Korean J Ophthalmol.
2006 Dec;20(4):254-255. 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.4.254.
Full Tendon Transposition Augmented with Posterior Intermuscular Suture and Recession-Resection Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shhan222@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 754594
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2006.20.4.254
Abstract
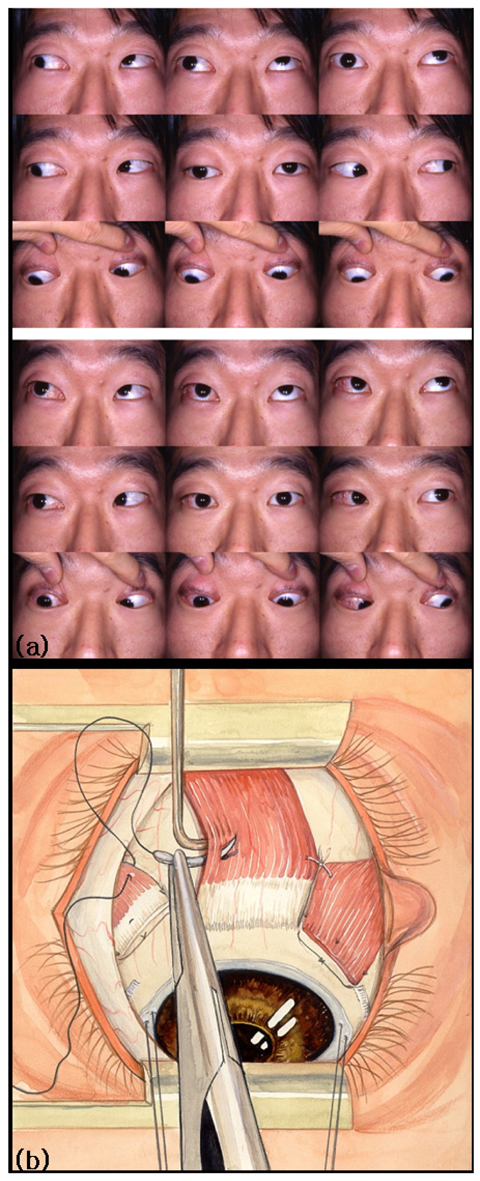
- PURPOSE: To report an effect of the full tendon transposition augmented with posterior intermuscular suture and recession-resection surgery, for the patient with monocular elevation deficiency (MED) and large exotropia. METHODS: Interventional case report. Full tendon transposition augmented with posterior intermuscular suture and recession-resection surgery was performed for a 26-year-old male patient had monocular elevation deficiency (MED) and large exotropia. RESULTS: Preoperative angle of deviation was 56 prism diopters (PD) hypotropia and 45 PD right exotropia, compared with 18 PD left hypertropia and 10 PD right esotropia postoperatively. Essotropia persisted after 2.5 years, however, and so the right medial rectus was recessed after removal of the previous posterior intermuscular suture. At a three-year follow-up after the second surgery, alignment was straight in the primary position at near and far distances. CONCLUSIONS: Full tendon transposition augmented with posterior intermuscular suture and recession-resection surgery was effective for a patient with MED associated with significant horizontal deviation, and a second operation was easily performed when overcorrection occurred.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Knapp P. The surgical treatment of double-elevator paralysis. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1969. 67:304–323.2. Foster RS. Vertical muscle transposition augmented with lateral fixation. J AAPOS. 1997. 1:20–30.3. Buckley EG, Townshend LM. A simple transposition procedure for complicated strabismus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991. 111:302–306.4. Hong S, Chang YH, Han SH, Lee JB. Effect of full tendon transposition augmented with posterior intermuscular suture for paralytic strabismus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 140:477–483.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recession-Resection Surgery Augmented with Botulinum Toxin A Chemodenervation for Paralytic Horizontal Strabismus
- Unilateral Recession-Resection Surgery with Inferior Displacement Combined with Augmented Anterior Transposition of Inferior Oblique Muscle
- Surgical Results of Duanes Retraction Syndrome
- The Result of Full Tendon Transposition in Paralyzed Strabismus
- Vertical Rectus Muscles Transposition in Large Exotropia with Medial Rectus Muscle Transection Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery