Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Sep;28(3):219-224. 10.6065/apem.2142246.123.
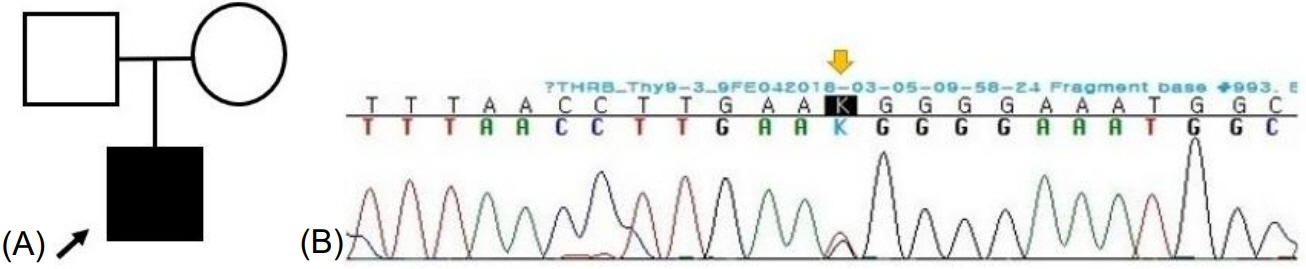
A novel variant of THRβ and its 4-year clinical course in a Korean boy with resistance to thyroid hormone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University school of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Deparment of Pediatrics, Keimyung University Daegu Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2546347
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2142246.123
Abstract
- Thyroid hormone resistance (RTH) is characterized by a decreased sensitivity of target tissues to thyroid hormones due to a defect in the THRα- and THRβ-encoded thyroid hormone receptors (THRs). The clinical manifestations range from no symptoms to simple goiter and hypo- or hyperthyroidism, depending on the receptor subtype distribution in the tissues. Here, we report the case of a thyroid hormone-resistant 12-month-old boy carrying a novel THRβ variant who was initially diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism. An extensive evaluation revealed increased free T4 level and inappropriately increased thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level; a normal lipid profile, sex hormone-binding globulin, and free alpha subunit of TSH; exaggerated TSH response to THR; and no radiological evidence of pituitary adenoma. A targeted next-generation sequencing panel identified a heterozygote c.993T>G (p.Asn331Lys) mutation in the THRβ gene. During the first year of life, a higher dose of levothyroxine was administered to the patient due to uncompensated RTH. Levothyroxine treatment was continued after 3 years to maintain TSH level <5 mIU/mL, but the observed weight gain was poor, height increase was insufficient, and bone development was delayed. However, neither hyperactivity nor developmental delay was observed. Patients with RTH exhibit various clinical features. Due to its heterogeneous nature, genetic test for accurate diagnosis is important to provide proper management.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Refetoff S, DeWind LT, DeGroot LJ. Familial syndrome combining deaf-mutism, stippled epiphyses, goiter and abnormally high PBI: possible target organ refractoriness to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967; 27:279–94.2. Tajima T, Jo W, Fujikura K, Fukushi M, Fujieda K. Elevated free thyroxine levels detected by a neonatal screening system. Pediatr Res. 2009; 66:312–6.3. Pappa T, Refetoff S. Resistance to thyroid hormone beta: a focused review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:316.4. Persani L, Campi I. Syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone action. Exp Suppl. 2019; 111:55–84.5. Chiesa A, Olcese MC, Papendieck P, Martinez A, Vieites A, Bengolea S, et al. Variable clinical presentation and outcome in pediatric patients with resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH). Endocrine. 2012; 41:130–7.6. Rivolta CM, Olcese MC, Belforte FS, Chiesa A, Gruñeiro-Papendieck L, Iorcansky S, et al. Genotyping of resistance to thyroid hormone in South American population. Identification of seven novel missense mutations in the human thyroid hormone receptor beta gene. Mol Cell Probes. 2009; 23:148–53.7. Olateju TO, Vanderpump MP. Thyroid hormone resistance. Ann Clin Biochem. 2006; 43(Pt 6):431–40.8. Igaz P, Patócs A. Genetics of endocrine diseases and syndromes. Cham (Switzerland): Springer, 2019. (Experientia supplementum; v. 111).9. Sun H, Cao L, Zheng R, Xie S, Liu C. Update on resistance to thyroid hormone syndromeβ. Ital J Pediatr. 2020; 46:168.10. Refetoff S, Dumitrescu AM. Syndromes of reduced sensitivity to thyroid hormone: genetic defects in hormone receptors, cell transporters and deiodination. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 21:277–305.11. Dumitrescu AM, Refetoff S. The syndromes of reduced sensitivity to thyroid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2013; 1830:3987–4003.12. Yen PM. Molecular basis of resistance to thyroid hormone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 14:327–33.13. Cardoso LF, de Paula FJ, Miceal LM. Resistance to thyroid hormone due to mutations in the TRHB gene impairs bone mass and affects calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. Bone. 2014; 67:222–7.14. Anselmo J, Refetoff S. Regression of a large goiter in a patient with resistance to thyroid hormone by every other day treatment with triiodothyronine. Thyroid. 2004; 14:71–4.15. Singh BK, Yen PM. A clinician’s guide to understanding resistance to thyroid hormone due to receptor mutations in the TRα and TRβ isoforms. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 3:8.16. Weiss RE, Dumitrescu A, Refetoff S. Approach to the patient with resistance to thyroid hormone and pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:3094–102.17. Gavin C, Meggison H, Ooi TC. Proposing a causal link between thyroid hormone resistance and primary autoimmune hypothyroidism. Med Hypotheses. 2008; 70:1024–8.18. Barkoff MS, Kocherginsky M, Anselmo J, Weiss RE, Refetoff S. Autoimmunity in patients with resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:3189–93.19. van Trotsenburg P, Stoupa A, Léger J, Rohrer T, Peters C, Fugazzola L, et al. Congenital hypothyroidism: a 2020-2021 Consensus Guidelines Update-An ENDO-European Reference Network Initiative Endorsed by the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and the European Society for Endocrinology. Thyroid. 2021; 31:387–419.20. Nakajima Y, Yamada M, Horiguchi K, Satoh T, Hashimoto K, Tokuhiro E, et al. Resistance to thyroid hormone due to a novel thyroid hormone receptor mutant in a patient with hypothyroidism secondary to lingual thyroid and functional characterization of the mutant receptor. Thyroid. 2010; 20:917–26.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resistance to thyroid hormone due to a novel mutation of thyroid hormone receptor beta gene
- Insulin Resistance and Intracellular Thyroid Hormone Dysfunction
- Monogenic Thyroid Disorder
- Mutations in Thyroid Hormone Receptor-beta Associated with Patients with Generalized Resistance and Pituitary Resistance to Thyroid Hormone
- A Case of Resistance Syndrome to Thyroid Hormone Associated with Mutation (G345D) in the Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta Gene