J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2024 Apr;41(2):61-73. 10.12701/jyms.2023.01347.
Comprehensive overview of the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury: a narrative review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Aging and Metabolism, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2554766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01347
Abstract
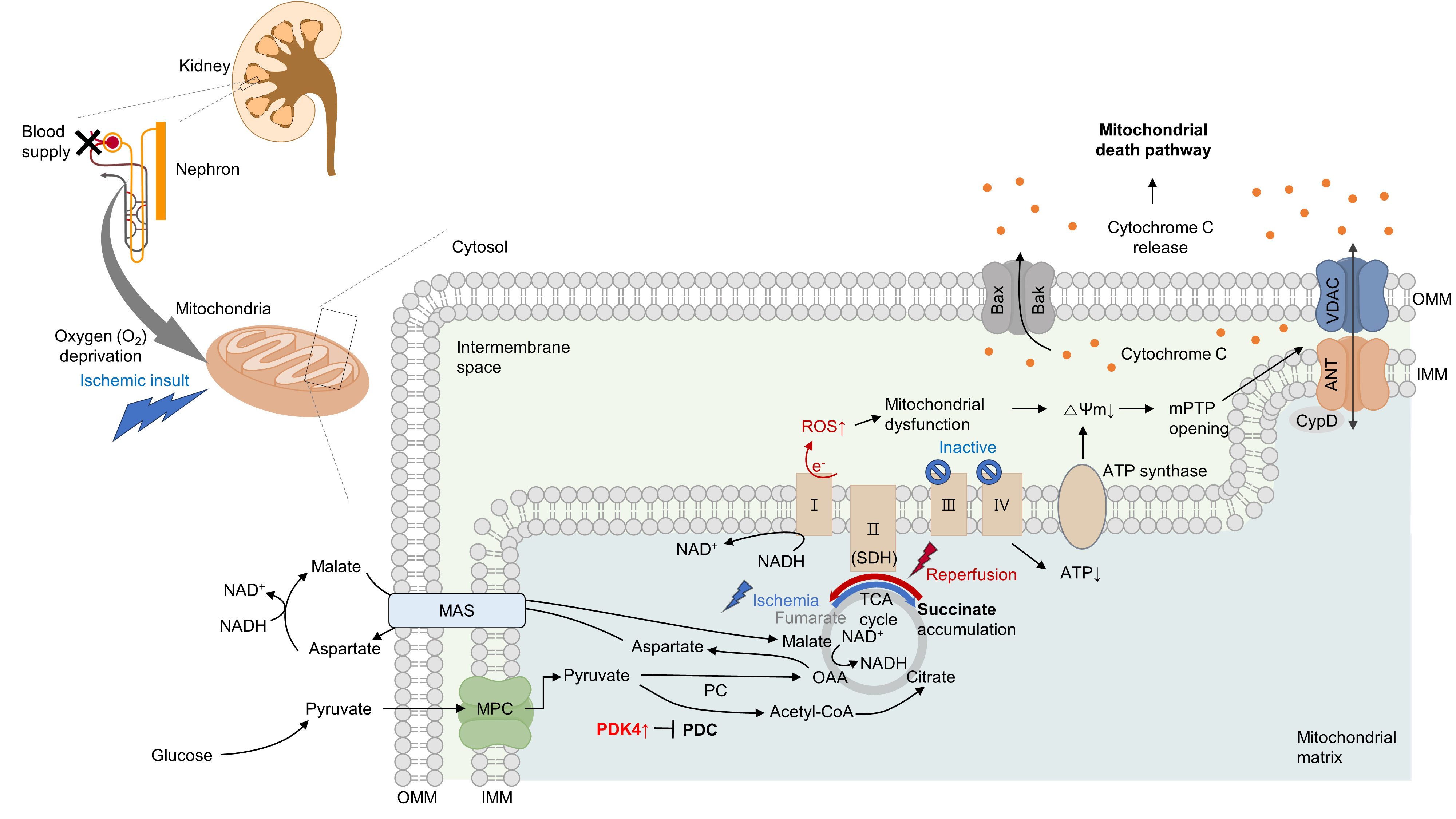
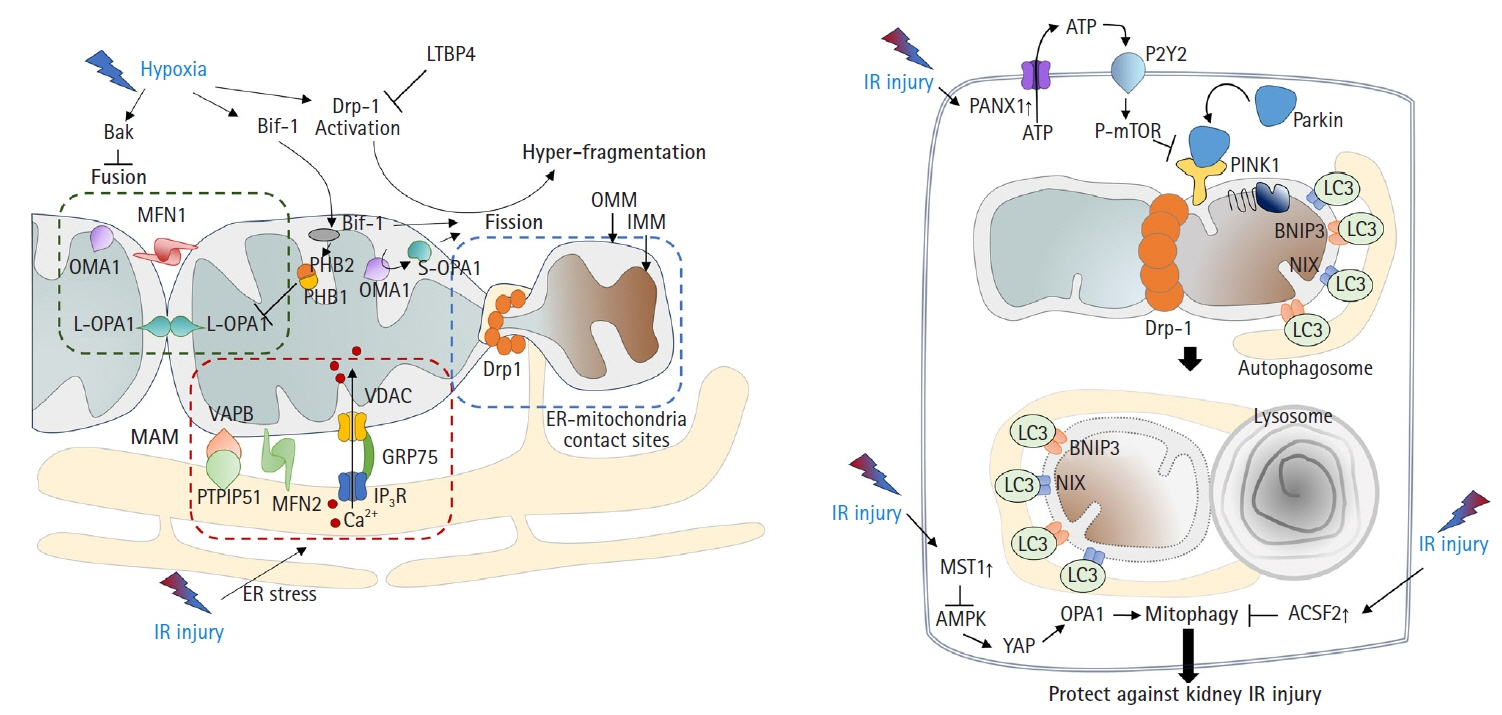
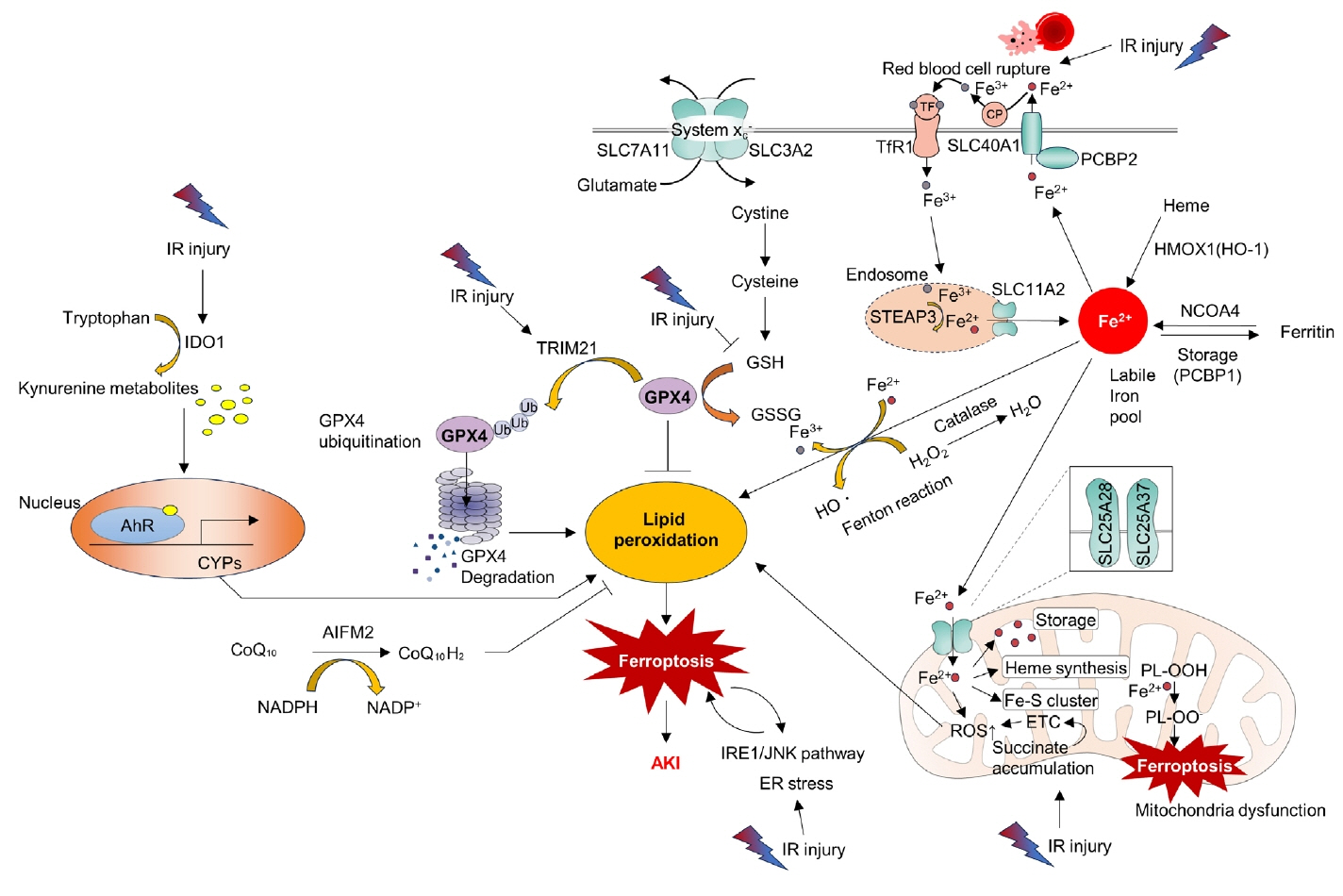
- Acute kidney ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury is a life-threatening condition that predisposes individuals to chronic kidney disease. Since the kidney is one of the most energy-demanding organs in the human body and mitochondria are the powerhouse of cells, mitochondrial dysfunction plays a central role in the pathogenesis of IR-induced acute kidney injury. Mitochondrial dysfunction causes a reduction in adenosine triphosphate production, loss of mitochondrial dynamics (represented by persistent fragmentation), and impaired mitophagy. Furthermore, the pathological accumulation of succinate resulting from fumarate reduction under oxygen deprivation (ischemia) in the reverse flux of the Krebs cycle can eventually lead to a burst of reactive oxygen species driven by reverse electron transfer during the reperfusion phase. Accumulating evidence indicates that improving mitochondrial function, biogenesis, and dynamics, and normalizing metabolic reprogramming within the mitochondria have the potential to preserve kidney function during IR injury and prevent progression to chronic kidney disease. In this review, we summarize recent advances in understanding the detrimental role of metabolic reprogramming and mitochondrial dysfunction in IR injury and explore potential therapeutic strategies for treating kidney IR injury.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012; 120:c179–84.
Article2. Rewa O, Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014; 10:193–207.
Article3. Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011; 17:1391–401.
Article4. Sabouny R, Shutt TE. The role of mitochondrial dynamics in mtDNA maintenance. J Cell Sci. 2021; 134:jcs258944.
Article5. Javadov S, Kozlov AV, Camara AK. Mitochondria in health and diseases. Cells. 2020; 9:1177.
Article6. Brooks C, Wei Q, Cho SG, Dong Z. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in acute kidney injury in cell culture and rodent models. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:1275–85.
Article7. Bhargava P, Schnellmann RG. Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017; 13:629–46.
Article8. Chouchani ET, Pell VR, Gaude E, Aksentijević D, Sundier SY, Robb EL, et al. Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. 2014; 515:431–5.
Article9. Oh CJ, Kim MJ, Lee JM, Kim DH, Kim IY, Park S, et al. Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 ameliorates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing succinate accumulation during ischemia and preserving mitochondrial function during reperfusion. Kidney Int. 2023; 104:724–39.
Article10. Nourbakhsh N, Singh P. Role of renal oxygenation and mitochondrial function in the pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2014; 127:149–52.
Article11. Yamamoto S, Yamamoto M, Nakamura J, Mii A, Yamamoto S, Takahashi M, et al. Spatiotemporal ATP dynamics during AKI predict renal prognosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 31:2855–69.
Article12. Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke GJ, Pischke SE, Berger SP, Sanders JS, Pol RA, Struys MM, et al. Ischemia and reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: relevant mechanisms in injury and repair. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:253.
Article13. Salvadori M, Rosso G, Bertoni E. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: pathogenesis and treatment. World J Transplant. 2015; 5:52–67.
Article14. Park JS, Pasupulati R, Feldkamp T, Roeser NF, Weinberg JM. Cyclophilin D and the mitochondrial permeability transition in kidney proximal tubules after hypoxic and ischemic injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011; 301:F134–50.
Article15. Wang C, Youle RJ. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis*. Annu Rev Genet. 2009; 43:95–118.
Article16. Zhang J, Zhang J, Ni H, Wang Y, Katwal G, Zhao Y, et al. Downregulation of XBP1 protects kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppressing HRD1-mediated NRF2 ubiquitylation. Cell Death Discov. 2021; 7:44.
Article17. Marin I, Boix O, Garcia-Garijo A, Sirois I, Caballe A, Zarzuela E, et al. Cellular senescence is immunogenic and promotes antitumor immunity. Cancer Discov. 2023; 13:410–31.
Article18. Rocca C, Soda T, De Francesco EM, Fiorillo M, Moccia F, Viglietto G, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction at the crossroad of cardiovascular diseases and cancer. J Transl Med. 2023; 21:635.
Article19. Ma H, Guo X, Cui S, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Shen X, et al. Dephosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase exacerbates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury via mitochondrial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2022; 101:315–30.
Article20. Yang X, Kang A, Lu Y, Li Y, Guo L, Li R, et al. Exploratory metabolomic analysis based on UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS to study hypoxia-reoxygenation energy metabolic alterations in HK-2 cells. Ren Fail. 2023; 45:2186715.
Article21. Singh P. Reprogramming of energy metabolism in kidney disease. Nephron. 2023; 147:61–4.
Article22. Lan R, Geng H, Singha PK, Saikumar P, Bottinger EP, Weinberg JM, et al. Mitochondrial pathology and glycolytic shift during proximal tubule atrophy after ischemic AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016; 27:3356–67.
Article23. Zhang J, Wang YT, Miller JH, Day MM, Munger JC, Brookes PS. Accumulation of succinate in cardiac ischemia primarily occurs via canonical krebs cycle activity. Cell Rep. 2018; 23:2617–28.
Article24. Spinelli JB, Rosen PC, Sprenger HG, Puszynska AM, Mann JL, Roessler JM, et al. Fumarate is a terminal electron acceptor in the mammalian electron transport chain. Science. 2021; 374:1227–37.
Article25. Beach TE, Prag HA, Pala L, Logan A, Huang MM, Gruszczyk AV, et al. Targeting succinate dehydrogenase with malonate ester prodrugs decreases renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. 2020; 36:101640.
Article26. Archer SL. Mitochondrial dynamics: mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:2236–51.
Article27. Xiao X, Hu Y, Quirós PM, Wei Q, López-Otín C, Dong Z. OMA1 mediates OPA1 proteolysis and mitochondrial fragmentation in experimental models of ischemic kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014; 306:F1318–26.
Article28. Zhan M, Brooks C, Liu F, Sun L, Dong Z. Mitochondrial dynamics: regulatory mechanisms and emerging role in renal pathophysiology. Kidney Int. 2013; 83:568–81.
Article29. McBride H, Soubannier V. Mitochondrial function: OMA1 and OPA1, the grandmasters of mitochondrial health. Curr Biol. 2010; 20:R274–6.
Article30. Liu Z, Li H, Su J, Xu S, Zhu F, Ai J, et al. Numb depletion promotes Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and exacerbates mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in acute kidney injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019; 30:1797–816.
Article31. Cho SG, Xiao X, Wang S, Gao H, Rafikov R, Black S, et al. Bif-1 Interacts with prohibitin-2 to regulate mitochondrial inner membrane during cell stress and apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019; 30:1174–91.
Article32. Qin N, Cai T, Ke Q, Yuan Q, Luo J, Mao X, et al. UCP2-dependent improvement of mitochondrial dynamics protects against acute kidney injury. J Pathol. 2019; 247:392–405.
Article33. Su CT, See DH, Huang YJ, Jao TM, Liu SY, Chou CY, et al. LTBP4 protects against renal fibrosis via mitochondrial and vascular impacts. Circ Res. 2023; 133:71–85.
Article34. Ge P, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. PINK1 and Parkin mitochondrial quality control: a source of regional vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2020; 15:20.
Article35. Durcan TM, Fon EA. The three ‘P’s of mitophagy: PARKIN, PINK1, and post-translational modifications. Genes Dev. 2015; 29:989–99.
Article36. Rüb C, Wilkening A, Voos W. Mitochondrial quality control by the Pink1/Parkin system. Cell Tissue Res. 2017; 367:111–23.
Article37. Grenier K, McLelland GL, Fon EA. Parkin- and PINK1-dependent mitophagy in neurons: will the real pathway please stand up? Front Neurol. 2013; 4:100.
Article38. Tang C, Han H, Yan M, Zhu S, Liu J, Liu Z, et al. PINK1-PRKN/PARK2 pathway of mitophagy is activated to protect against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy. 2018; 14:880–97.
Article39. Li N, Wang H, Jiang C, Zhang M. Renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced mitophagy protects against renal dysfunction via Drp1-dependent-pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018; 369:27–33.
Article40. Livingston MJ, Wang J, Zhou J, Wu G, Ganley IG, Hill JA, et al. Clearance of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy is important to the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning in kidneys. Autophagy. 2019; 15:2142–62.
Article41. Su L, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang X, Cao E, Yang C, et al. Pannexin 1 targets mitophagy to mediate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Commun Biol. 2023; 6:889.
Article42. Feng J, Li H, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Zhao S, Meng P, et al. Mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 deletion alleviates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury via modulating mitophagy and the AMPK-YAP signalling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 51:2359–76.
Article43. Shi H, Qi H, Xie D, Zhuang J, Qi H, Dai Y, et al. Inhibition of ACSF2 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via mediating mitophagy in proximal tubular cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023; 198:68–82.
Article44. Tang C, Han H, Liu Z, Liu Y, Yin L, Cai J, et al. Activation of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10:677.
Article45. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012; 149:1060–72.
Article46. Hosohata K, Harnsirikarn T, Chokesuwattanaskul S. Ferroptosis: a potential therapeutic target in acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23:6583.
Article47. Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Filippidis G, Liakopoulos V, Stefanidis I. Reoxygenation induces reactive oxygen species production and ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Mol Med Rep. 2021; 23:41.48. Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Golfinopoulos S, Liakopoulos V, Stefanidis I. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in ischemia-reperfusion injury of renal tubular epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2021; 23:472.
Article49. Sun X, Huang N, Li P, Dong X, Yang J, Zhang X, et al. TRIM21 ubiquitylates GPX4 and promotes ferroptosis to aggravate ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Life Sci. 2023; 321:121608.
Article50. Liang Y, Liu Z, Qu L, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Liang L, et al. Inhibition of the IRE1/JNK pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells attenuates ferroptosis in acute kidney injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:927641.
Article51. Tao W, Liu F, Zhang J, Fu S, Zhan H, Qian K. miR-3587 Inhibitor attenuates ferroptosis following renal ischemia-reperfusion through HO-1. Front Mol Biosci. 2021; 8:789927.
Article52. Corridon PR. Enhancing the expression of a key mitochondrial enzyme at the inception of ischemia-reperfusion injury can boost recovery and halt the progression of acute kidney injury. Front Physiol. 2023; 14:1024238.
Article53. Liu Z, Li Y, Li C, Yu L, Chang Y, Qu M. Delivery of coenzyme Q10 with mitochondria-targeted nanocarrier attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 131:112536.
Article54. Kubat GB, Kartal Y, Atalay O, Ulger O, Ekinci O, Celik E, et al. Investigation of the effect of isolated mitochondria transplantation on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021; 433:115780.
Article55. Doulamis IP, Guariento A, Duignan T, Kido T, Orfany A, Saeed MY, et al. Mitochondrial transplantation by intra-arterial injection for acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020; 319:F403–13.
Article56. Li L, Zhang L, Cao Y, Chen X, Gong H, Ma Y, et al. NDUFV1 attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial homeostasis. J Cell Mol Med. 2023; 27:1341–52.
Article57. Doke T, Mukherjee S, Mukhi D, Dhillon P, Abedini A, Davis JG, et al. NAD+ precursor supplementation prevents mtRNA/RIG-I-dependent inflammation during kidney injury. Nat Metab. 2023; 5:414–30.58. Morevati M, Egstrand S, Nordholm A, Mace ML, Andersen CB, Salmani R, et al. Effect of NAD+ boosting on kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2021; 16:e0252554.59. Mao H, Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Zhu Z, Wang L, Liu X. Mitochondria-Targeted antioxidant mitoquinone maintains mitochondrial homeostasis through the Sirt3-dependent pathway to mitigate oxidative damage caused by renal ischemia/reperfusion. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:2213503.
Article60. Cheng L, Yang X, Jian Y, Liu J, Ke X, Chen S, et al. SIRT3 deficiency exacerbates early-stage fibrosis after ischaemia-reperfusion-induced AKI. Cell Signal. 2022; 93:110284.
Article61. Yu X, Xu M, Meng X, Li S, Liu Q, Bai M, et al. Nuclear receptor PXR targets AKR1B7 to protect mitochondrial metabolism and renal function in AKI. Sci Transl Med. 2020; 12:eaay7591.
Article62. Wang D, Wang Y, Zou X, Shi Y, Liu Q, Huyan T, et al. FOXO1 inhibition prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via cAMP-response element binding protein/PPAR-γ coactivator-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis. Br J Pharmacol. 2020; 177:432–48.
Article63. Hurtado KA, Janda J, Schnellmann RG. Lasmiditan promotes recovery from acute kidney injury through induction of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023; 324:F56–63.
Article64. Gibbs WS, Collier JB, Morris M, Beeson CC, Megyesi J, Schnellmann RG. 5-HT1F receptor regulates mitochondrial homeostasis and its loss potentiates acute kidney injury and impairs renal recovery. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018; 315:F1119–28.65. Tang Y, Leng YF, Wang W, Zhang J, Yuan TL, Wang J. Protective effect of Saxagliptin on diabetic rats with renal ischemia reperfusion injury by targeting oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway through activating Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling. Transpl Immunol. 2023; 76:101762.
Article66. Barati A, Rahbar Saadat Y, Meybodi SM, Nouraei S, Moradi K, Kamrani Moghaddam F, et al. Eplerenone reduces renal ischaemia/reperfusion injury by modulating Klotho, NF-κB and SIRT1/SIRT3/PGC-1α signalling pathways. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023; 75:819–27.
Article67. Li J, Jiang Y, Dai Q, Yu Y, Lv X, Zhang Y, et al. Protective effects of mefunidone on ischemia-reperfusion injury/folic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:1043945.
Article68. Kawabata C, Hirakawa Y, Inagi R, Nangaku M. Acetate attenuates kidney fibrosis in an oxidative stress-dependent manner. Physiol Rep. 2023; 11:e15774.
Article69. Liu D, Shu G, Jin F, Qi J, Xu X, Du Y, et al. ROS-responsive chitosan-SS31 prodrug for AKI therapy via rapid distribution in the kidney and long-term retention in the renal tubule. Sci Adv. 2020; 6:eabb7422.
Article70. Nowak G, Megyesi J. γ-tocotrienol protects against mitochondrial dysfunction, energy deficits, morphological damage, and decreases in renal functions after renal ischemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22:12674.
Article71. Ding M, Tolbert E, Birkenbach M, Gohh R, Akhlaghi F, Ghonem NS. Treprostinil reduces mitochondrial injury during rat renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021; 141:111912.
Article72. Ji X, Chu L, Su D, Sun J, Song P, Sun S, et al. MRPL12-ANT3 interaction involves in acute kidney injury via regulating MPTP of tubular epithelial cells. iScience. 2023; 26:106656.
Article73. Wang J, Zhu P, Li R, Ren J, Zhang Y, Zhou H. Bax inhibitor 1 preserves mitochondrial homeostasis in acute kidney injury through promoting mitochondrial retention of PHB2. Theranostics. 2020; 10:384–97.
Article74. Thomas K, Zondler L, Ludwig N, Kardell M, Lüneburg C, Henke K, et al. Glutamine prevents acute kidney injury by modulating oxidative stress and apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells. JCI Insight. 2022; 7:e163161.
Article75. Wang S, Zhu H, Li R, Mui D, Toan S, Chang X, et al. DNA-PKcs interacts with and phosphorylates Fis1 to induce mitochondrial fragmentation in tubular cells during acute kidney injury. Sci Signal. 2022; 15:eabh1121.
Article76. Shen L, Zhang Q, Tu S, Qin W. SIRT3 mediates mitofusin 2 ubiquitination and degradation to suppress ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Exp Cell Res. 2021; 408:112861.
Article77. Yang W, Li X, He L, Zhu S, Lai S, Zhang X, et al. Empagliflozin improves renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing inflammation and enhancing mitochondrial fusion through AMPK-OPA1 pathway promotion. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023; 28:42.
Article78. Wang Y, Liu Q, Cai J, Wu P, Wang D, Shi Y, et al. Emodin prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppression of CAMKII/DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022; 916:174603.
Article79. Wang Q, Xu J, Li X, Liu Z, Han Y, Xu X, et al. Sirt3 modulate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through enhancing mitochondrial fusion and activating the ERK-OPA1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234:23495–506.
Article80. Fu ZJ, Wang ZY, Xu L, Chen XH, Li XX, Liao WT, et al. HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. 2020; 36:101671.
Article81. Sun Z, Gao Z, Wu J, Zheng X, Jing S, Wang W. MSC-derived extracellular vesicles activate mitophagy to alleviate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via the miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. Stem Cells Int. 2022; 2022:6852661.
Article82. Kamarauskaite J, Baniene R, Trumbeckas D, Strazdauskas A, Trumbeckaite S. Increased succinate accumulation induces ROS generation in in vivo ischemia/reperfusion-affected rat kidney mitochondria. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:8855585.
Article83. Scantlebery AM, Tammaro A, Mills JD, Rampanelli E, Kors L, Teske GJ, et al. The dysregulation of metabolic pathways and induction of the pentose phosphate pathway in renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. 2021; 253:404–14.
Article84. Gao Z, Zhang C, Peng F, Chen Q, Zhao Y, Chen L, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate renal fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion injure by restoring CPT1A mediated fatty acid oxidation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13:191.
Article85. Kim IY, Song SH, Seong EY, Lee DW, Bae SS, Lee SB. Akt1 is involved in renal fibrosis and tubular apoptosis in a murine model of acute kidney injury-to-chronic kidney disease transition. Exp Cell Res. 2023; 424:113509.
Article86. Lin HY, Chen Y, Chen YH, Ta AP, Lee HC, MacGregor GR, et al. Tubular mitochondrial AKT1 is activated during ischemia reperfusion injury and has a critical role in predisposition to chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2021; 99:870–84.
Article87. Granata S, Votrico V, Spadaccino F, Catalano V, Netti GS, Ranieri E, et al. Oxidative stress and ischemia/reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: focus on ferroptosis, mitophagy and new antioxidants. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11:769.
Article88. Song J, Sheng J, Lei J, Gan W, Yang Y. Mitochondrial targeted antioxidant SKQ1 ameliorates acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:2223957.
Article89. Batirel S, Bozaykut P, Mutlu Altundag E, Kartal Ozer N, Mantzoros CS. The effect of Irisin on antioxidant system in liver. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014; 75(Suppl 1):S16.
Article90. Zhang J, Bi J, Ren Y, Du Z, Li T, Wang T, et al. Involvement of GPX4 in irisin’s protection against ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236:931–45.
Article91. Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014; 16:1180–91.
Article92. Tschopp J. Mitochondria: sovereign of inflammation? Eur J Immunol. 2011; 41:1196–202.
Article93. Su X, Liu B, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhou H, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome: a potential therapeutic target to minimize renal ischemia/reperfusion injury during transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 2022; 75:101718.
Article94. Yin L, Zhao H, Zhang H, Li Y, Dong Y, Ju H, et al. Remdesivir alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:652446.
Article95. Cao JY, Zhou LT, Li ZL, Yang Y, Liu BC, Liu H. Dopamine D1 receptor agonist A68930 attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 143:226–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney injury, inflammation, and disease: potential therapeutic approaches
- Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury with respect to oxidative stress and inflammatory response: a narrative review
- Kidney transplantation and ischemic conditioning: past, present and future perspectives
- Flavonoids as therapeutics for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a comprehensive review on preclinical studies
- Mechanism of Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury to the Heart: From the Viewpoint of Nitric Oxide and Mitochondria