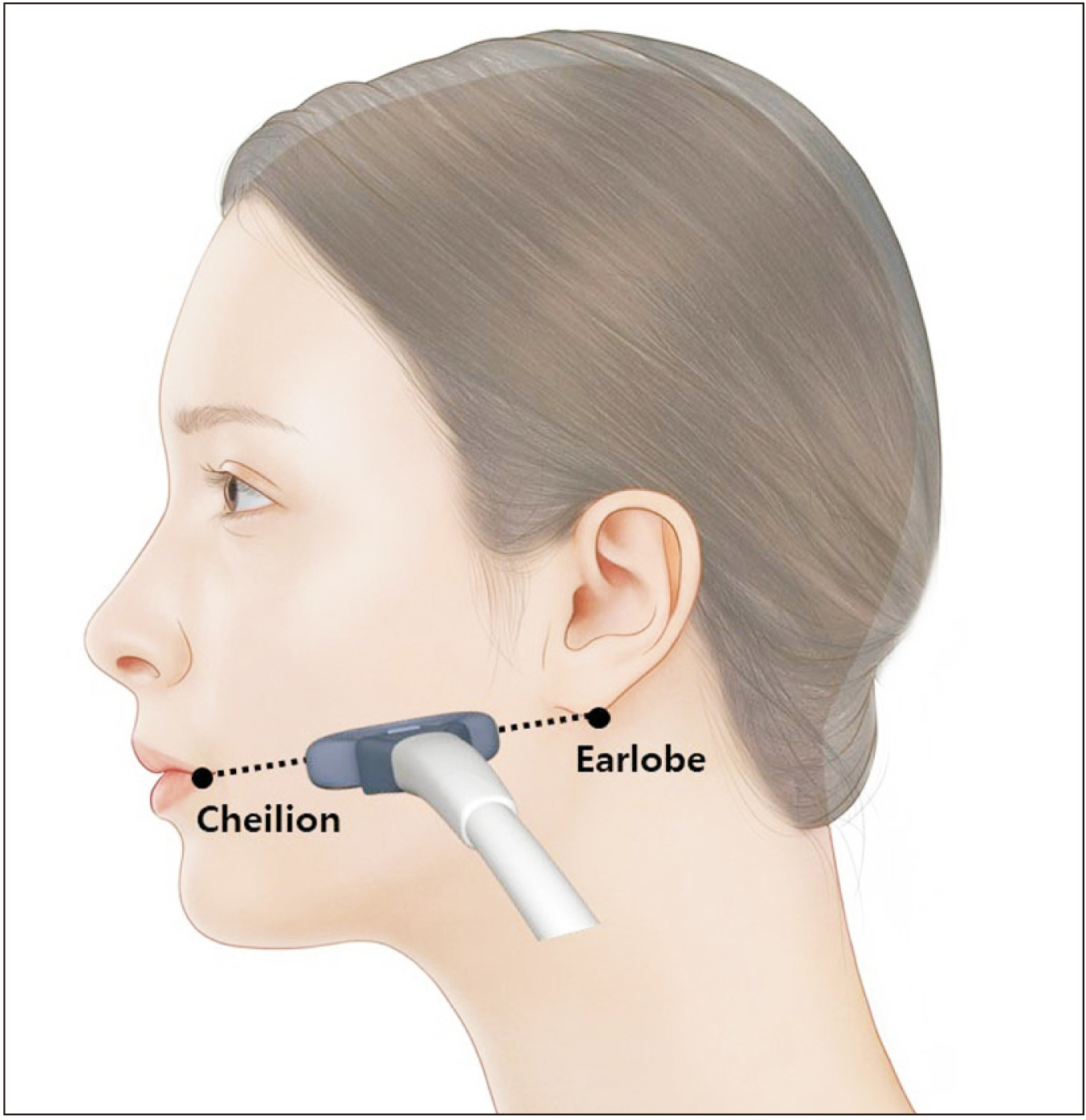
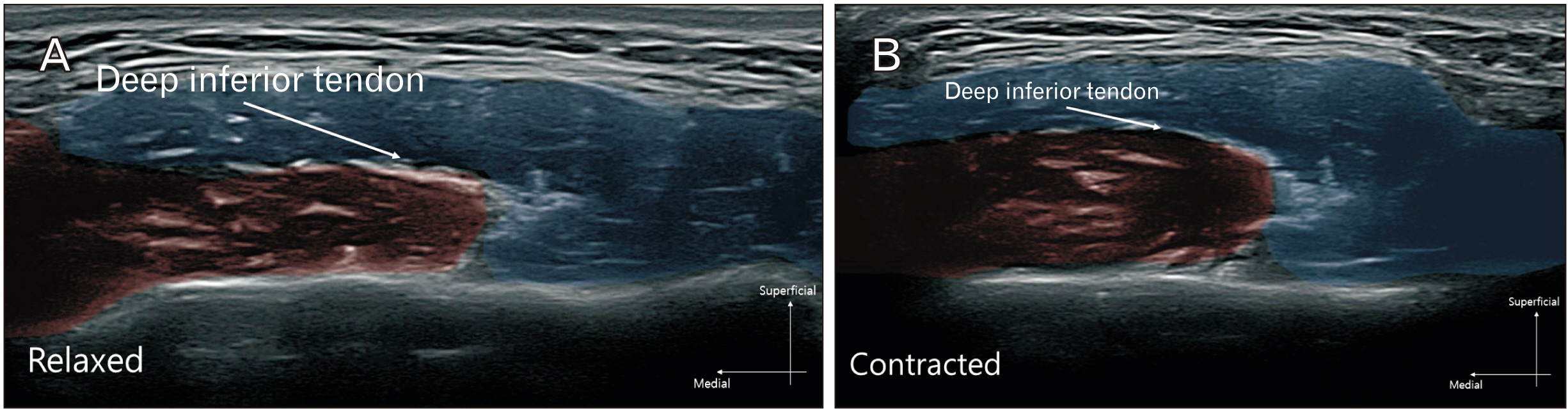
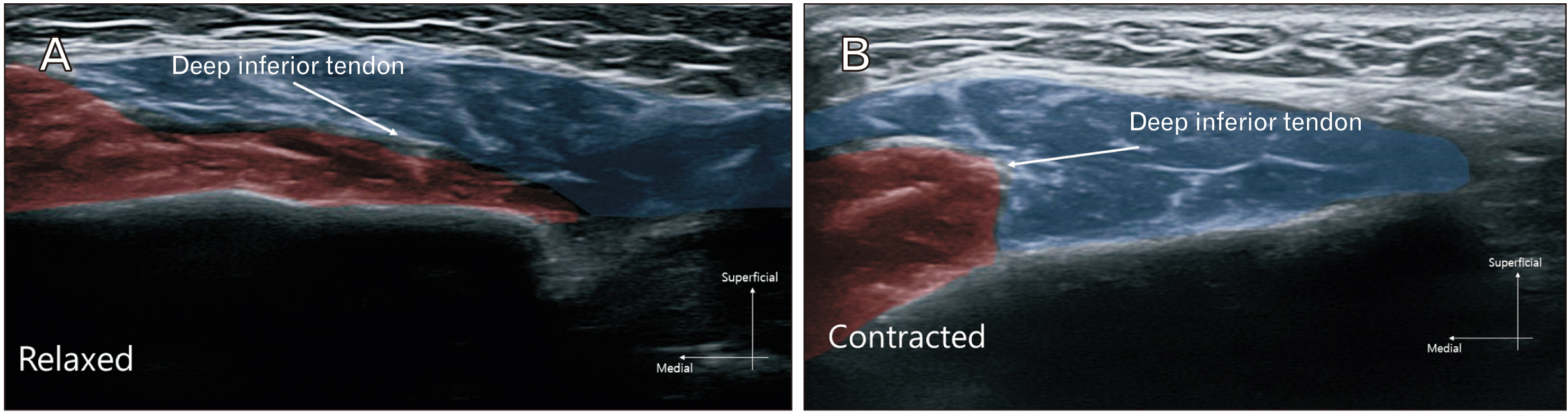
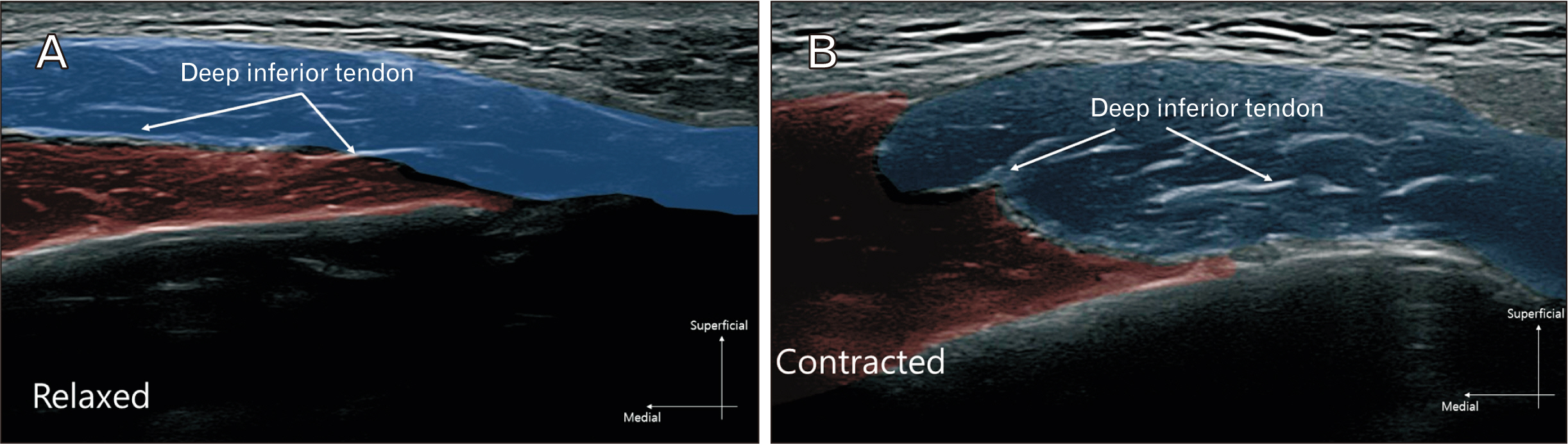
Anat Cell Biol.
2024 Mar;57(1):13-17. 10.5115/acb.23.234.
Sonographic observation of the paradoxical masseteric bulging and clinical implication of functional compartment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Human Identification Research Institute, BK21 PLUS Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- 2Maylin Clinic (Apgujeong), Seoul, Korea
- 3Wyne Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Clinic, Chungju, Korea
- 4Yonsei E1 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Anyang, 5 Dr Youth Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2554236
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.23.234
Abstract
- Masseter are commonly botulinum neurotoxin targeted muscle for facial contouring in aesthetic field. However, paradoxical masseteric bulging is common adverse effect that has not been discussed with ultrasonographic observations. Retrospective study has been conducted from October, 2021 to January, 2023, out of 324 patients have done blinded botulinum neurotoxin injection in the masseter at the middle and lower portion of the masseter with each side of 25 units (letibotulinum neurotoxin type A), 3 patients demonstrated paradoxical masseteric bulging has been reported and the image observed by ultrasonography by physician. Based on the observations made, we can infer that the function of the moving muscle involves twisting of the muscle fibers during contraction, along with the twisting of the deep inferior tendon, which causes the muscle to be divided into anterior and posterior compartments rather than into superficial and deep compartments of masseter. In ultrasonographic observe the skin surface of a patient with paradoxical masseteric bulging, it is observable that either the anterior or posterior part contracts significantly. The functional units of anterior and posterior compartment are observable as muscular contraction of inward movement of the muscle from either the anterior or posterior functional unit.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Hur HW, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injection for facial contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 150:562e–71e. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009444. PMID: 35759641.
Article2. Lee HJ, Kang IW, Seo KK, Choi YJ, Kim ST, Hu KS, Kim HJ. 2016; The anatomical basis of paradoxical masseteric bulging after botulinum neurotoxin type A injection. Toxins (Basel). 9:14. DOI: 10.3390/toxins9010014. PMID: 28042813. PMCID: PMC5308246.
Article3. Kim JH, Shin JH, Kim ST, Kim CY. 2007; Effects of two different units of botulinum toxin type A evaluated by computed tomography and electromyographic measurements of human masseter muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg. 119:711–7. DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000239453.67423.99. PMID: 17230111.
Article4. Rice SM, Nassim JS, Hersey EM, Kourosh AS. 2021; Prevention and correction of paradoxical masseteric bulging following botulinum toxin injection for masseter hypertrophy. Int J Womens Dermatol. 7(5Part B):815–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.03.002. PMID: 35028386. PMCID: PMC8714579.
Article5. Bae JH, Choi DY, Lee JG, Seo KK, Tansatit T, Kim HJ. 2014; The risorius muscle: anatomic considerations with reference to botulinum neurotoxin injection for masseteric hypertrophy. Dermatol Surg. 40:1334–9. DOI: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000223. PMID: 25393348.6. Lee SJ, Kang JM, Kim YK, Park J, Kim DY. 2012; Paradoxical bulging of muscle after injection of botulinum neurotoxin type A into hypertrophied masseter muscle. J Dermatol. 39:804–5. DOI: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01539.x. PMID: 22413811.
Article7. Yeh YT, Peng JH, Peng HP. 2018; Literature review of the adverse events associated with botulinum toxin injection for the masseter muscle hypertrophy. J Cosmet Dermatol. 17:675–87. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.12721. PMID: 30091170.
Article8. Kim HJ, Youn KH, Kim JS, Kim YS, Hong SO, Na J. Ultrasonographic anatomy of the face and neck for minimally invasive procedures : an anatomic guideline for ultrasonographic-guided procedures. Springer;2021. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-6560-1.9. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim GY, Yoon SW, Oh W, Kim HJ. 2022; Novel anatomical proposal for botulinum neurotoxin injection targeting lateral canthal rhytids. Toxins (Basel). 14:462. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14070462. PMID: 35878200. PMCID: PMC9316553.
Article10. Yi KH, Lee KL, Lee JH, Hu HW, Kim HJ. 2022; Guidance to trigger point injection for treating myofascial pain syndrome: intramuscular neural distribution of the quadratus lumborum. Clin Anat. 35:1100–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23918. PMID: 35655442.
Article11. Yi KH, Lee JH, Kim HM, Kim HJ. 2022; The botulinum neurotoxin for pain control after breast reconstruction: neural distribution of the pectoralis major muscle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:322–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102653. PMID: 35039438.
Article12. Yi KH, Lee HJ, Seo KK, Kim HJ. 2022; Intramuscular neural arborization of the latissimus dorsi muscle: application of botulinum neurotoxin injection in flap reconstruction. Toxins (Basel). 14:107. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14020107. PMID: 35202134. PMCID: PMC8878018.
Article13. Bae H, Kim J, Seo KK, Hu KS, Kim ST, Kim HJ. 2020; Comparison between conventional blind injections and ultrasound-guided injections of botulinum toxin type A into the masseter: a clinical trial. Toxins (Basel). 12:588. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12090588. PMID: 32932891. PMCID: PMC7551286.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case report of Peroneal Compartment Syndrome
- The Influence of Changes in Cervical Lordosis on Bulging Disk and Spinal Stenosis: Functional MR Imaging
- A study of masseteric silent period of deep bite, open bite and normal over bite
- Thenar Compartment syndrome: A Case Report
- Idiopathic Compartment Syndrome of the Forearm