Korean J Schizophr Res.
2023 Oct;26(2):46-51. 10.16946/kjsr.2023.26.2.46.
Clozapine Dose-Concentration Relationship and Other Factors Associated With Clozapine Plasma Concentration in Korean Schizophrenia Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Jeollabuk-do Maeumsarang Hospital, Wanju, Korea
- KMID: 2547421
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2023.26.2.46
Abstract
Objectives
Some reports suggest that the concentration-to-dosage ratio (C/D ratio) of clozapine (CZP) in Asian treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS) patients differs from that of Caucasian TRS patients. However, there is insufficient research on the differences in C/D ratio between Korean TRS patients and Caucasian TRS patients. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate prescribed CZP dosage, CZP concentration and C/D ratio in Korean TRS patients.
Methods
The study included TRS patients aged 18 years or older who were prescribed CZP for at least 12 weeks at a psychiatric hospital in Korea. We collected demographic information, smoking status, hospitalization status, CZP serum concentration, total CZP dosage, and norclozapine (NCZP) serum concentration and analyzed their statistical correlations.
Results
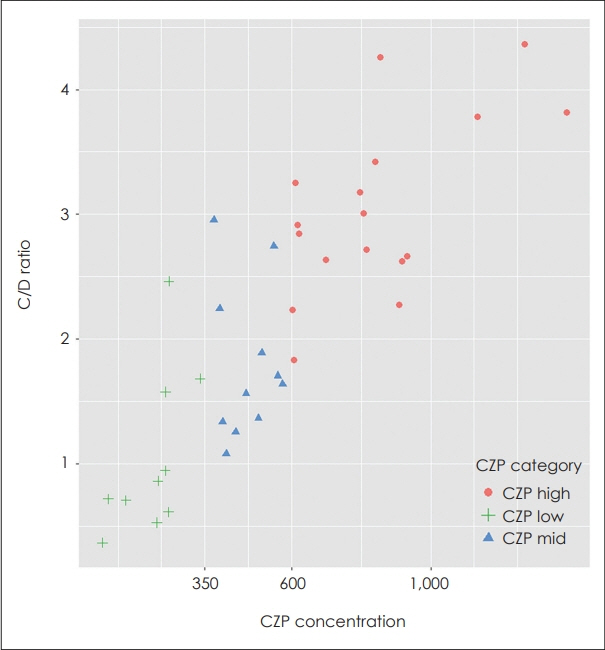
The study found that the average daily CZP dosage was 266.1 mg, and the average CZP concentration was 568.0 ng/mL. There was a significant correlation between CZP serum concentration and smoking status, as well as sex. CZP dosage was not significantly associated with age, weight, BMI, or metabolic rate. The study also found a significant difference in C/D ratio between groups based on CZP serum concentration.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that recommended CZP dosages for Caucasians may not be suitable for Koreans due to C/D ratio differences. We found a relationship between CZP serum concentration and C/D ratio in Korean TRS patients. Therefore, it is crucial to confirm CZP serum concentration to avoid side effects and to find optimal dosage.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lewis SW, Barnes TRE, Davies L, Murray RM, Dunn G, Hayhurst KP, et al. Randomized controlled trial of effect of prescription of clozapine versus other second-generation antipsychotic drugs in resistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2006; 32:715–723.
Article2. McEvoy JP, Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, Davis SM, Meltzer HY, Rosenheck RA, et al. Effectiveness of clozapine versus olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in patients with chronic schizophrenia who did not respond to prior atypical antipsychotic treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 2006; 163:600–610.
Article3. Keepers GA, Fochtmann LJ, Anzia JM, Benjamin S, Lyness JM, Mojtabai R, et al. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia. AJP. 2020; 177:868–872.
Article4. Barnes TR, Drake R, Paton C, Cooper SJ, Deakin B, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia: Updated recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2020; 34:3–78.
Article5. Hiemke C, Baumann P, Bergemann N, Conca A, Dietmaier O, Egberts K, et al. AGNP Consensus Guidelines for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Psychiatry: Update 2011. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2011; 44:195–235.
Article6. Spina E, de Leon J. Clinical applications of CYP genotyping in psychiatry. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015; 122:5–28.
Article7. Perry PJ, Miller DD, Arndt SV, Cadoret RJ. Clozapine and norclozapine plasma concentrations and clinical response of treatment-refractory schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1991; 148:231–235.8. Hasegawa M, Gutierrez-Esteinou R, Way L, Meltzer HY. Relationship between clinical efficacy and clozapine concentrations in plasma in schizophrenia: effect of smoking. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1993; 13:383–390.9. Wetzel H, Anghelescu I, Szegedi A, Wiesner J, Weigmann H, Härter S, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions of clozapine with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: differential effects of fluvoxamine and paroxetine in a prospective study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1998; 18:2–9.
Article10. Ruan CJ, Zang YN, Wang CY, Cheng YH, Sun C, Spina E, et al. Clozapine Metabolism in East Asians and Caucasians: a Pilot Exploration of the Prevalence of Poor Metabolizers and a Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2019; 39:135.11. Ng CH, Chong SA, Lambert T, Fan A, Peter Hackett L, Mahendran R, et al. An inter-ethnic comparison study of clozapine dosage, clinical response and plasma levels. International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2005; 20:163–168.
Article12. Kang SH, Lee HW. Prescribing Pattern of Clozapine and Clinical Factors associated with Discontinuation of Clozapine. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2019; 22:1.
Article13. Iglesias García C, Iglesias Alonso A, Bobes J. Concentrations in plasma clozapine levels in schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment. 2017; 10:192–196.
Article14. Reeves S, Bertrand J, Obee SJ, Hunter S, Howard R, Flanagan RJ. A population pharmacokinetic model to guide clozapine dose selection, based on age, sex, ethnicity, body weight and smoking status. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023; 1–11.
Article15. Albitar O, Harun SN, Zainal H, Ibrahim B, Sheikh Ghadzi SM. Population Pharmacokinetics of Clozapine: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:9872936.
Article16. Smith RL, O’Connell K, Athanasiu L, Djurovic S, Kringen MK, Andreassen OA, et al. Identification of a novel polymorphism associated with reduced clozapine concentration in schizophrenia patients—a genome-wide association study adjusting for smoking habits. Transl Psychiatry. 2020; 10:1–10.
Article17. McGraw J, Waller D. Cytochrome P450 variations in different ethnic populations. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012; 8:371–382.
Article18. Qurashi I, Stephenson P, Nagaraj C, Chu S, Drake R, Couchman L, et al. Changes in smoking status, mental state and plasma clozapine concentration: retrospective cohort evaluation. BJPsych Bull. 2019; 43:271–274.
Article19. Rostami-Hodjegan A, Amin AM, Spencer EP, Lennard MS, Tucker GT, Flanagan RJ. Influence of Dose, Cigarette Smoking, Age, Sex, and Metabolic Activity on Plasma Clozapine Concentrations: A Predictive Model and Nomograms to Aid Clozapine Dose Adjustment and to Assess Compliance in Individual Patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2004; 24:70–78.
Article20. Tsai YW, Tsai TI, Yang CL, Kuo KN. Gender Differences in Smoking Behaviors in an Asian Population. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2008; 17:971–978.
Article21. Cao XL, Li Y, Zhong BL, Chiu HFK, Ungvari GS, Ng CH, et al. Current cigarette smoking in Chinese female patients with schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Research. 2016; 235:203–205.
Article22. Xu YM, Chen HH, Li F, Deng F, Liu XB, Yang HC, et al. Prevalence and Correlates of Cigarette Smoking among Chinese Schizophrenia Inpatients Receiving Antipsychotic Mono-Therapy. PLOS ONE. 2014; 9:e88478.
Article23. Willcocks IR, Legge SE, Nalmpanti M, Mazzeo L, King A, Jansen J, et al. Clozapine Metabolism is Associated With Absolute Neutrophil Count in Individuals With Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:658734.
Article24. Schoretsanitis G, Kane JM, Ruan CJ, Spina E, Hiemke C, de Leon J. A comprehensive review of the clinical utility of and a combined analysis of the clozapine/norclozapine ratio in therapeutic drug monitoring for adult patients. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019; 12:603–621.
Article25. Couchman L, Bowskill SVJ, Handley S, Patel MX, Flanagan RJ. Plasma clozapine and norclozapine in relation to prescribed dose and other factors in patients aged <18 years: data from a therapeutic drug monitoring service, 1994-2010: Plasma clozapine: patients aged <18 years. Early Intervention in Psychiatry. 2013; 7:122–130.
Article26. Kuzin M, Haen E, Hiemke C, Bochon B, Bochon K, Gründer G, et al. Body mass index as a determinant of clozapine plasma concentrations: A pharmacokinetic-based hypothesis. J Psychopharmacol. 2021; 35:273–278.
Article27. Ismail Z, Wessels AM, Uchida H, Ng W, Mamo DC, Rajji TK, et al. Age and sex impact clozapine plasma concentrations in inpatients and outpatients with schizophrenia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012; 20:53–60.
Article28. Castberg I, Westin AA, Skogvoll E, Spigset O. Effects of age and gender on the serum levels of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017; 136:455–464.
Article29. Lane HY, Chang YC, Chang WH, Lin SK, Tseng YT, Jann MW. Effects of gender and age on plasma levels of clozapine and its metabolites: analyzed by critical statistics. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999; 60:36–40.
Article30. Ulrich S, Baumann B, Wolf R, Lehmann D, Peters B, Bogerts B, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of clozapine and relapse--a retrospective study of routine clinical data. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003; 41:3–13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Factors Affecting Constipation in Patients with Schizophrenia Taking Clozapine
- Plasma Concentrations of Clozapine and its Metabolites and FMO3 Variations in Korean Schizophrenic Patients
- Effect of Clozapine on Plasma Prolactin Levels in Schizophrenic Patients
- Relationship of Change in Plasma Clozapine/N-desmethylclozapine Ratio with Cognitive Performance in Patients with Schizophrenia
- Current Status of Clozapine for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia