Trutwin MC, Saragosti S, et al. Identification of a new human immunodeficiency virus type 1 distinct from group M and group O. Nat Med. 1998. 4:1032–1037.
Article12. Chesebro B, Wehrly K, Nishio J, Perryman S. Mapping of independent V3 envelope determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 macrophage tropism and syncytium formation in lymphocytes. J Virol. 1996. 70:9055–9059.
Article13. Hwang SS, Boyle TJ, Lyerly HK, Cullen BR. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991. 253:71–74.
Article14. Robbins KE, Lemey P, Pybus OG, Jaffe HW, Youngpairoj AS, Brown TM, et al. U.S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epidemic: date of origin, population history, and characterization of early strains. J Virol. 2003. 77:6359–6366.15. XING Hui, LIANG Hao, HONG Kun xue, et al. The potential relationship between variation in the env V3-V4 region of HIV-1 predominant strains in China and virus biological feature. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology. 2005. 25:185–189.16. Han XX, Shang H, Zhou LP, Wang YN, Zhang ZN, Jiang YJ. Mutation of envelop protein V3 loop in HIV-1 epidemic in Liaoning province. Chin J Epidemiol (Chin). 2003. 24:704–707.17. Zhao QB, Pan PL, Wen N, Xing H, Chen Z, Wei M, et al. Study on sequence variation in the V3 loop of HIV-1 strains prevalent in China. Chin J STD/AIDS Prev Control (Chin). 2002. 8:208–211.18. UN epidemiological fact sheets on HIV/AIDS and sexually transmitted infections. 2002. Geneva: UNAIDS;1–92.19. Su B, Liu L, Wang F, Gui X, Zhao M, Tien P, et al. HIV-1 subtype B' dictates the AIDS epidemic among paid blood donors in the Henan and Hubei provinces of China. AIDS. 2003. 17:2515–2520.
Article20. Zhang L, Chen Z, Cao Y, Yu J, Li G, Yu W, et al. Molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and hepatitis C virus in paid blood donors and injection drug users in China. J Virol. 2004. 78:13591–13599.
Article21. Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of HIV/AIDS in China (2005). Chin Med J (Engl). 2006. 119:1589–1608.22. Feng TJ, Zhao GL, Chen L, Wang XH, Shi XD. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains epidemic in Shenzhen. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2006. 28:637–641. Chinese.23. Zhang L, Chen Z, Cao Y, Yu J, Li G, Yu W, et al. Molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and hepatitis C virus in paid blood donors and injection drug users in China. J Virol. 2004. 78:13591–13599.
Article24. XING Hui, WANG Zhe, et al. Study on subtype and sequence of the C2-V3 region of env gene among HIV-1 strains in Henan province. China J AIDS/STD. 2004. 12. 10(6):
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Molecular Epidemiology of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Tat-Mediated Cellular Response in Myeloid Cells
- Prevalence of Peripheral Vestibular Impairment in Adults with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Ocular Findings in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome