Lab Med Online.
2023 Jan;13(1):22-26. 10.47429/lmo.2023.13.1.22.
Aggressive NK Cell Leukemia with RAB29-NUCKS1 Gene Rearrangement: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yongin, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine , Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yongin, Korea
- KMID: 2552719
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2023.13.1.22
Abstract
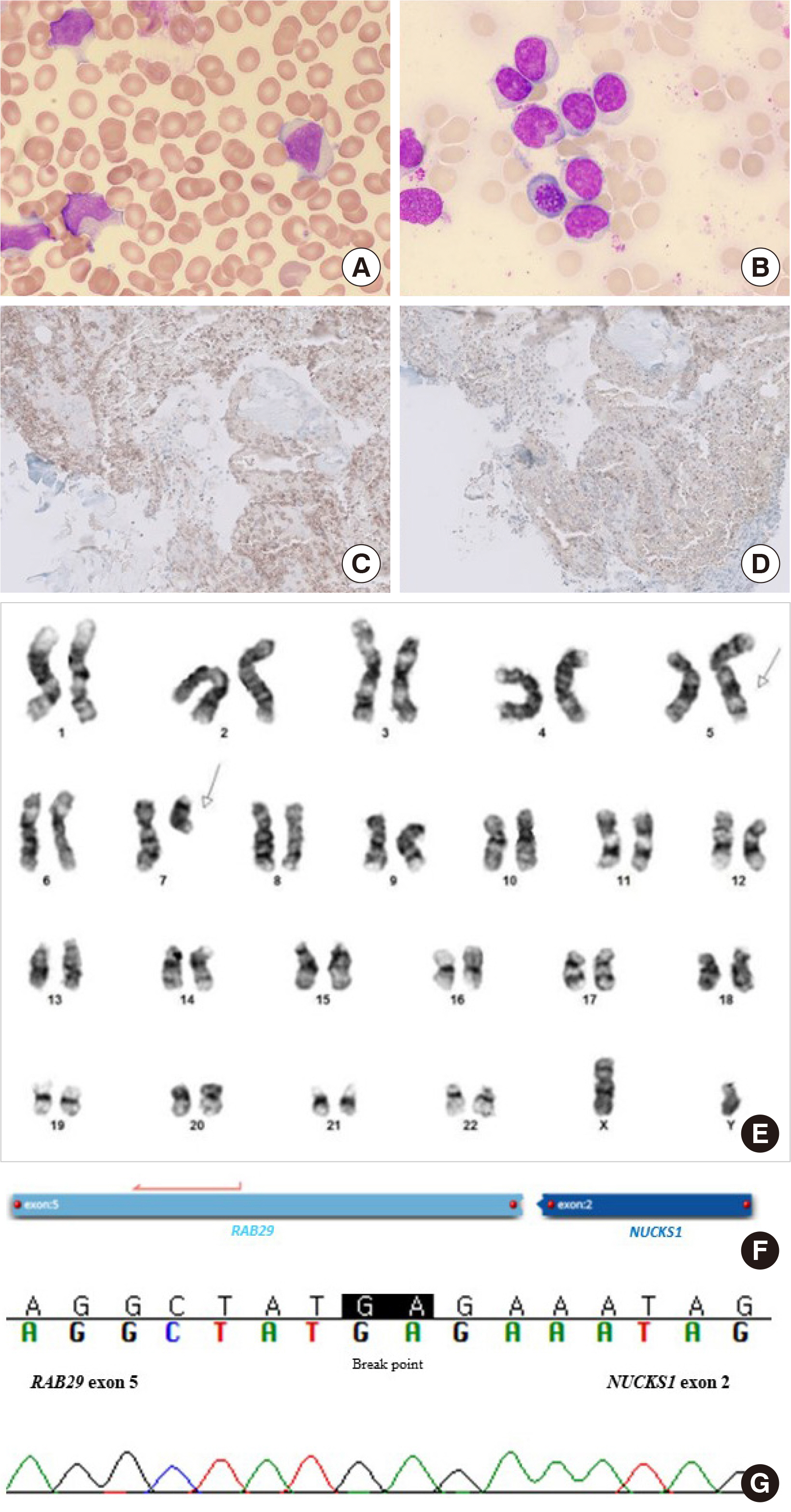
- Aggressive natural killer (NK) cell leukemia (ANKL) is a rare form of leukemia that may be accompanied by various chromosomal abnormalities such as del(6)(q21q25) or del(11q). Here, we describe a case of a patient with ANKL and an RAB29-NUCKS1 rearrangement that has never been described before. An RNA fusion panel test found a gene fusion between exon 5 of RAB29 and exon 2 of NUCKS1 at chromosome 1q32.1. Additionally, reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and Sanger sequencing confirmed cryptic RAB29-NUCKS1 fusion. RAB29 encodes a protein that regulates exocytic and endocytic pathways. NUCKS1 encodes a chromatin-associated protein involved in DNA damage responses. Further studies will be necessary to understand the molecular pathogenesis of ANKL related to an RAB29-NUCKS1 rearrangement.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruskova A, Thula R, Chan G. 2004; Aggressive natural killer-cell leukemia: report of five cases and review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. 45:2427–38. DOI: 10.1080/10428190400004513. PMID: 15621755.2. Park S, Ko YH. 2014; Epstein-Barr virus-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. J Dermatol. 41:29–39. DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.12322. PMID: 24438142.3. Ryder J, Wang X, Bao L, Gross SA, Hua F, Irons RD. 2007; Aggressive natural killer cell leukemia: report of a Chinese series and review of the literature. Int J Hematol. 85:18–25. DOI: 10.1532/IJH97.A10612. PMID: 17261497.4. Yang L, Rau R, Goodell MA. 2015; DNMT3A in haematological malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:152–65. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3895. PMID: 25693834. PMCID: PMC5814392.5. Hutchens C, Ketterling RP, Van Dyke DL. 2012; When are apparently non-clonal abnormalities in bone marrow chromosome studies actually clonal? Cancer Genet. 205:405–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2012.04.003. PMID: 22868001.6. Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Nakamura S, Aoki S, Notoya A, Ozaki S, et al. 2004; Aggressive natural killer-cell leukemia revisited: large granular lymphocyte leukemia of cytotoxic NK cells. Leukemia. 18:763–70. DOI: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403262. PMID: 14961041.7. Heyer EE, Deveson IW, Wooi D, Selinger CI, Lyons RJ, Hayes VM, et al. 2019; Diagnosis of fusion genes using targeted RNA sequencing. Nat Commun. 10:1388. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09374-9. PMID: 30918253. PMCID: PMC6437215.8. Singh S, Qin F, Kumar S, Elfman J, Lin E, Pham LP, et al. 2020; The landscape of chimeric RNAs in non-diseased tissues and cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:1764–78. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz1223. PMID: 31965184. PMCID: PMC7038929.9. Biernaux C, Loos M, Sels A, Huez G, Stryckmans P. 1995; Detection of major bcr-abl gene expression at a very low level in blood cells of some healthy individuals. Blood. 86:3118–22. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V86.8.3118.3118. PMID: 7579406.10. Bose S, Deininger M, Gora-Tybor J, Goldman JM, Melo JV. 1998; The presence of typical and atypical BCR-ABL fusion genes in leukocytes of normal individuals: biologic significance and implications for the assessment of minimal residual disease. Blood. 92:3362–7. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V92.9.3362. PMID: 9787174.11. Oh S, Shao J, Mitra J, Xiong F, D'Antonio M, Wang R, et al. 2021; Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes. Nature. 595:735–40. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03577-1. PMID: 34040254.12. Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ. 2011; Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev. 91:119–49. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00059.2009. PMID: 21248164. PMCID: PMC3710122.13. Wang S, Ma Z, Xu X, Wang Z, Sun L, Zhou Y, et al. 2014; A role of Rab29 in the integrity of the trans-Golgi network and retrograde trafficking of mannose-6-phosphate receptor. PLoS One. 9:e96242. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096242. PMID: 24788816. PMCID: PMC4008501.14. Gary-Bobo M, Nirdé P, Jeanjean A, Morère A, Garcia M. 2007; Mannose 6-pho-sphate receptor targeting and its applications in human diseases. Curr Med Chem. 14:2945–53. DOI: 10.2174/092986707782794005. PMID: 18220730. PMCID: PMC2793280.15. Abdoli Z, Assarehzadegan MA, Pipelzadeh MH, Iranparast S, Dashti Gerdabi N, Parsanahad M, et al. 2021; Leukemia inhibitory factor suppresses NKG2D mRNA expression and presentation on human natural killer cells. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 20:98–105. DOI: 10.18502/ijaai.v20i1.5416. PMID: 33639636.16. Parplys AC, Zhao W, Sharma N, Groesser T, Liang F, Maranon DG, et al. 2015; NUCKS1 is a novel RAD51AP1 paralog important for homologous recombination and genome stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:9817–34. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv859. PMID: 26323318. PMCID: PMC4787752.17. Huang P, Cai Y, Zhao B, Cui L. 2018; Roles of NUCKS1 in diseases: Susceptibility, potential biomarker, and regulatory mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 2018:7969068. DOI: 10.1155/2018/7969068. PMID: 29619377. PMCID: PMC5830027.18. Frattini V, Trifonov V, Chan JM, Castano A, Lia M, Abate F, et al. 2013; The integrated landscape of driver genomic alterations in glioblastoma. Nat Genet. 45:1141–9. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2734. PMID: 23917401. PMCID: PMC3799953.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Aggressive NK/T-cell Lymphoma/Leukemia with Cutaneous Involvement in Adolescence
- A Case of Nasal-type T/NK-cell Lymphoma Resembling Cellulitis
- Usefulness of Chromosomal Microarray in Hematologic Malignancies: A Case of Aggressive NK-cell Leukemia with 1q Abnormality
- A Case of Aggressive T/NK-cell Lymphoma/leukemia with Cutaneous Involvement
- A Case of CD7+, CD4-, CD8-, CD3-acute T cell lymphoblastic leukemia