Korean J Ophthalmol.
2008 Jun;22(2):104-110. 10.3341/kjo.2008.22.2.104.
Vertical Rectus Muscles Transposition in Large Exotropia with Medial Rectus Muscle Transection Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Wonju Christian Hospital Yonsei University, Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Ophthalmology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang-city, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. liy690725@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1099004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2008.22.2.104
Abstract
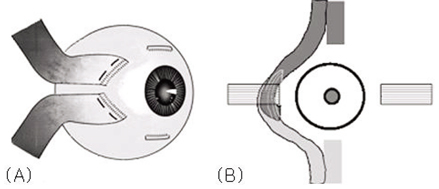
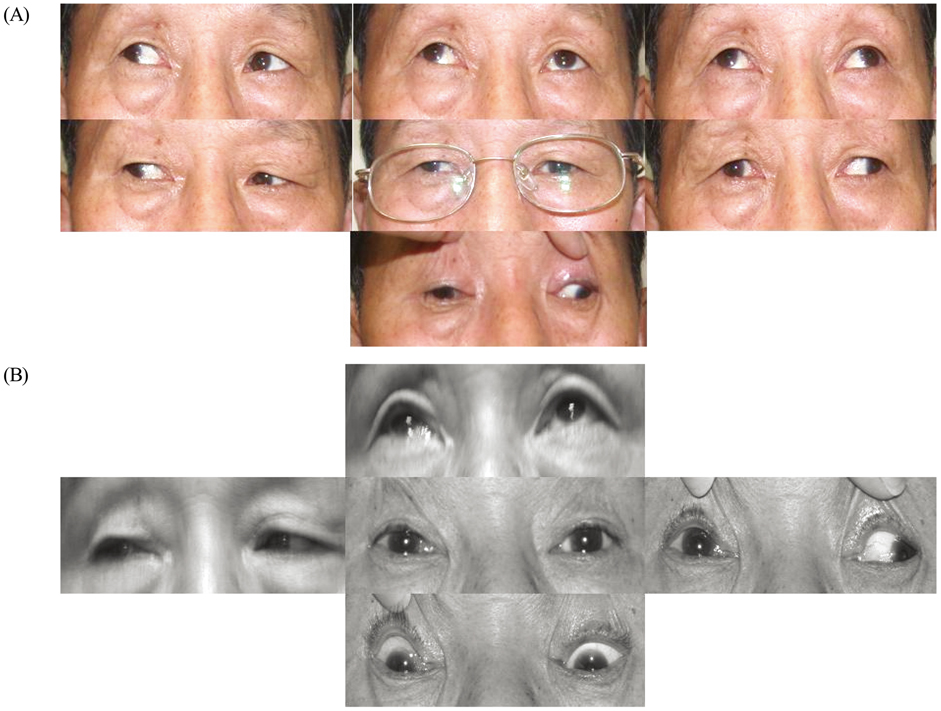
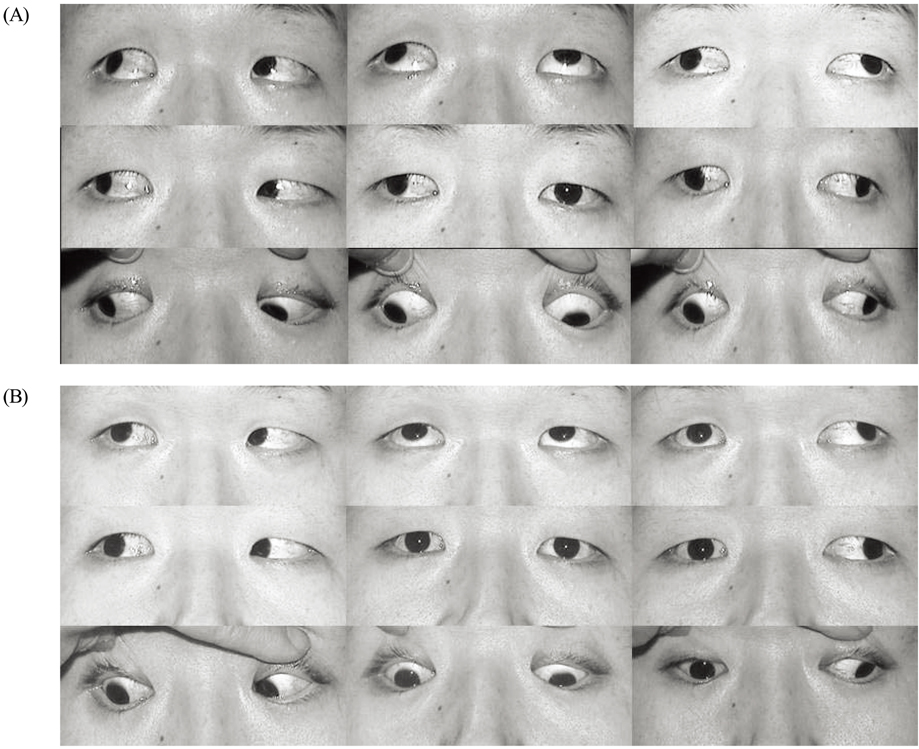
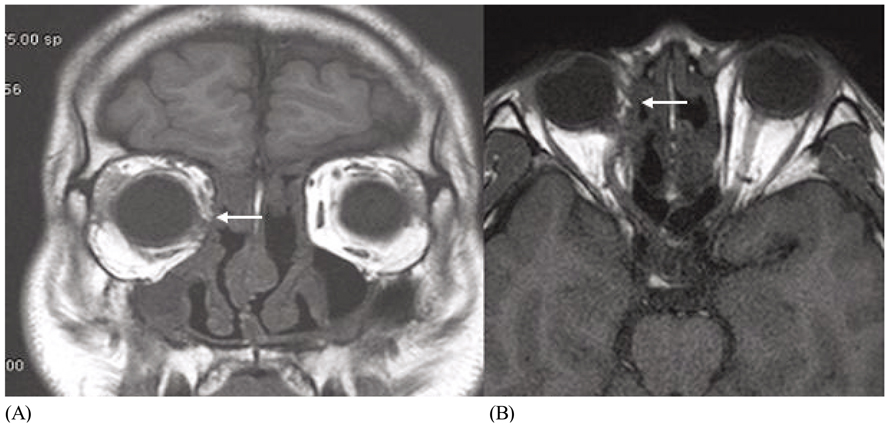
- PURPOSE: To evaluate the effect of transposition procedures on the vertical rectus muscle (VRM) in the patients who underwent a medial rectus muscle (MR) transection after endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS). METHODS: In 4 patients with exotropia (XT) and a lack of adduction after ESS, orbital CT or MRI revealed a complete transection of the midportion of the MR. Full-tendon VRM transposition was performed within 3 months after injury (early surgery) in 2 patients with 40delta XT. Two patients with 70delta and 85delta XT underwent an X-type augmented Hummelsheim procedure, which involved pulling each half-tendon and crossing it through the undersurface of the severed MR to the other end of the MR insertion, concurrently with an ipsilateral lateral rectus (LR) recession 11 months and 36 months after ESS, respectively. The adduction deficits were divided into -1 through to -8. The patients were followed up for more than than 1.5 years. RESULTS: Postoperatively, 3 patients showed orthophoria and no diplopia in the primary position. The adduction deficits improved to -3.5 or -4. One patient who underwent an X-type augmented Hummelsheim procedure showed a residual XT of 25delta. CONCLUSIONS: VRM transposition is effective in correcting a large XT secondary to a MR transection after ESS. When a longstanding large-angle XT with severe contracture of the ipsilateral LR and massive scarring of the adjacent tissues is present, the X-type augmented Hummelsheim procedure coupled with an ipsilateral LR recession had an augmenting effect.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Endoscopy/*adverse effects
Exotropia/diagnosis/etiology/*surgery
Eye Movements
Female
Humans
*Iatrogenic Disease
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Oculomotor Muscles/injuries/pathology/*surgery
Paranasal Sinus Diseases/*surgery
Tendon Transfer/*methods
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Vision, Binocular
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Fixation of the Eyeball to the Periosteum Over the Posterior Lacrimal Crest in Inveterate Exotropia
Bo Ram Seol, Sang In Khwarg, Seong-Joon Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(3):408-415. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.3.408.
Reference
-
1. Freedman H, Kern E. Complications of intranasal ethmoidectomy.: a review of 1,000 consecutive operations. Laryngoscope. 1979. 89:421–434.2. Dutton JJ. Orbital complications of paranasal sinus surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986. 2:119–127.3. Sonn UK, Kim JK, Kim SD. Case report of blindness after intranasal ethmoidectomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995. 36:147–152.4. Kwon IT, Kim JH, Shin HH. Ophthalmic Complications after paranasal sinus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993. 34:672–677.5. Schaefer SD, Manning S, Close LG. Endoscopic paranasal sinus surgery: Indications and consideration. Laryngoscope. 1989. 99:1–5.6. Kim H, Cho JS, Lee KH, et al. Analysis of the intraoperative complications of endoscopic sinus surgery. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2002. 45:777–780.7. Bhatti MT, Giannoni CM, Raynor E, et al. Ocular motility complications after endoscopic sinus surgery with powered instrumentation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001. 125:501–509.8. Buus DR, Tse DT, Farris BK. Ophthalmic complication of sinus surgery. Ophthalmology. 1990. 97:612–619.9. Stankiewicz JA. Complications in endoscopic intranasal ethmoidectomy: an update. Laryngoscope. 1989. 99:686–690.10. Neuhaus RW. Orbital complications secondary to endoscopic sinus surgery. Ophthalmology. 1990. 97:1512–1518.11. Kim HC, Kim JH, Lee SY. A case of medial rectus muscle injury and optic nerve transaction developed during functional endoscopic sinus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:2705–2710.12. Thacker NM, Velez FG, Demer JL, Rosenbaum AL. Strabismic complications following endoscopic sinus surgery: diagnosis and surgical management. J AAPOS. 2004. 8:488–494.13. Mark LE, Kennerdell JS. Medial rectus injury from intranasal surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979. 97:459–461.14. Flynn JT, Mitchell KB, Fuller DG, et al. Ocular motility complications following intranasal surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979. 97:453–458.15. Huang CM, Meyer DR, Patrinely JR, et al. Medial rectus muscle injuries associated with functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 19:25–37.16. Lee MH, Kim SD, Hur YJ. A case of medial rectus muscle injury after functional endoscopic sinus polypectomy and ethmoidectomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002. 43:934–939.17. Rene C, Sose GE, Lenthall R, Moseley I. Major orbital complications of endoscopic sinus surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001. 85:598–603.18. Foster RS. Vertical muscle transpositions augmented with lateral fixation. J AAPOS. 1997. 1:20–30.19. Kaufmann VH. chap. 5. Strabismus. 2004. 3rd ed. New York: Thieme;546–547.20. Eitzen JP, Elsas JP. Strabismus following endoscopic intranasal sinus surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991. 28:168–170.21. McNeer KW, Magoon EH, Scott AB. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP, editors. Chemodenervation therapy:Technique and indications. Clinical Strabismus management. 1999. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;chap. 32.22. Olitsky SE, Brooks S. Treatment of subtotal medial rectus myectomy complicating functional endoscopic sinus surgery. J AAPOS. 2001. 5:64.23. Penne RB, Flanagan JC, Stefanyszyn MA, Nowinski T. Ocular motility disorders secondary to sinus surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993. 9:53–61.24. Scott MG, Jeffrey AN. Orbital complications in endoscopic sinus surgery using powered instrumentation. Laryngoscope. 2003. 113:874–878.25. Trotter WL, Kaw P, Meyer DR, Simon JW. Treatment of subtotal medial rectus myectomy complicating functional endoscopic sinus surgery. J AAPOS. 2000. 4:250–253.26. France TD, Simon JW. Anterior segment ischemia syndrome following muscle surgery: the AAPO & S experience. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986. 23:87–91.27. Elsas FJ, Witherspoon CD. Anterior segment ischemia after strabismus surgery in a child. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987. 103:833–834.28. Cho YA, Won JS. Two cases of anterior segment ischemia after strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995. 36:97–102.29. Brooks SE, Olitsky SE, Ribeiro G. Augmented Hűmmelsheim procedure for paralytic strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2000. 37:189–195.30. McKweown CA. Techniques for preserving the anterior ciliary vessels in strabismus surgery. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 1992. 5:143.31. Vleming M, Middleweerd RJ, Vries N. Complication of endoscopic sinus surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992. 118:617–623.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sequential Correction for Large Exotropia: A Case of Iatrogenic Exotropia Developed after Excision of Medial Rectus Muscle During Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
- Medial transposition of the lateral rectus muscle in experimentally induced medial rectus paralysis
- Surgical Correction of Exotropia due to Oculomotor Nerve Palsy
- Medial Transposition of the Lateral Rectus Muscle in the Experimentally Induced Medial Rectus Paralysis
- Effect of Vertical Displacement of Bilateral Horizontal Muscles in AV Syndrome