J Rhinol.
2016 May;23(1):44-48. 10.18787/jr.2016.23.1.44.
Three Cases of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Nasal Cavity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otoloaryngology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yschung@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2165154
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2016.23.1.44
Abstract
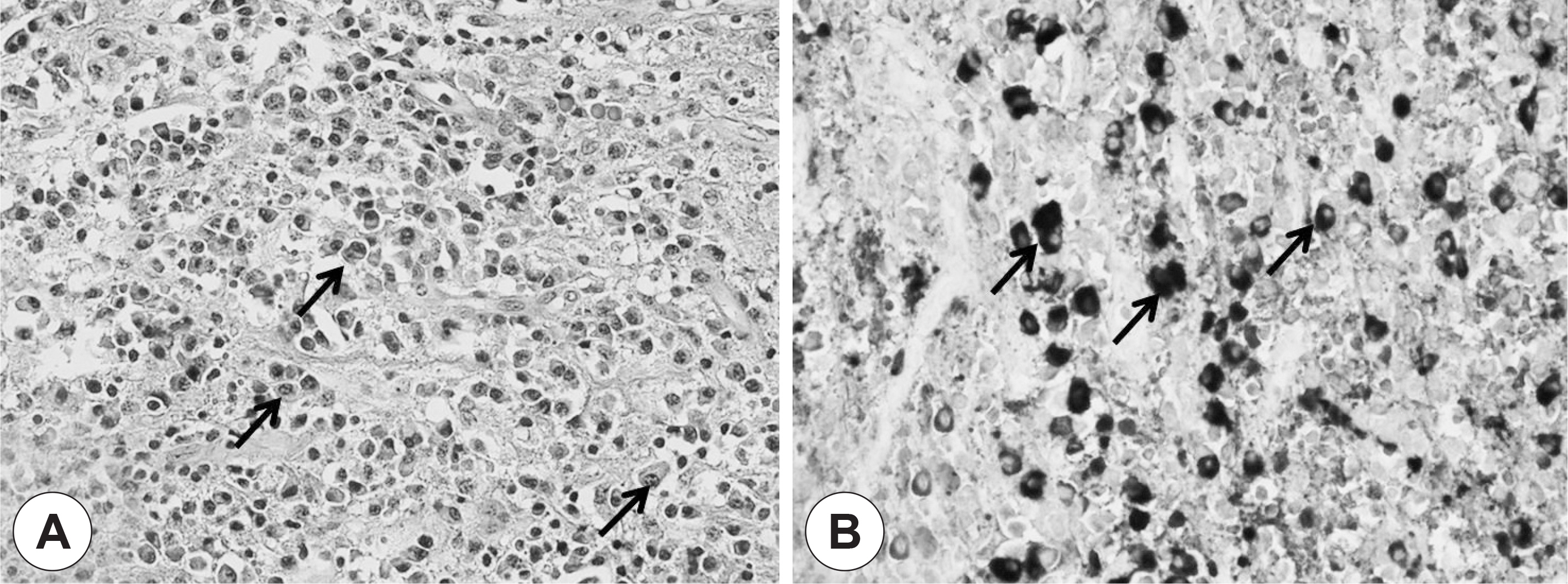
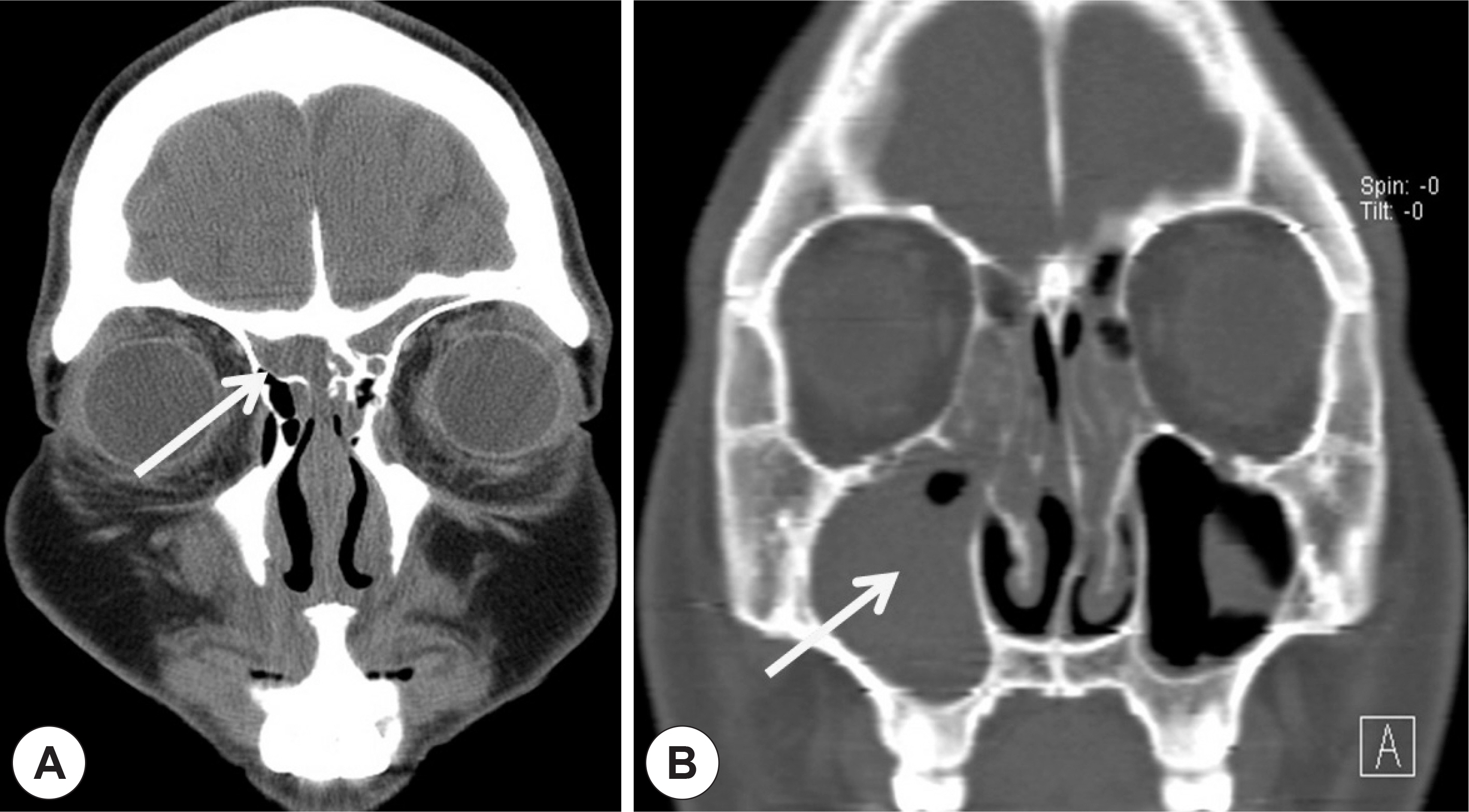
- IgG4-related sclerosing disease (IgG4-RSD) is characterized by extensive IgG4-positive plasma cell and T-lymphocyte infiltration of various organs. However, the nasal cavity is an extremely rare site of involvement. The authors experienced three cases of igG4-RSD in the nasal cavity. A 54-year-old woman presented with a nasal cavity mass on endoscopic exam and computed tomography (CT) revealed not only a hypoenhancing mass in the right nasal cavity but also a pituitary gland macroadenoma. Endoscopic removal and endoscopic TSA were performed. A 20-year-old man diagnosed with chronic sinusitis, underwent endoscopic sinus surgery. A 26-year-old woman showed thickening of the nasal septum and cribriform plate, and an infiltrating soft tissue lesion in right the alveolar process on CT and an endoscopic biopsy was performed. Pathologic specimens of all cases showed IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration, consistent with IgG4-RSD. Serum IgG4 levels were checked in two of the cases, and the results were within normal range. All cases were further treated with methylprednisolone and all showed clinical improvement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease of the Paranasal Sinus Mimicking Nasal Malignancy
Juyong Chung, Jae Hoon Lee
J Rhinol. 2017;24(1):60-64. doi: 10.18787/jr.2017.24.1.60.A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease not Responded to Steroid in Nasal Cavity
Seok Hwa Ko, Hyung Joon Yoon, Tao Zheng, Jin Hyeok Jeong
J Rhinol. 2017;24(2):138-142. doi: 10.18787/jr.2017.24.2.138.A Case of IgG4-Related Disease With Sino-Nasal Involvement
Young Seok Han, Jun Sang Cha, Min Jung Jung, Joo Yeon Kim
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2022;65(11):705-712. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2021.00598.
Reference
-
References
1). Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–51.
Article2). Kim KC, Park JH, Ban GY, Yoo HS, Shin YS, Park HS, et al. Kartagener's syndrome with immunoglobulin G subclass deficiency. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:288–91.
Article3). Suzuki M, Nakamaru Y, Akazawa S, Mizumachi T, Maeda M, Takagi D, et al. Nasal manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:829–34.
Article4). Himi T, Takano K, Yamamoto M, Naishiro Y, Takahashi H. A novel concept of Mikulicz's disease as IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012; 39:9–17.
Article5). Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–4.
Article6). Leporati P, Landek-Salgado MA, Lupi I, Chiovato L, Caturegli P. IgG4-related hypophysitis: A new addition to the hypophysitis spectrum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:1971–80.
Article7). Okazaki K, Uchida K, Koyabu M, Miyoshi H, Takaoka M. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:277–88.
Article8). Sah RP, Chari ST. Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:108–13.
Article9). Fujita A, Sakai O, Chapman MN, Sugimoto H. IgG4-related disease of the head and neck: CT and MR imaging manifestations. Radiographics. 2012; 32:1945–58.
Article10). Allen SD, Harvey CJ. Imaging of Wegener's granulomatosis. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:757–65.
Article11). Muhle C, Reinhold-Keller E, Richter C, Duncker G, Beigel A, Brinkmann G, et al. MRI of the nasal cavity, the paranasal sinuses and or-bits in Wegener's granulomatosis. Eur Radiol. 1997; 7:566–70.
Article12). Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Levy MJ, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: Clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:706–15.
Article13). Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, Shimosegawa T, Tanaka M. Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis III: Treatment and prognosis of AIP. J Gastroenterol. 2010; 45:471–7.
Article14). Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:1755–62.
Article15). Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, Stone JH. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons from 10 consecutive Patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012; 91:57–66.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease not Responded to Steroid in Nasal Cavity
- Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis
- Advances in IgG4-related Hepatobiliary Disease
- Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Mimicking Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- Poor positive predictive value of serum immunoglobulin G4 concentrations in the diagnosis of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease