Lab Med Online.
2023 Apr;13(2):109-113. 10.47429/lmo.2023.13.2.109.
A Case of T-Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Submicroscopic 1p33 Deletion Resulting in STIL-TAL1 Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2552734
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2023.13.2.109
Abstract
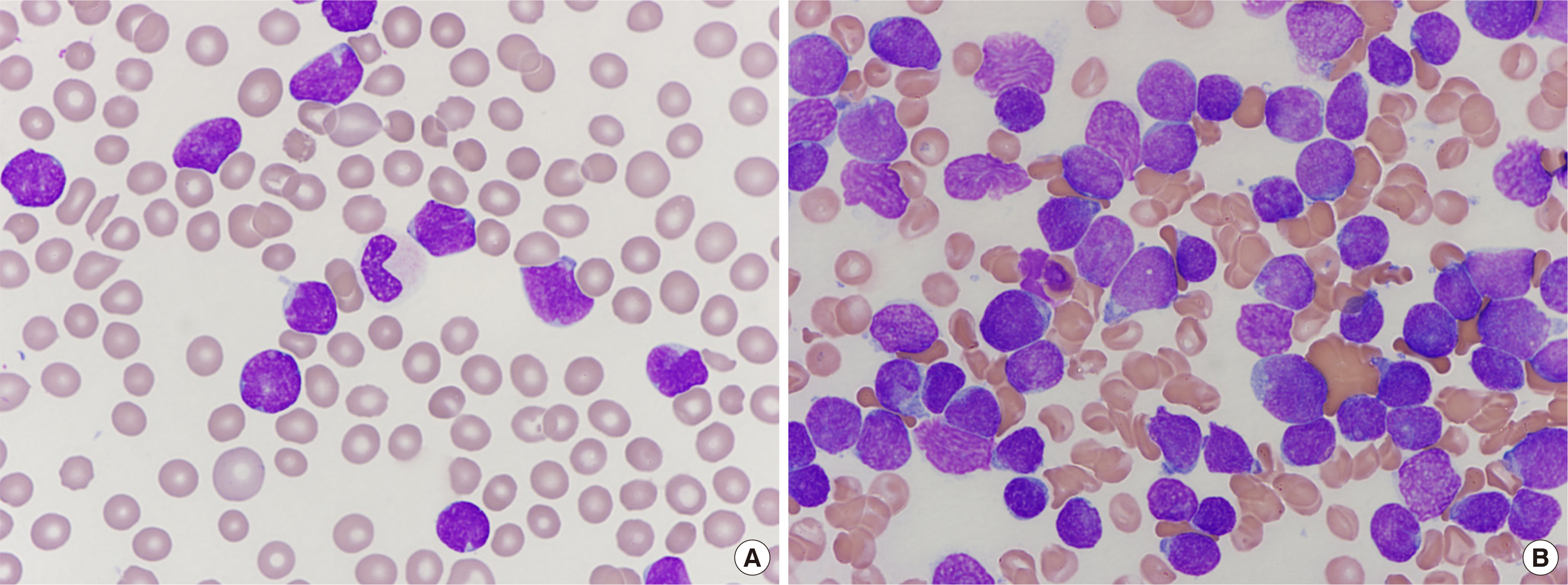
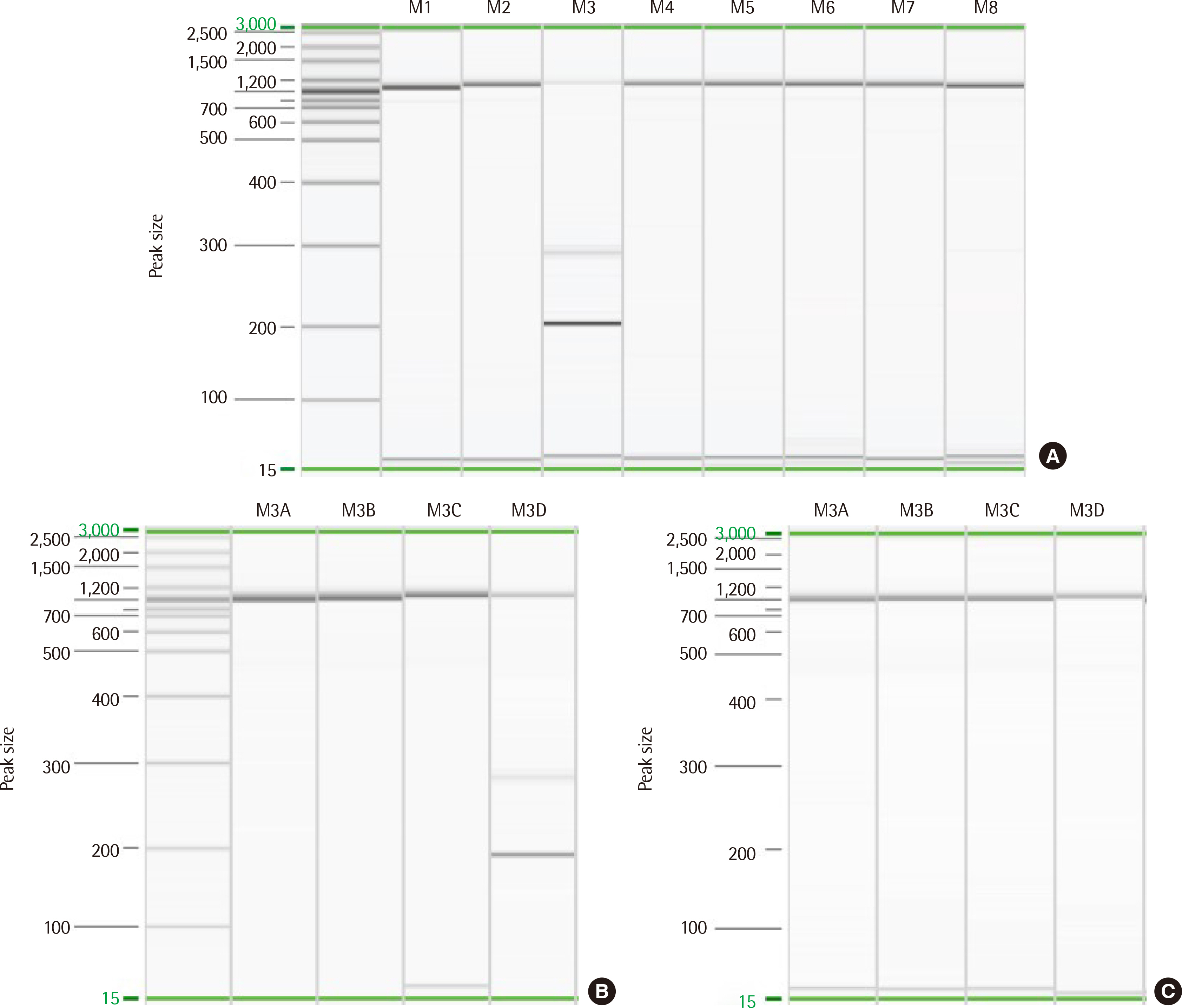
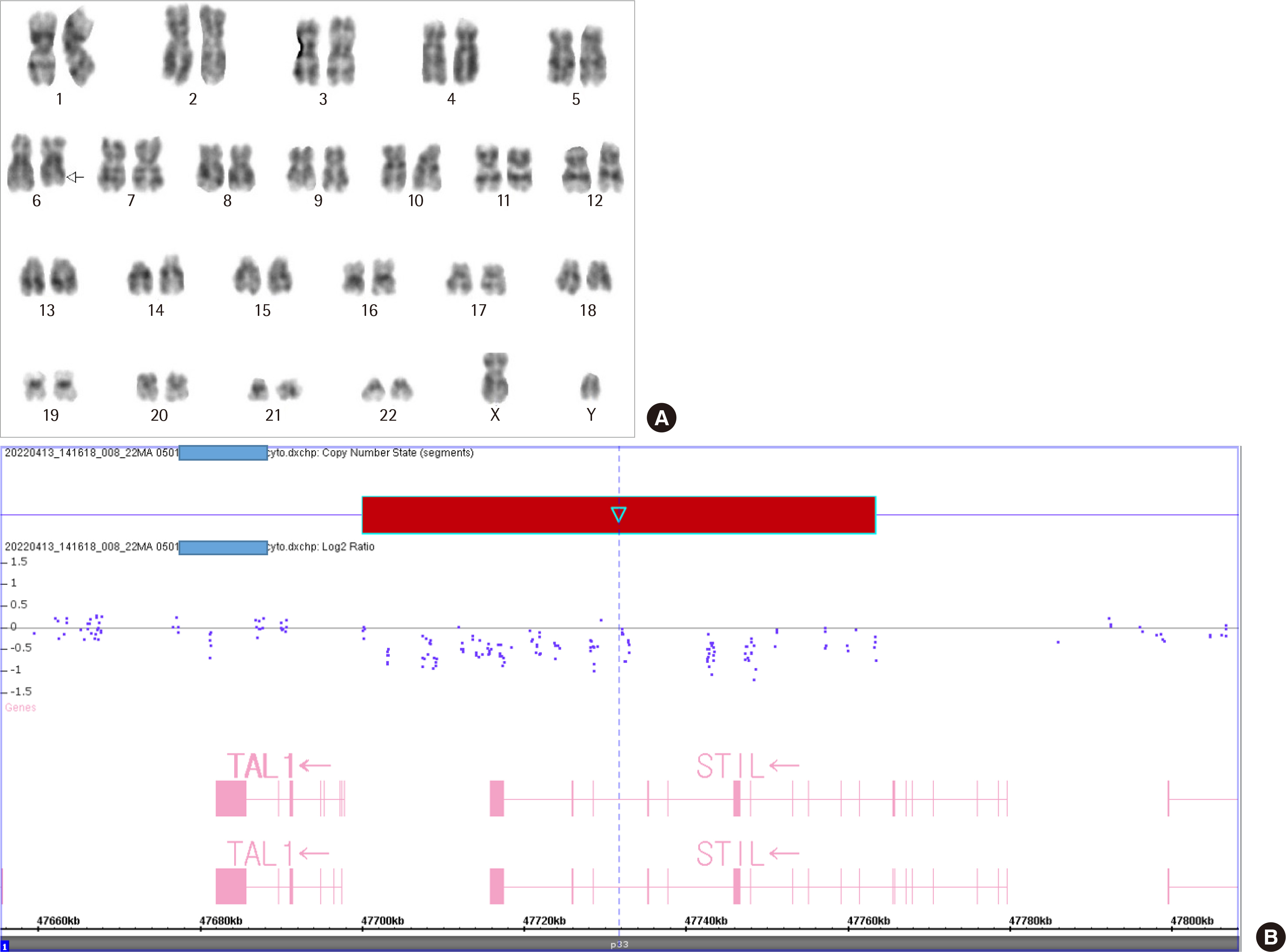
- T-lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematologic malignancy associated with poor outcomes. The genetic background of T-ALL is widely heterogeneous and the TAL1 gene is overexpressed in approximately half of all cases. A submicroscopic interstitial deletion on chromosome 1p33 results inSTIL-TAL1 fusion, causing inappropriate overexpression of TAL1, which promotes T cell leukemogenesis. T-ALL with STIL-TAL1 exhibits distinct characteristics, such as a mature cortical T cell immunophenotype, low incidence of NOTCH1 mutation, privileged association with PTEN inactivation, deletion of 6q14–q16, MYC translocation, high leukocyte count, poor response to treatment, and low event-free survival. However, the clinical relevance and prognostic value of this rearrangement remain unclear. Here, we report the first case of T-ALL with a 1p33 deletion resulting in STIL-TAL1 fusion in Korea, which was detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and confirmed by chromosomal microarray analysis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bardelli V, Arniani S, Pierini V, Di Giacomo D, Pierini T, Gorello P, et al. 2021; T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: biomarkers and their clinical usefulness. Genes. 12:1118. DOI: 10.3390/genes12081118. PMID: 34440292. PMCID: PMC8394887.2. Van Vlierberghe P, Ferrando A. 2012; The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 122:3398–406. DOI: 10.1172/JCI61269. PMID: 23023710. PMCID: PMC3461904.3. D'Angiò M, Valsecchi MG, Testi AM, Conter V, Nunes V, Parasole R, et al. 2015; Clinical features and outcome of SIL/TAL1-positive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and adolescents: a 10-year experience of the AIEOP group. Haematologica. 100:e10–3. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2014.112151. PMID: 25304610. PMCID: PMC4281327.4. Tan TK, Zhang C, Sanda T. 2019; Oncogenic transcriptional program driven by TAL1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Hematol. 109:5–17. DOI: 10.1007/s12185-018-2518-z. PMID: 30145780.
Article5. Furness CL, Mansur MB, Weston VJ, Ermini L, van Delft FW, Jenkinson S, et al. 2018; The subclonal complexity of STIL-TAL1+ T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leukemia. 32:1984–93. DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0046-8. PMID: 29556024. PMCID: PMC6127084.
Article6. Panagopoulos I, Heim S. 2021; Interstitial deletions generating fusion genes. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 18:167–96. DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20251. PMID: 33893073. PMCID: PMC8126330.7. Chopra A, Soni S, Verma D, Kumar D, Dwivedi R, Vishwanathan A, et al. 2015; Prevalence of common fusion transcripts in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report of 304 cases. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 11:293–8. DOI: 10.1111/ajco.12400. PMID: 26264145.
Article8. Yu L, Slovak ML, Mannoor K, Chen C, Hunger SP, Carroll AJ, et al. 2011; Microarray detection of multiple recurring submicroscopic chromosomal aberrations in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 25:1042–6. DOI: 10.1038/leu.2011.33. PMID: 21383747.9. Girardi T, Vicente C, Cools J, De Keersmaecker K. 2017; The genetics and molecular biology of T-ALL. Blood. 129:1113–23. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-706465. PMID: 28115373. PMCID: PMC5363819.10. Wang D, Zhu G, Wang N, Zhou X, Yang Y, Zhou S, et al. 2013; SIL-TAL1 rearrangement is related with poor outcome: a study from a Chinese institution. PLoS One. 8:e73865. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073865. PMID: 24040098. PMCID: PMC3767609.11. Zhao X, Hong Y, Qin Y, Xu Y, Chang Y, Wang Y, et al. 2017; The clinical significance of monitoring the expression of the SIL-TAL1 fusion gene in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Lab Hematol. 39:613–9. DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12711. PMID: 28736882.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel Translocation t(1;5)(p32;q31) that Was Not Associated with the TAL1 Rearrangement in a Case of T Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
- A Case of STIL-TAL1-positive T-lymphoblastic Leukemia With a Minor Philadelphia-positive Clone
- Submicroscopic Deletions of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene (IGH) in Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia with IGH Rearrangements
- A Case of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with ider(9)(q10)t(9;22)(q34;q11.2)
- The e1a3 BCR-ABL1 Fusion Transcript in Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia