J Rhinol.
2024 Nov;31(3):179-183. 10.18787/jr.2024.00025.
A Rare Presentation of IgG4-Related Sinusitis With Chronic Nasal Obstruction and Headache: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2561502
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2024.00025
Abstract
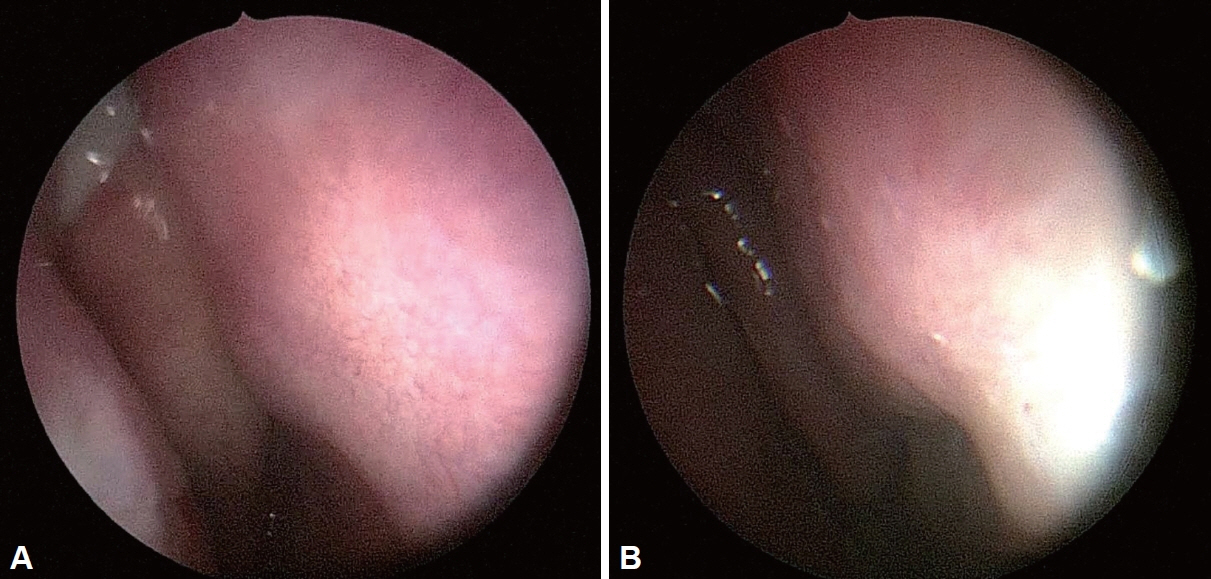
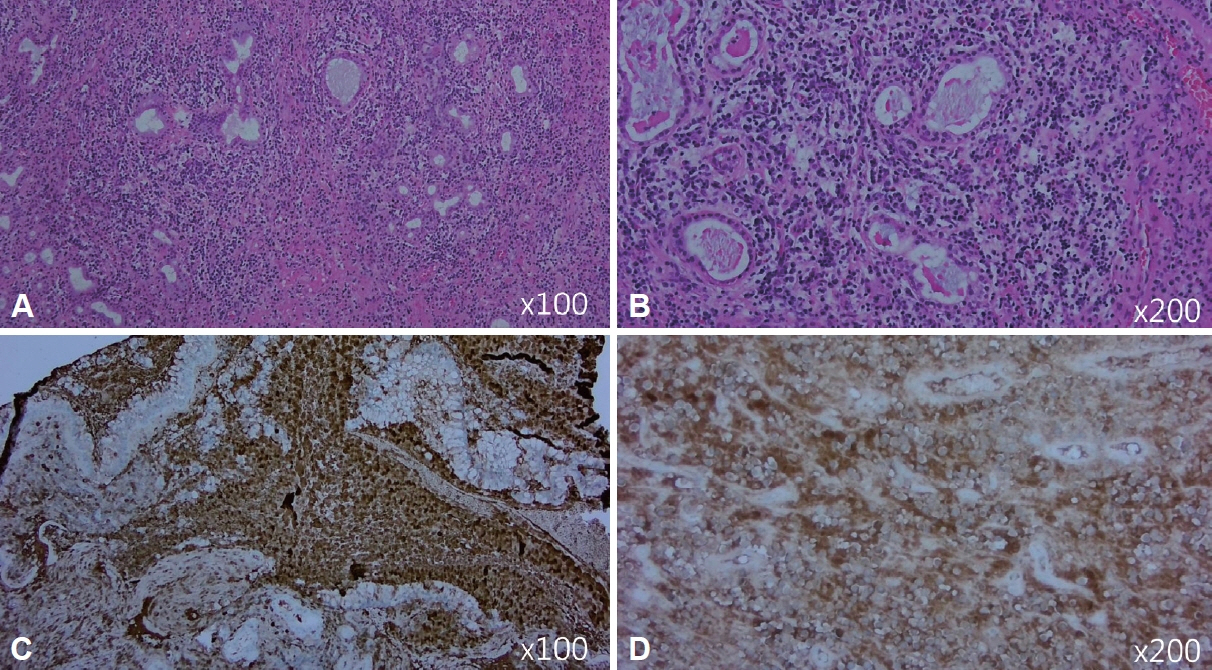
- IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic inflammatory condition characterized by tissue infiltration with IgG4-positive plasma cells and a tendency to form mass-like lesions in various organs. IgG4-related sinusitis, although a relatively rare manifestation of IgG4- RD, significantly impacts the paranasal sinuses. A 52-year-old man presented with persistent rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction, and headaches. He was diagnosed with IgG4-RD involving the bilateral nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, submandibular glands, lacrimal glands, and parotid glands. We recently managed a case of IgG4-related sinusitis, which was successfully diagnosed and treated. This condition represents a distinct subset of chronic rhinosinusitis, with unique pathophysiological and clinical features. Accurate diagnosis and effective management of IgG4-related sinusitis require a high index of suspicion and a multidisciplinary approach.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366(6):539–51.
Article2. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22(1):1–14.
Article3. Moteki H, Yasuo M, Hamano H, Uehara T, Usami S. IgG4-related chronic rhinosinusitis: a new clinical entity of nasal disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011; 131(5):518–26.
Article4. Della-Torre E, Lanzillotta M, Doglioni C. Immunology of IgG4-related disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015; 181(2):191–206.
Article5. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38(10):982–4.
Article6. Wallace ZS, Stone JH. An update on IgG4-related disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015; 27(1):83–90.
Article7. Kawa S, Hamano H, Ozaki Y, Ito T, Kodama R, Chou Y, et al. Long-term follow-up of autoimmune pancreatitis: characteristics of chronic disease and recurrence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7(11 Suppl):S18–22.
Article8. Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, Witzig TE, Wallace ZS, Hart PA, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74(6):1171–7.
Article9. Lee JR, Lee BJ, Chung YS. Three cases of IgG4-related sclerosing disease in nasal cavity. J Rhinol. 2016; 23(1):44–8.
Article10. Chung J, Lee JH. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease of the paranasal sinus mimicking nasal malignancy. J Rhinol. 2017; 24(1):60–4.
Article11. Ko SH, Yoon HJ, Zheng T, Jeong JH. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease not responded to steroid in nasal cavity. J Rhinol. 2017; 24(2):138–42.
Article12. Mun SJ, Shin NR, Koh JH, Roh HJ. A case of IgG4 related disease in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinus: a rare cause of nasal bleeding. J Clin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019; 30(1):116–21.
Article13. Han YS, Cha JS, Jung MJ, Kim JY. A case of IgG4-related disease with sino-nasal involvement. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2022; 65(11):705–712.
Article14. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25(9):1181–92.
Article15. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22(1):21–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Nasal Cavity
- A Case of Nasal Swell Body (Septal Turbinate) Combined with Pneumatization of Perpendicular Plate of the Ethmoid Bone
- A Case of Acute Aggravation of Fungal Maxillary Sinusitis after Zygomaplasty
- A Case of Olfactory Neuroblastoma in Sphenoid Sinus
- Coexisting Upper Airway Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Literature